Determine the percentage change in profit. How to calculate the magnification of a telescope. What can you see through a telescope at different magnifications?
Percentage example
Example task 1
Question:
Example task 2
Question:
A percentage (or ratio) of two numbers is the ratio of one number to the other multiplied by 100%.
The percentage relationship between two numbers can be written as follows:
Percentage example
For example, there are two numbers: 750 and 1100.
The percentage ratio of 750 to 1100 is equal to
The number 750 is 68.18% of 1100.
The percentage ratio of 1100 to 750 is
The number 1100 is 146.67% of 750.
Example task 1
The plant's standard for car production is 250 cars per month. The plant assembled 315 cars in a month. Question: By what percentage did the plant exceed the plan?
Percentage ratio 315 to 250 = 315:250*100 = 126% .
The plan was completed by 126%. The plan was exceeded by 126% - 100% = 26%.
Example task 2
The company's profit for 2011 amounted to $126 million, in 2012 the profit amounted to $89 million. Question: By what percentage did profits fall in 2012?
Percentage ratio 89 million to 126 million = 89:126*100 = 70.63%
Profit fell by 100% - 70.63% = 29.37%
A percentage (meaning "per hundred") is a comparison with 100.
Percent symbol %. So, for example, 5 percent is written as 5%.
Let's assume there are 4 people in the room.
50% is half - 2 people.
25% is a quarter - 1 person.
0% is nothing - 0 people.
100% is whole - all 4 people in the room.
If 4 more people enter the room, then their number becomes 200%.
1% is $\frac(1)(100)$
If there are 100 people in total, then 1% of them are one person.
To express mathematically the number X as a percentage of Y you do the following:
$X: Y \times 100 = \frac(X)(Y) \times 100$
Example: What percentage of 160 is 80?
Solution:
$\frac(80)(160) \times 100 = 50\%$
Increase/Decrease percentage
When a number increases relative to another number, the amount of increase is represented as:
Increase = New number - Old number
However, when a number decreases relative to another number, then this value can be represented as:
Decrease = Old number - New number
An increase or decrease in a number is always expressed based on the old number.
That's why:
%Increase = 100 ⋅ (New number - Old number) Old number
%Decrease = 100 ⋅ (Old number - New number) Old number
For example, you had 80 postage stamps and you started collecting more this month until the total number of postage stamps reached 120. The percentage increase in the number of stamps that you have is equal to
$\frac(120 - 80)(80) \times 100 = 50\%$
When you had 120 stamps, you and your friend agreed to trade the Lego game for a few of these stamps. Your friend took some stamps that he liked, and when you counted the remaining stamps, you found that you had 100 stamps left. The percentage reduction in the number of brands can be calculated as:
$\frac(120 - 100)(120) \times 100 = 16.67\%$
Percentage Calculator
| What if % from ? | Result: | |
| what percentage is this? ? | Answer: % | |
| This % from what? | Answer: | |
How percentages help in real life
There are two ways that percentages help solve our everyday problems:
1. We are comparing two different quantities when all quantities are related to the same basic quantity of 100. To explain this, let's look at the following example:
Example: Tom opened a new grocery store. In the first month he bought groceries for $650 and sold them for $800, and in the second he bought them for $800 and sold them for $1200. We need to calculate whether Tom makes more profit or not.
Solution:
We cannot directly tell from these numbers whether Tom’s income is growing or not, because expenses and revenue are different every month. In order to solve this problem, we need to relate all values to a fixed base value of 100. Let's express the percentage of his income to expenses in the first month:
(800 - 650) 650 ⋅ 100 = 23.08%
This means that if Tom spent $100, he made a profit of 23.08 in the first month.
Now let's apply the same to the second month:
(1200 - 800) 800 ⋅ 100 = 50%
So, in the second month, if Tom spent $100, then his income was $50 (because $100⋅50% = $100⋅50100=$50). Now it is clear that Tom’s income is growing.
2. We can determine the amount of a part of a larger quantity if the percentage of this part is known. To explain this, let's consider the following example:
Example: Cindy wants to buy 8 meters of hose for her garden. She went to the store and discovered that there was a hose reel 30 meters long. However, she noticed that the reel said that 60% had already been sold. She needs to find out if the remaining hose is enough for her.
Solution:
The sign says that
$\frac(Sold\ length)(Total\ length) \times 100 = 60\%$
$Sold\ length = \frac(60 \times 30)(100) = 18m$
Therefore, the remainder is 30 - 18 = 12m, which is quite enough for Cindy.
Examples:
1. Ryan loves collecting sports cards of his favorite players. He has 32 baseball cards, 25 football cards, and 47 basketball cards. What is the percentage of each sport's cards in his collection?
Solution:
Total number of cards = 32 + 25 + 47 = 104
Baseball card percentage = 32/104 x 100 = 30.8%
Football card percentage = 25/104 x 100 = 24%
Basketball card percentage = 47/104 x 100 = 45.2%
Please note that if you add up all the percentages, you get 100%, which represents the total number of cards.
2. There was a math test in class. The test consisted of 5 questions; for three of them they gave three 3 points each, and for the remaining two - four points. You managed to correctly answer two questions worth 3 points and one question worth 4 points. What percentage of points did you receive on this test?
Solution:
Total = 3x3 + 2x4 = 17 points
Points received = 2x3 + 4 = 10 points
Percentage of points received = 10/17 x 100 = 58.8%
3. You bought a video game for $40. Then the prices for these games were raised by 20%. What is the new price of a video game?
Solution:
The price increase is 40 x 20/100 = \$8
The new price is 40 + 8 = \$48
A percentage (or ratio) of two numbers is the ratio of one number to the other multiplied by 100%.
The percentage relationship between two numbers can be written as follows:
Percentage example
For example, there are two numbers: 750 and 1100.
The percentage ratio of 750 to 1100 is equal to
The number 750 is 68.18% of 1100.
The percentage ratio of 1100 to 750 is
The number 1100 is 146.67% of 750.
Example task 1
The plant's standard for car production is 250 cars per month. The plant assembled 315 cars in a month. Question: By what percentage did the plant exceed the plan?
Percentage ratio 315 to 250 = 315:250*100 = 126% .
The plan was completed by 126%. The plan was exceeded by 126% - 100% = 26%.
Example task 2
The company's profit for 2011 amounted to $126 million, in 2012 the profit amounted to $89 million. Question: By what percentage did profits fall in 2012?
Percentage ratio 89 million to 126 million = 89:126*100 = 70.63%
Profit fell by 100% - 70.63% = 29.37%
That is, there is a numerical value that has changed over time due to circumstances. To find the percentage difference, you need to use the formula:
(“new” number – “old” number) / “old” number * 100%.
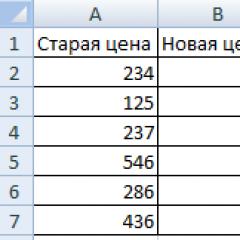
Task: Find the difference in percentage between the “old” and “new” supplier prices.

- Let's make the third column “Dynamics in percentage”. Let's assign a percentage format to the cells.
- Place the cursor in the first cell of the column and enter the formula: =(B2-A2)/B2.
- Press Enter. And let's drag the formula down.

The percentage difference has a positive and negative value. Establishing a percentage format allowed us to simplify the original calculation formula.
The percentage difference between two numbers in the default cell format (General) is calculated using the following formula: =(B1-A1)/(B1/100).
How to multiply by percentages in Excel
Problem: 10 kg of salt water contains 15% salt. How many kilograms of salt are in water?
The solution comes down to one action: 10 * 15% = 10 * (15/100) = 1.5 (kg).
How to solve this problem in Excel:
- Enter the number 10 in cell B2.
- Place the cursor in cell C2 and enter the formula: =B2 * 15%.
- Press Enter.

We didn't have to convert percentages to numbers because... Excel recognizes the "%" sign perfectly well.
If numerical values are in one column and percentages are in another, then in the formula it is enough to make references to the cells. For example, =B9*A9.
Calculation of interest on a loan in Excel
Task: They took out 200,000 rubles on credit for a year. Interest rate – 19%. We will repay in equal payments over the entire term. Question: what is the size of the monthly payment under these loan conditions?

Important conditions for choosing a function: constant interest rate and monthly payment amounts. A suitable function option is “PLT()”. It is located in the section “Formula” - “Financial” - “PLT”

- Rate – the interest rate on the loan, divided by the number of interest periods (19%/12, or B2/12).
- Nper – the number of loan payment periods (12).
- PS – loan amount (RUB 200,000, or B1).
- We will leave the argument fields “BS” and “Type” without attention.

The result is with a “-” sign, because the borrower will repay the money.
Everyone who chooses their first telescope pays attention to such a characteristic as the magnification of the telescope. How do you know what magnification a telescope gives? What magnification is needed to see craters on the Moon, the rings of Saturn, and the moons of Jupiter? What is maximum useful magnification? We will try to answer all these important questions in this article.
Is magnification the most important characteristic of a telescope?
Details of the surface of Mars at the same magnification with a telescope of different apertures.
Almost every novice space enthusiast believes that the magnification of a telescope is its main characteristic and tries to choose a telescope with the highest possible magnification. But is telescope magnification really important? Undoubtedly, telescope magnification is one of the main characteristics of a telescope, but not the only significant one. To obtain an image of an object through a telescope that is not only large, but as detailed as possible, it is necessary that the telescope uses high-quality glass optics, refractors use complex coated lenses, and reflectors use parabolic mirrors. The quality of the eyepieces you use is also important.
How to calculate the magnification of a telescope?

View of Saturn at 200x and 50x magnification.
The possible magnification of a telescope depends on its initial parameters: aperture diameter, focal length and eyepieces used. Changing magnification is achieved by changing eyepieces and combining them with a Barlow lens. To calculate the magnification of a telescope, you need to use a simple formula: Г=F/f, Where G- telescope magnification, F– focal length of the telescope, f– focal length of the eyepiece. The focal length of a telescope is usually written on its body or in its description, and the focal length of an eyepiece is always written on its body. Let's give an example. The focal length of the Sky-Watcher 707AZ2 telescope is 700 mm; when observed with an eyepiece with a focal length of 10 mm, it gives a magnification of 70 times (700/10 = 70). If we install an eyepiece with a focal length of 25 mm, we will get a magnification of 28 times (700/25 = 28). When using a Barlow lens, high magnifications can be achieved, since the Barlow lens increases the focal length of the telescope several times, depending on the magnification of the Barlow lens itself. For example, when using a 2x Barlow lens with a Sky-Watcher 707AZ2 telescope and an eyepiece with a focal length of 10 mm, we will get a magnification of not 70, but 140 times.
The maximum usable magnification of a telescope.

The focal length of the eyepiece is indicated on its body.
In optics there is such a thing as the maximum useful magnification of a telescope. These are the magnification values that the telescope's optical system can achieve without losing image quality. Theoretically, using combinations of short-focus eyepieces and powerful Barlow lenses, even on small telescopes, very high magnification values can be obtained, but such manipulations do not make sense, since the optical system of a telescope is limited by its diameter and the quality of the optics.

View of Saturn at insufficient, optimal and excessive magnification.
At very high magnifications you will not get a sufficiently bright and clear picture. Therefore, when choosing a telescope, it is important to pay attention to such a characteristic as the maximum useful magnification. The maximum useful magnification is calculated for each telescope individually using a simple formula Г max=2*D, Where G max- maximum useful magnification, and D– aperture (diameter of the lens or primary mirror). For example, if a telescope has an aperture of 130 mm, then the maximum useful magnification for such a telescope will be 260 times.

Moon at 50x magnification.
Be careful when studying the telescope parameters in its description. Sometimes manufacturers claim too high figures, for example magnifications of up to 600 times. You must understand that such values can be achieved with an aperture diameter of at least 300 mm, and then most likely at such a magnification you will encounter another problem - strong distortions from the earth’s atmosphere.
What can you see through a telescope at different magnifications?

Lunar relief at 350x magnification.
- For observation full moon, so that its disk completely fits into the field of view, a magnification of 30-40 times is sufficient. The Moon is a very close and large object, in the sky the full lunar disk occupies 0.5 degrees, and if you put an eyepiece giving 100x or more, then you will be able to examine the lunar relief in quite small details - you will see craters of various diameters, mountain ranges and seas.
- To view details on the surface planets, you should use higher magnifications - from 100 times or more, because planetary disks have small angular dimensions. With a magnification of 100x or more it is possible to see disk of Saturn and its rings with the largest satellites, Jupiter's cloud cover and its 4 largest satellites, see Martian surface with dark areas and polar caps.
- In order to consider deep space objects, such as star clusters, hydrogen nebulae and galaxies, you will need different magnifications - for extended faint objects, such as nebulae - wide-angle eyepieces with a field of view of 60 degrees and additional filters for greater contrast.
- If you have chosen a bright compact object for observation, such as planetary nebula, for example, the M57 Ring Nebula, you will need high magnifications of 200x or more, as well as filters for observing nebulae.
- When observing single stars It makes no sense to use high magnifications in a telescope, because at any magnification, a star in a telescope looks like a shining point. If the star looks like a pancake or a ring, it means the focusing is done incorrectly or your telescope does not have high-quality optics.
- Higher magnification must be used if you want to observe binary and multiple star systems, with visible components through a telescope.
Advice:
When choosing a telescope, pay attention to its equipment. It is necessary that the kit includes various eyepieces that allow you to achieve different magnifications, including the most useful one. Sometimes manufacturers skimp on accessories, focusing on the quality of the telescope itself. In this case, you need to purchase additional eyepieces yourself. This usually happens with high-end models with expensive optics, with which it is necessary to use eyepieces of the same high class.
In order to calculate the increase (in absolute or percentage terms), it is necessary to have the current value and the one with which the comparison is being made. To establish the dynamics of growth, the time intervals must be equal (for example, a week, month, or year).
Calculation of growth is used in the management of financial and economic activities, as well as in statistics. Using a simple mathematical formula, you can find out how much your costs or income have increased (personal or for the enterprise as a whole) over a certain period of time, calculate the increase in customers, and much more. As an example, let's try to calculate the increase as a percentage using a special formula.
Formulas for calculating growth
To begin with, you need to have some value that is taken as a starting point. For example, the population of city M on January 1, 2013 amounted to 100 thousand people.
If you want to know the growth for the year, you will need the population of city M as of January 1, 2014. Let’s say 150 thousand people. Now you can calculate the increase.
The increase in absolute value will be equal to the difference between the current value and the previous one:
- From the population in 2014, subtract the number in 2013: 150,000 - 100,000 = 50,000;
- Total: annual growth is 50 thousand people.
The percentage increase is equal to the ratio of the current value to the previous one, minus 1, multiplied by 100%:
- We divide the current value of 150,000 by the data from the previous period of 100,000. We get 1.5;
- Subtract one: 1.5 - 1 = 0.5;
- Convert to percentages: 0.5 * 100% = 50%;
- Total: population growth over the year is 50%.
To calculate population growth dynamics, you will need annual data as of January 1 of each year.
If the growth value turns out to be negative, it means that there was a decline during the year (in this case, the population in city M would decrease).
The manager of an enterprise is always interested in the question: how will the amount of profit change depending on changes in revenue. It has been established that the percentage of profit growth is higher than revenue. This phenomenon in theory is called operational (production) leverage, which is explained by the disproportionate impact of fixed and variable costs on the results of financial and economic activities (profit).
The strength of the operating leverage is determined by the formula:
F= , (15)
where F is the force of the operating lever,
M in - gross margin (M in = M + I post), rub.,
M - profit, rub.
Let's look at this using the example above. In our case, the force of influence of the operating lever according to formula (15) will be equal to:
 =
7,7
=
7,7
This means that every 1% change in revenue causes a 7.7% change in profit. For example, with an increase in revenue by 10%, the profit of a bakery increases by 10% x 7.7 = 77%. This is confirmed by the following calculation: sales revenue (586 million rubles) increased by 10%, which amounted to 586 x 1.1 = 644.6 million rubles. Gross margin (B r - I per) is equal to: 644.6 - 492.8 = 151.8 million rubles. (where 492.8 = 448 x 1.1). This means that profit increased by RUB 133.8 million. (151.8 - 18), or by 77%.
When considering this issue, it should be borne in mind that if profitability threshold passed and the share of fixed costs in the amount of total costs is decreasing, then the force of the operating lever decreases. And vice versa, with an increase in the share of fixed costs, the effect of the production lever increases.
When sales revenue decreases, operating leverage increases. Thus, a decrease in sales revenue by 5% will lead to a very large drop in profit at the bakery: 5% x 7.7 = 38.5%. The profit in this case will be 11.3 million rubles: 18 - (37 x 18): 100 = 11.3 million rubles.
3. Practice exercise
Analysis of the use of working time fund is to identify the amount of losses and unproductive downtime. At the shipyard, it is important to reduce day-long and intra-shift downtime.
Labor intensity is the amount of labor measured in standard hours that a machine operator needs to expend to perform a certain type of work.
Initial data:
The duration of the working day in the machine shop of the SRZ is 8 hours (480 minutes), the loss of working time per shift in the base period was 25 minutes, the cost of producing a unit of production was 15 minutes.
You need to determine:
How much will output increase in the planning period if, as a result of the implementation of measures, it is planned to eliminate the loss of working time and reduce the labor intensity per unit of production by 2 minutes?
Practical lesson No. 3.
1. Survey on topics:
Topic 5. Providing a ship repair enterprise with working capital
5.1. Economic content, composition and structure of working capital
5.2. Rationing of working capital
5.3. Organization of logistics
5.4. Inventory Management
Topic 6. Management of a ship repair enterprise is the most important condition for ensuring the growth of its economy
6.1. Essence, types of management and its functions
6.2. Organizational management structures
6.3. Management decision making
6.4. Main directions for improving management
6.5. Information technologies in the management of a ship repair enterprise
2. Subject part:
1.5. Analysis of profit sensitivity to price changes and cost structure
This method is based on the calculation of the sales volume, which should provide the required amount of profit when the price or cost structure changes (fixed and variable costs).
If fixed costs (expenses) change, then the volume of sales that provides the desired amount of profit is determined by the formula:
M o =
 :Ts,(16)
:Ts,(16)
If variable costs change, the calculation is made using the following formula:
M o =
 :Ts,(17)
:Ts,(17)
If the price changes, the calculation is carried out using the following formula:
M o =
 :C P
,
(18)
:C P
,
(18)
where M int is the new gross margin, rub.,
M o - desired profit, rub..
a n is the initial percentage of gross margin to sales revenue,
M vi - initial gross margin, rub.,
a n is the new percentage of gross margin to sales revenue.
Let us consider the nature of these changes using the example of a bakery, which has the following indicators:
Annual production of loaves – 100,000 pcs.;
The price of one loaf is 2,860 rubles/piece;
Average variable costs - RUB 1,800/piece.
With such sales volume, price and variable costs, the bakery has the following indicators:
Sales revenue (2,860 x 100,000) = 286 million rubles;
Variable expenses (1,800 x 100,000) = 180 million rubles;
Gross margin = RUB 106 million;
Fixed expenses = 53 million rubles.
Profit is 53 million rubles.
Let's say the price increased by 10%. In this case, it is important for the management of the enterprise to know: how the amount of profit will change and what the volume of sales should be in order to maintain the same level of profit.
So: new price (2860 + 286) = 3146 rubles/piece;
new revenue 3146 rub./piece. x 100%;
variable expenses (1800 x 100) = 180 million rubles, or 57%;
gross margin RUB 134.6 million, or 43%;
fixed costs 53 million rubles, or 17%.
The profit is equal to 81.6 million rubles, or 26%.
As you can see, profit increased from 53 million to 81.6 million rubles, or by 53%. The volume of sales required to achieve the same profit with an increase in price according to formula (45) will be:
 :
3146
= 79.8 thousand pcs.
:
3146
= 79.8 thousand pcs.
All this can be arranged as shown in table. 6.
Table 6. Sensitivity analysis of indicators for a bakery with a price increase of 10%
|
Indicators |
Initial volume, 100,000 pcs. | |||
|
Revenues from sales | ||||
|
Variable expenses | ||||
|
Gross Margin | ||||
|
Fixed expenses | ||||
Thus, an increase in price by 10% compensates for a reduction in sales volume by 21% and increases profit by 53% (from 53 million to 81.6 million rubles).
What will happen to the indicators when the cost structure changes? Let’s say that as a result of modernization, a bakery managed to reduce fixed costs by 10%. Then, with the initial sales volume, profit should increase by 5.3 million rubles. and amount to (53 + 5.3) 58.3 million rubles, and fixed costs - (53 million rubles + 47.7 million rubles) 100.7 million rubles. The sales volume that the bakery can achieve while maintaining the same profit (53 million rubles) will be:
 :Ts=
:Ts=
 :2860 = 95.2 thousand/pcs.
:2860 = 95.2 thousand/pcs.
These calculations can be done as shown in table. 7.
Table7. Sensitivity analysis for an enterprise when reducing fixed costs by 10%
|
Indicators |
Initial volume, 100,000 tons. |
A volume that ensures a constant profit of 78.4 thousand rubles/piece. |
||
|
Revenues from sales | ||||
|
Variable expenses | ||||
|
Gross Margin | ||||
|
Fixed expenses | ||||
We will analyze the impact of changes in sales volume using the operating leverage effect:
F=
 =
= =
2.
=
2.
This means that if a bakery increases sales volume by 10%, then revenue also increases by 10%, and profit, taking into account the operating leverage, will be equal to (M = 10x2) 20%. Let's check the result:
new revenue with a 10% increase in volume will be:
(286+ 28,6) = 314,6;
variable expenses (180 + 18) = 198.0;
gross margin = 116.6;
fixed costs = 53.0;
Profit is 63.6.
As you can see, profit increased by 10.6 million rubles. (63.6 - 53), i.e. by 20% (10.6: 53 x 100).
Based on the adopted sensitivity analysis scheme, it is possible to determine and distribute the elements of profitability according to the degree of their influence on the profit received by the bakery.
So, promotion prices by 10% increases profits by 53%; increase the volume of product sales by 10% causes an increase in profits by 20%; decrease variable costs by 10% leads to profit growth by 88%; A 10% change in fixed costs increases profit growth by 10%.
In this regard, it is important for the management of the enterprise to know the boundaries within which it can change the indicators. This is determined by establishing a margin of financial strength. First, the profitability threshold and annual sales volume are calculated.
R n
=
 =
= x100 = 156.8 million rubles.
x100 = 156.8 million rubles.
Q n
=
 =
= 548 pcs.,
548 pcs.,
where And post - fixed costs, thousand rubles,
R n - threshold profitability, million rubles,
Q n - threshold sales volume, pcs.
and pr - percentage of income (gross margin) from coverage to sales revenue, percent.,
C - price of a loaf, rub.
The margin of financial strength in this case is: 3 pr = (B p - R n) = 286 million rubles. - 156.8 million rubles. = 129.2 million rubles, or almost 45% of revenue (129.2: 286).
As we can see, the bakery has a large margin of financial strength, allowing it to fearlessly operate with factors influencing its value. In this case, the management of the bakery should focus on pricing policy and reducing variable costs, which have the greatest impact on the resulting mass of profits.
The growth rate is an important indicator that characterizes an increase in profits, product output, etc. However, not everyone knows the formulas that allow one to calculate this important indicator. Our article will tell you how to determine the growth rate.
Growth rate
- TR = (PTP-PPP)/PPP x 100%, where TR is the growth rate, PTP is the indicator for the current period, PPP is the indicator for the previous period.
For example, in 2012 your company earned 287 million rubles, and in 2013 the profit amounted to 299 million rubles. Let's calculate the percentage of growth rate:
- TR = (299 - 287)/287 x 100% = 4.18%
It turns out that in 2013 the profit of your company increased by 4.18%.
Growth rate of decline
If your productivity or income does not increase, but decreases, then in this case the percentage of decrease in growth is calculated.
If it is necessary to calculate the average growth rate for several equal periods of time, use the following formula:
- TPp =((PTP/PPP) 1/ n -1) x 100%, where TPp is the growth rate for a certain period, and n is the number of such periods.
For example, if we needed to find the average growth rate of your business for each month, the formula would look like this:
- TPp=((299/287) 1/12 - 1) x 100% = 0.31%
But determining the growth rate over one period of time is not very indicative. Carry out a similar calculation for several different similar periods. Enter the data into a table, or better yet, build a graph. And you can analyze how the growth rate has changed over different times. For example, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in calculating the rate of growth or decline if you know the appropriate formulas and know how to use them. And for analyzing profitability or loss, this indicator is indispensable.