Do-it-yourself rejuvenation of fruit trees. Rejuvenating pruning in the city: why do we need trees "under the telegraph pole"? Correct anti-aging pruning of trees
The yield of fruit trees, including apple trees, decreases over time. One way to increase yields is to prune old branches to encourage new growth. Anti-aging pruning of apple trees has a number of features that are taken into account before starting work.
Pros and cons of rejuvenating apple trees by pruning
The main benefits of anti-aging pruning:
- a powerful crown is formed;
- increases the life of the tree;
- new strong branches appear;
- productivity increases;
- the crown is better ventilated, and the fruits receive more sunlight;
- the risk of developing diseases is reduced;
- trees are less susceptible to pest attack.
Disadvantages of apple pruning:
- the procedure is stressful for plants;
- it is important to observe the timing and order of trimming;
- pruned apple trees provide additional care.
Pruning timing
For anti-aging pruning choose:
- late autumn;
- early spring.
The tree should be at rest when sap flow is slow. In autumn, this period begins in October after leaf fall. The main disadvantage of processing at the end of the season is that the apple tree takes longer to heal the damage. For trees older than 10 years, winter pruning is practiced when the snow has already fallen.
If spring anti-aging pruning is planned, then it is important to complete it before the buds appear. If you do not guess with the timing and start the procedure too late, then the tree will lose a lot of juice. The best time is March, in colder regions April. In the summer, sanitization is carried out, which does not harm the tree.
How to make anti-aging pruning of an apple tree
There are 4 options for anti-aging pruning. Each of them has its own nuances, advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a particular method, the age and condition of the tree are taken into account.
Shock pruning to rejuvenate old apple trees
This method is suitable for old neglected apple trees that practically do not bear fruit. Such trees have a spreading crown and reach a height of 12 m. Shock anti-aging pruning is carried out for plants with a strong central conductor and healthy side shoots. There should be no cracks, lichen, hollows on the trunk.
Important! After a shock pruning, an apple tree needs a lot of strength to recover. The culture is susceptible to disease and freezing in winter and may die as a result.
The procedure for shock pruning for apple tree rejuvenation:
- First, sanitize: remove old and broken branches.
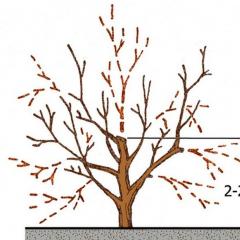
- The central conductor is shortened to a height of 3.5-4 m. 2-3 thin shoots are left under the cut. The top is cut off in several stages so that it does not harm when it falls.
- The remaining skeletal shoots are shortened to 2 m. It is advisable to leave fruit-bearing branches at the age of 3-4 years.
- Places of cuts are treated with garden pitch.
- In the spring, the trunk is cleaned and whitewashed.

Gentle anti-aging pruning of an old apple tree
A more gentle way to rejuvenate an apple tree is to gradually cut off the shoots. There are 2-3 years between procedures. As a result, all shoots are shortened to a length of 2 m. After such pruning, the crop yield decreases, which is restored within 5 years.
Gradual pruning
A softer way is gradual anti-aging pruning. This process takes 3 to 10 years. Every 2 years, branches with a diameter of more than 10 cm are cut off. Diseased and dry shoots are eliminated annually, and the crown of the tree is also pruned. Gradual processing maintains a stable yield of the tree.
Anti-aging treatment algorithm for the apple tree:
- In the spring, when frosts pass, the tree is inspected. First, broken and dry branches are removed.
- On the central conductor, healthy shoots are selected at the age of 4-5 years, growing at an acute angle.
- The top is cut off to make a round cut. Instead, a side branch remains.
- Then the crown is thinned out: thickening shoots and branches growing inward are removed.
- Places of cuts are covered with garden pitch.

Modern Method
The modern way to rejuvenate an apple tree involves following a number of principles:
- the crown is cut from the south side;
- the cut sector should be up to 3 m high and no more than 2 m wide;
- the number of cuts is minimized;
- from the side of the cropped crown, the roots are shortened at a depth of 70 cm;
- saw cuts are covered with garden pitch;
- slices larger than 5 cm are wrapped in dark polyethylene, which is removed only in September;
- after a few years, the northern part of the apple tree is cut off in a similar way.

Pruning scheme for apple tree rejuvenation
The order of anti-aging pruning changes depending on the season. The most intensive processing is carried out in the fall, more gentle methods are left for the spring. In general, the pruning order remains the same: choose the appropriate method, eliminate diseased and old shoots, shorten the top or length of the branches.
Scheme of anti-aging pruning of apple trees in spring
In the spring, a gentle pruning of the apple tree is carried out. The tree is sensitive to warming and an increase in the length of daylight hours. Sap flow begins before the kidneys swell, so it is important not to delay the processing. A dry cloudy day is best suited for work, when there is no strong wind.
In spring, anti-aging pruning consists of the following steps:
- Choose the time and method of processing.
- Prepare tools and disinfect them with a solution of potassium permanganate. Pruning requires a sharp pruner and a saw.
- First of all, remove damaged and broken shoots.
- Eliminate branches directed inward of the crown.
- Perform cropping according to the selected method.
- Process all slices.
- Perform cleaning and whitewashing of the bole.

For processing sections, a garden pitch is prepared from paraffin, rosin and vegetable oil in a ratio of 6: 3: 2. First melt the paraffin, then add rosin and mineral oil. The mixture is boiled for 20-30 minutes, then cooled. Instead of paraffin, beeswax is also used.
Important! Sections left from large branches are wrapped in dark polyethylene. The film is removed in early autumn, when the damage has healed.
Additionally, the apple tree is inspected after bud break to eliminate frozen and dry shoots. If during the season the tree suffered from diseases, then only the affected fruits and leaves are cut off. Pruning of diseased branches is left for the fall.
Scheme for pruning an apple tree and rejuvenating an old bush in autumn
Autumn is considered the best time for shock pruning to rejuvenate the apple tree. During this period, the top and old powerful shoots are cut off. It is recommended to remove a few large branches, rather than many thinner ones. Processing is carried out in cloudy weather, when there is no rain and strong wind.
Autumn anti-aging pruning of an apple tree includes a number of stages:
- First of all, old, broken, weak, diseased shoots are eliminated.
- Prepare tools: sharpened pruner and saw. They are disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate.
- Eliminate shoots directed down or inside the crown.
- Cut off other branches in accordance with the selected scheme.
- Shorten the top of the tree.
- In the near-trunk circle, all shoots are eliminated.
- Slices are smeared with garden pitch.

After rejuvenating pruning, all diseased shoots are burned. The tool used is disinfected to eliminate the source of infection. If the apple tree has been exposed to diseases, it is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or a solution of copper sulfate. The treatment is repeated in early spring, until the leaves have blossomed.
In the video, anti-aging pruning of an apple tree in the fall for beginners:
Tree care after pruning
After anti-aging treatment, it is important not only to treat all damage, but also to feed the apple tree. Any pruning is stressful for the tree. Minerals are needed to restore strength and build new shoots.
In autumn, the trunk circle is dug up and 2 buckets of humus, 100 g of superphosphate and 60 g of potassium salt are added. Nitrogen fertilizers, including organics, are used only in spring.
Advice! In order for the apple tree to survive the winter better after pruning, it is watered abundantly in late autumn. The trunk is spudded, and the trunk circle is mulched with humus.
When the snow melts and the buds begin to swell, the apple tree is watered with mullein infusion. After 2 weeks, a complex fertilizer is prepared for top dressing: 30 g of urea, 80 g of superphosphate and 50 g of potassium sulfate.

After rejuvenating pruning, the apple tree is susceptible to fungal diseases and pest attacks. Therefore, it is important to carry out preventive treatments. The garden is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or a solution of iron sulfate. Insecticides Iskra or Karbofos are effective against pests. During the season, the site is treated once every 3-4 weeks. Chemical preparations stop using 3 weeks before the fruit is removed.
Conclusion
Rejuvenating pruning of apple trees is a necessary step in the care of the garden. It is carried out at certain times when the plants have a dormant period. The pruning scheme is chosen depending on the age and condition of the apple tree. If the procedure is successful, the tree will be able to grow new shoots and bring a good harvest. To help the culture recover, it is provided with special care: top dressing, protection from diseases, pests and frost.
1Almost every gardener is faced with the fact that the fruit trees in the garden are aging and the yield is significantly reduced. There is an opinion that such trees cannot be restored and the only way to rejuvenate the garden is to uproot and plant new seedlings. But! This opinion is erroneous. There are several ways to rejuvenate old trees, which will be discussed in this article.
How to rejuvenate old trees
Crown pruning. This method of rejuvenation is usually used for neglected trees that are more than ten years old. Branches should be cut at a slight angle. Remove only those shoots that grow towards the center and do not allow the sun's rays to fully penetrate inside the crown. It is also necessary to get rid of all dry branches and those that prevent other fruitful branches from growing. Immediately after pruning, it is necessary to cover the place of the cut with clay so that any infection does not get into it. Such pruning allows you to clear the tree of branches, which in vain pull strength from the tree and do not allow it to bear fruit well. After this rejuvenation procedure, the tree becomes stronger, and the harvest is much larger and juicier.
thinning. After thinning the center, it is necessary to cut the side branches. First you need to remove all damaged, broken and dry branches. Next, you need to cut all the branches that are too close, soon they will interfere with each other. It is also necessary to cut branches that are too long, they spend a lot of effort just to keep themselves on weight. Such thinning pruning should be carried out at least three times a year and then the tree will not suffer from various kinds of diseases, the yield will increase significantly.
Pruning drooping branches. Hanging branches must be pruned, as they will not have enough strength to withstand large fruits. Branches should be cut almost in half so that they stick up and can continue to actively grow, bear fruit, and not pull vitality from the tree in vain.
Pruning in the zone of receding growth. The best time for this pruning is early spring. It is necessary to conduct it, since it is this zone that absorbs the most energy and nutrients. In order not to harm the tree, it is necessary to remove large branches in parts. First, file at the base, and then slowly cut off small pieces from the top.

Removing extra tops. The most difficult is trimming tops. The active growth of tops begins due to an excess of nitrogen in the soil, so if there are too many of them, then you should stop feeding with a high nitrogen content. It is necessary to remove the wolf only when there are enough fruitful branches on the tree. If there are not quite a lot of them, then the tops need to be shortened, but not removed, since good fruitful branches can soon grow out of them.
Tree care after rejuvenation
- After rejuvenating pruning, the plant needs special care. Sections after trimming must be covered with clay or paint so that the wounds heal faster.
- In winter, it is necessary to throw more snow on the branches, this will help protect the tree from freezing.
- After rejuvenating pruning, it is imperative to feed the trees. For this, wood ash is excellent, which is rich in microelements necessary for garden trees.
- In the spring, you also need to fertilize. You can fertilize the soil with humus, or use special balanced fertilizers for fruit trees, which can be purchased at any gardening store.

"I LOVE YOU MY OLD GARDEN!" GARDEN REJUVENATION
This article is about the beloved old garden. It is written for those who, like me, give it all their free time. Who, sparing no effort, makes the world cozier and more beautiful, at least on their small piece of land.
It is very difficult to maintain the beauty and health of the garden. He, like a person, ages over time ... Is it possible to prolong his youth? Yes! It's quite real. You just need to decide which plants to rejuvenate, which ones to remove, and which ones to add.
TREE REJUVENATION
The garden bears fruit well for no more than 30 years. After that, diseased fruit trees must be uprooted and replaced with new quality varieties. And old, but still healthy plants can be given a second youth: to extend their life for another 30 years, while maintaining their yield!
Step by step pruning
Anti-aging pruning is done in 2 stages with a break of 3-4 years.
Stage 1
Root rejuvenation. This work must be done in October so that the tree can grow roots before frost. From the south side plants dig a semicircular trench half the diameter of the near-stem circle. For pears and apple trees, a trench is made 70 cm deep and wide, departing from the trunk about 2 m. For plums and cherries, the depth and width are 50 cm, and the distance from the trunk is 1.5 m. Old roots that have opened in the trench are cut with a shovel or axe. Very thick - cut with a saw, and the cuts are cleaned and treated with garden pitch. Then, wood ash is poured into the bottom of the trench with a layer of 1-2 cm, thin fibrous roots are laid and covered with enriched soil, consisting of garden soil, humus or compost with the addition of complex fertilizer (“Marathon”). The trunk circle is lightly tamped and mulched with peat.
Rice. Rejuvenation of tree roots
1) mark and dig a trench on the south side of the tree; 2) thin fibrous roots are bent, and thick skeletal ones are cut with a saw; 3) small roots are folded into a trench and covered with earth.
Attention!
Do not plant flowers or vegetables under fruit trees, since 90% of small roots are located in the upper soil layer, they can be damaged even with shallow loosening, which will negatively affect the growth of the tree.
Crown rejuvenation
Rice. Tree crown rejuvenation.
1) shortening (cut branches are highlighted in color); 2) thinning.

Spring crown from the south side of the tree thin out cutting off perennial branches. This stimulates the awakening of dormant buds at the base of the skeletal branches and on the trunk of the tree. Then vertical long shoots (tops) will grow from these buds. These tops greatly thicken the crown, so next year they are cut out “on the ring”, making a cut on top of the annular influx at the base of the branch.
Rice. Trimming "on the ring"
1) wrong - there was a stump; 2) wrong - deep cut; 3) correct - the cut is made on top of the annular influx.

Thin branches are cut with secateurs. Thick branches are cut in three stages. First, they make the lower washed down, stepping back 30 cm from the base. Then they make the second washed down 15 cm higher. As a result, the branch breaks off. After that, the resulting stump is cut off.
Rice. Three stages of cutting thick branches.
1) the first washed down, 2) the second washed down, 3) tenderloin.

The remaining branches are shortened, leaving two lateral buds. Then shoots will grow from them and form a crown. pruning(branch shortening) is used to change the direction of growth of a branch, reduce the crown, strengthen the branching of the old crown, restore frozen branches. Weak pruning - removal of less than 1/4 of the length of the branch, medium - 1/2 of the length, strong - 3/4 of the length. On a one-year or two-year-old branch, a cut is made above the kidney at an angle of 45 ° with a sharp knife.
Rice. Growth of a branch after shortening to different lengths: 1) the original branch; 2) regrowth without pruning; 3) regrowth when shortened by 1/4; 4) regrowth when shortened by 1/2; 5) regrowth when shortened by 3/4.

Very old branches recommended cut "with translation" over a side branch growing in the desired direction. The angle between the side branch and the cut line should be 30°. Thick branches are cut down, leaving a small stump. After the “translated” cut, the branch grows in the right direction.
Rice. Pruning "with translation": 1) on a branch growing outward; 2) on a branch growing upwards (cut branches are indicated by a dotted line).

Unnecessary shoots no longer than 10 cm long can simply be broken out. Breakout usually done after pruning the tops of the trees.
Stage 2
Root rejuvenation. After 3-4 years, anti-aging pruning must be repeated already. from the north side tree, first cut off the roots, as in stage 1, and then the crown.
Crown rejuvenation. The crown is rejuvenated, as in stage 1, only on the north side of the tree. You should not force the rejuvenation of the garden, shortening the crown of trees by more than 3 times in width and height. With such excessive pruning, the tree can freeze even in a mild winter and die in 2-3 years. Therefore, pruning should be done in stages over several years, gradually shortening the main branches of the crown. In a couple of years it will be possible to collect large fruits from the updated tree.
Even in an old garden, you can grow new varieties of fruit trees if you regraft some of the skeletal branches and even tops. Cross-pollination of several varieties contributes to a plentiful and high-quality harvest.
Rice. Methods for regrafting fruit trees: 1) copulation; 2) in a trihedral cut; 3) under the bark

Attention!
If your garden has wild hawthorn and mountain ash, chokeberry or irga, do not rush to uproot them! These plants can be successfully grafted with pears of the Chizhovskaya, Vidnaya, Thumbelina, and Veles varieties. Already in the third year they will give a good harvest and will bear fruit for about 20 years.
Shrub rejuvenation
You can rejuvenate old shrubs and give them an original shape by pruning, which “inspires” young shoots to grow quickly and bloom lushly.
Rice. Rejuvenating pruning of shrubs
In addition, old bushes need thin out after 2-4 years, completely cutting out branches with pruners that overlap each other and grow inward crowns. Most shrubs tolerate thinning very well.

Shaping haircut shrubs should be done at least once a year. From time to time, a rejuvenated plant can be given the desired shape with a curly haircut.
Rice. Formation of the crown of shrubs
1) first pruning; 2) bush after pruning; 3) second cut; 4) a bush in autumn after the second pruning

For complete rejuvenation of the bush, its entire aerial part is cut into a black head. It is restored due to young shoots that have grown from dormant buds of the above-ground trunk. Complete rejuvenation is needed for very old bushes, the aerial part of which is severely frozen or mutilated by improper pruning.
REMOVING OLD PLANTS
Trees in which large hollows have formed, the blackened bark is separated from the trunk, the crown is severely frozen or the trunks are split, are removed from the garden. A single tree is cut down at a height of 40-50 cm from the ground. If trees and shrubs grow densely near it, then to preserve them, the skeletal branches of the old tree are first cut down (starting from the bottom), and then the remaining bare trunk (as low as possible). Then they get rid of the stump by making the deepest holes in it with a drill and pouring potassium nitrate powder into it. For a hole 50 cm deep and 5 cm in diameter, you need about 200 g of potassium nitrate (not ammonium - it decomposes too quickly!). Then water is poured into the holes, stirred with a stick and a cork is hammered into it. The stump is covered with a plastic bag and tied with twine. In a month, saltpeter will turn the stump into dust. A new plant is planted in the vacant place.
Attention!
After an apple tree, you can not plant an apple tree, and after a plum tree, a plum tree. In place of the uprooted fruit tree, place a fruit tree of a different type. So, in place of an apple tree, a pear, plum or cherry should grow.
To remove the shrub, first cut off the old branches, then dig around the roots and pull the plant with a cable tied to thick roots. The root shoots of sea buckthorn, blackthorn, snowberry, elderberry, willow and chaenomeles remaining in the soil should be regularly weeded. Old climbing vines are removed in the same way as shrubs.
The article was prepared based on the materials of the magazine "Garden of my dreams"
Blooming garden at their summer cottage (photof0
In accordance with the growing conditions of fruit plantations, their species and varietal composition, age and applied agricultural technology, which determined the nature and degree of frost damage to orchards, various methods of their resuscitation are outlined. The restoration of old trees is carried out by repairing the surviving fruit plantations and laying new ones both in the place of dead orchards and in other areas.
Repair of fruit plantations is carried out by replanting trees in places that have fallen out, grafting trees with a dead above-ground part, but a well-preserved root system, compacting existing fruit plantations and restoring trees due to regrowth.
Repair of old trees is carried out in gardens, where the trees have damaged to varying degrees or died above ground, but in the majority they retain a vital root system.
Rejuvenation of the old garden is useless if the trees are in the last period of life. If more than half of the landings have died, the second is no longer being repaired. Such gardens are to be replaced by new ones.
One way to rejuvenate an old garden is to plant new seedlings nearby. Tree replanting is carried out both in young and fruit-bearing orchards in places of finally dead or dying trees. Orchards under the age of 15-20 years, having a fall of less than half of the total number of trees, should be planted with old varieties, if they are standard, stable and meet the planned targets. When more than half of the garden trees fall out, replanting is done with both old and new varieties. The replanting of older fruit trees, regardless of the percentage of lunge, is carried out with more early-ripening varieties in order to create a garden array with more or less the same lifespan of trees.
Uprooting of fallen trees with simultaneous preparation of planting pits is carried out in advance: during spring planting - from autumn, during autumn - no later than a month before planting.
In young gardens, holes should be dug of the usual size, i.e. 1-1.25 m wide and 0.6 m deep; in fruit-bearing - depending on the age of the trees, but not less than 1.5-2 m wide and 0.6-0.7 m deep.
Before restoring the garden, it is necessary to add 30–40 kg of rotted manure or compost to each new planting pit, and 15–20 kg each in smaller pits with the addition of mineral fertilizers: 300–400 g of superphosphate, 60 g of potassium salt or 200 g of ash and 60 g of ammonium nitrate. The fertilizer must be thoroughly mixed with the soil.
How to graft an old fruit tree in the garden
One of the most important ways to rejuvenate a tree is grafting. This method is relevant if the plant is not more than 30 years old. In older gardens, grafting is usually not done. Grafting gives the best results on young trees under the age of 10-15 years, since their more vital root system provides better nutrition for the grafted tree and faster fruiting - 3-4 years after grafting, and often even earlier.
Depending on the condition and regrowth of the affected old tree, grafting is carried out in various ways.
- In the presence of a well-preserved lower part of the trunk with a healthy and juicy bark, they are grafted with a cutting into the root neck or slightly higher, having previously cut down the tree trunk here. 2-4 cuttings are inserted into the stump “with a saddle behind the bark”, depending on the size of the cut area.
- With complete death or severe damage to the trunk, along with the root neck, but with well-growing shoots from the base or root offspring, the vaccination is carried out either in one or the other. Shoots for grafting are chosen most firmly attached to the root neck of the tree, approximately at a depth of 10-15 cm, which further protects young trees from breaking off.
It is preferable to graft on highly developed root suckers located near the base of the tree. Subsequently, having separated from the mother tree, they develop their own root system well and form long-lived trees.
If there are several shoots or offspring near the trunk (stump) of a dead tree, 2-4 best ones are selected for grafting, allowing them to develop well within 2-4 years.
During the repair of trees in the garden, depending on the age and development of shoots or offspring, grafting is performed either at the base or in the crown, leaving the "wild" trunk. Trees on such trunks are more resistant to frost burns. In the case of the formation of a crown on them, the grafting is done into each main branch, and in the absence of a well-laid crown, directly into the trunk, but at the height of the crown.
Grafting should be done by cuttings or budding (sleeping eye), depending on the age and condition of the stock, as well as the availability of cuttings for grafting (or budding). Shoots and offspring that are thicker than cuttings are grafted using one of the cutting grafting methods (saddle by the bark, butt, gaisfus, split, etc.), and those having the same thickness as them are grafted using the improved copulation method.
To rejuvenate fruit trees with a well-preserved root system, but severe damage to the entire aerial part, including the root collar, with weak regrowth or even complete absence of regrowth of shoots and offspring, grafting with a cutting is carried out directly into the main roots by the method of lateral grafting or a saddle behind the bark.
In this case, the roots are either cut off from the root neck, or left uncut. To plant a cutting, the roots are dug to a depth of 10-15 cm. Later, after the root grows together with the scion and the last shoots up to 10-15 cm are formed, the root with the base of the graft is covered with earth, which can cause the scion to form its own roots.
For a better fusion of the cutting and the stock, the grafting site must be firmly tied with a washcloth or twine, applying garden putty over the bandage. The cut surface of the tree is also carefully smeared.
After about a month, the bandage on the graft must be loosened so that it does not cut into the thickened wood, does not hamper development, and does not cause a fracture of the cutting at the grafting site.
When rejuvenating old trees, in order to protect the grafted cuttings from breaking (by wind, birds, tools during processing, etc.), they are tied to pegs placed on the grafted trees, and the growing shoots of the grafted cuttings are tied to them.
To get a stronger growth of shoots on grafted cuttings, it is necessary to leave one shoot on them, usually the top shoot, and pinch the rest. Developing shoots on the stumps of grafted trees are removed.
During the summer, the bandage and putty are checked and corrected and, if the latter has fallen off, a secondary cut putty is made. A repeated garter is also made to the pegs of the growing shoots of the graft.
By the end of summer, vaccinations usually give an increase in shoots of about one meter.
How an old tree is grafted is shown in the video below:
How to graft an old tree in the garden with cuttings? Grafting with cuttings is carried out at the beginning of increased sap flow at the rootstocks - in the first half of May, and budding with a sleeping eye - in late July - early August.
For spring grafting, cuttings of the corresponding varieties are harvested in late autumn (October - November) or early spring - in late March - early April (before bud break). For cuttings, locally available growing trees are used, and in their absence, cuttings are purchased from nearby nurseries.
To avoid premature bud break before grafting, harvested cuttings should be stored in a cool place (in snow or glacier).
And how to graft onto an old tree by budding with a sleeping eye? To do this, the cuttings are cut immediately before budding itself.
Trees that are renewed by grafting in the indicated ways are grown in semi-stem and low-stem forms, but more often in bush forms, the basis of which is laid by the graft itself in several cuttings. For this purpose, next spring, all strong one-year-old shoots are cut to a crown at a height of 60-70 cm from the grafting site, and during the summer they form the crown of a standard tree or bush.
In subsequent years, in order to further form the crown and regulate the growth and fruit branches, the crown is mainly cut - the removal of less important and thickening branches from it and partial pruning of the ends of the branches.
In order to avoid breaking off the grafted trees by the wind at the grafting sites for 2-3 years, until a strong union occurs, they are tied to stakes.
For a stronger adhesion of the scion to the stock, especially when placing several vaccinations in one stump, it is recommended to furrow the bark at the grafting sites (in the second or third year). Furrowing - a longitudinal section of the bark - is done in the spring after the leaves bloom; in this case, the incision should pass through the rootstock and the base of the scion.
Regrafting of fruit trees. Trees of non-standard and low-value varieties should be transferred to the crown with standard varieties. It is also necessary to graft into the crown trees - "grain" (seedlings of cultivars) and wild, if there are any in the plantations. Regrafting of trees can be done at any age, except for the period of dying. However, it is advisable to do it on trees no older than 35 years and healthy.
Re-grafting with cuttings is done in the spring, from the beginning of sap flow to mid-May, guided by the following guidelines.
- To rejuvenate fruit trees before grafting, you need to cut off all skeletal branches, starting from the top.
- Cut the upper branches closer to the main branch, and the lower branches further so that there is no excess in the flow of nutrients to the upper branches.
- The diameter of cut branches should not exceed 3-4 cm, as large cuts do not grow well and crack.
- Completely cut off excess branches from the crown.
Regrafting of old trees with a large number of branches should be done within 2 years.
Regrafting is done in various ways: saddle by the bark, stock, improved copulation, lateral, etc.
As shown in the photo, the regrafting of old trees begins with the upper branches, gradually moving to the lower ones:








In branches with a diameter of 3-4 cm, 2 cuttings should be placed to ensure better overgrowing of the cut. The development of vaccinations must be strictly monitored, simultaneously loosening the tie and tying up the grafted cuttings, along with the shoots growing from them, to thin pegs fixed to the branch below the vaccination site.
The re-grafted crown is periodically pruned in subsequent years, depending on the development of the branches. Regrafted trees from the 3-4th year (sometimes from the 2nd) begin to bear fruit.
On the video "Rejuvenation of trees" you can see how grafting and regrafting is done:
Compaction of fruit trees in the garden
As mentioned above, denser stands create better conditions for mutual protection from adverse meteorological influences. Meanwhile, in industrial orchards (especially young ones), based on tractor cultivation of row spacings, distances between trees were given as 10 x 10 m or 10 x 8 m. These distances significantly exceed those required even with the full development of trees. At such distances, young trees remain solitary for a number of years and experience the harmful effects of winds, dry winds, and frosts, especially in the absence of good protection. Significant loss of trees from freezing to an even greater extent increases the sparseness of gardens.
It is advisable to compact such gardens by planting fruit trees and especially early-ripening species - berries and stone fruits.
Compaction of fruit trees in the garden can be done according to the following schemes.
- In young orchards with wide row spacing, simultaneously with planting in the places of fallen trees, plant new rows of trees in the middle of the row spacing (one per row spacing), maintaining the existing distance in the rows. Thus, at a distance of 10x10 and 10x8 m, a dense planting will be with a distance of 10x5 and 8x5 m. This feeding area is quite sufficient for the normal development and fruiting of trees.
- Only in rows, planting one tree at a time between apple trees: either apple trees are early-ripening and early-fruiting varieties, or stone fruits (cherries and plums).
- Berry bushes (currants and gooseberries), planting them in rows between apple trees, with a distance of 1.25 - 1.5 m between the bushes.
Compaction of plantings should be carried out taking into account the possibility of mechanized tillage.
Condensed plantations, as mentioned above, by the time the trees of the main planting are fully developed, are rarefied: berry stands - after 12-15 years, stone fruits - after 20-25 years.
Watch the video "Rejuvenation of the old garden" to better understand how restoration activities are carried out:
Proper pruning of old fruit trees for rejuvenation
Restoration of trees is possible due to regrowth. Slightly damaged plants can be restored by growing the surviving parts.
In fruit-bearing and young trees with the trunk and main skeletal branches of the crown preserved to some extent, it is necessary to prune (rejuvenate) all frozen and dried branches to healthy parts that can shoot mainly from dormant buds. Due to these shoots, the crown of the tree is restored.
Pruning of old fruit trees in gardens with completely damaged crowns and partially trunks is done in spring to a healthy place. At the same time, when pruning old trees with a well-preserved trunk or most of it, in the presence of regrowth of lateral shoots on it, to restore the crown, leave only 3-5 shoots uncut, thus initiating the formation of a tree in a low-stem form (crown reduction). In case of a strong deviation towards the upper shoot, it must be tied to the left stump.
When pruning fruit trees for rejuvenation and severely damaged young trees, during the growth of cultivated shoots, one of them, the best in development and position, is left in the lower part of the trunk, the rest are cut out. The left shoot in order to straighten it and protect it from breaking off must be tied to a stump or a nearby peg. By the end of growth, the shoot will be a well-developed one-year-old.
The following spring, after proper pruning, the crown is restored for all old fruit trees due to shoots growing on the trunks. Next, hemp is cut out, and the sections are covered with garden putty. The lateral shoots of the crown and the continuation shoots are cut to 14-1/3 of the length in order to form, and the same-year-old trees are cut at a height of 60-70 cm per crown. In the future, the formation of the crown is carried out by the usual methods.
To restore an old fruit tree by pruning for rejuvenation, 3-5 best shoots are left, growing from a well-preserved and healthy lower part of the trunk. With a weak development of shoots or the presence of damage in the lower part of the trunks, the bush is renewed due to stronger offspring, selected in the number of 3-5 and distributed more or less evenly within the near-trunk circle with an area of about 1 sq. m.
In autumn or spring, all unnecessary, not going to restore the bushes, offspring are dug up both in rows and between rows.
Cherry and plum plantations restored by pruning old trees for rejuvenation, representing a type of nest planting, as they develop in the coming years, create favorable conditions for the mutual protection of both individual nest plants and the entire plantation. They also contribute to greater snow accumulation, improving the regime of soil moisture and air temperature within the crown. After pruning trees for rejuvenation, one can hope for good growth, a healthy state of the plantation and an annual high yield.
In gardens, which are continuous thickets from the growth of shoots and offspring, they are first dug up (uprooting) in the aisles and rows, and in the near-trunk circles a few more shoots and offspring are left than is required for a normal bush. A year later, the final thinning (normalization) of the bushes is carried out, leaving 3-5 shoots or offspring in them.
When uprooting and thinning, care must be taken to maintain the correct direction of the rows, the distance between them and the bushes in the rows. The row spacing should correspond to the varietal characteristics of the crop and the conditions of mechanized processing.
In trees (bushes) with intact trunks and bases of skeletal branches, the crown is restored by rejuvenation.
All grafted trees with a dead aerial part are uprooted, and new ones are planted instead.
Ecological garden: What associations do we have with the old garden? First of all, these are old, abandoned gardens, sadly sung in the works of Russian writers and poets, in Russian romances; our ideas about how much the old garden has seen in its lifetime and how many secrets it holds
What associations does the old garden evoke in us? First of all, these are old, abandoned gardens, sadly sung in the works of Russian writers and poets, in Russian romances; our ideas about how much the old garden has seen in its lifetime and how many secrets it keeps under the canopy of its overgrown trees. Or maybe thoughts about how many secrets were told in him and tears were shed.
The cozy corners of the garden were hidden from prying eyes and gave joyful moments of solitude. And also, if this is your old garden, it can give childhood memories and remind you of important events in your life. Now that you have grown up, matured, you want to change. And the garden needs updating.
It also happens that people do not deal with the garden of their childhood, but they simply got it originally in its old form, then it will not be so pitiful to reconstruct it, although the best in the old garden should still be preserved. Gardening specialists consider it expedient to rejuvenate the garden when the trees reach 18-20 years of age and older, when the yield is significantly reduced and the quality of the fruits deteriorates, and annual growths are only 10-12 cm.
In order to correctly orient readers, we first give the opinions of famous gardeners and designers on this issue.
Uprooting trees and shrubs.
First of all, it must be remembered that the old garden needs periodic renovation. In an adult fruit-bearing garden, thinning should be carried out systematically: this is the uprooting of old and selective significant pruning of individual trees and shrubs. Sometimes, although rarely, it happens that a tree has to be uprooted after severe damage by mice, hares, other pests or diseases. It happens that part of the crown collapses under the weight of the crop and the wind. Here you need to think about how best to proceed: whether to restore it (although this is usually difficult to do), or to completely remove this part.
A positive factor when uprooting dead, old, diseased, non-winter-hardy fruit trees is that a significant area is immediately released in the garden, which can be used for planting other crops, depending on their demands for light.
Tree pruning.
It leads, first of all, to an improvement in the illumination of the garden. It is carried out, for example, as follows: a frost-resistant tree is selected from the south side of the site, its entire crown is cut off and re-grafted with a new one or several varieties. A mature orchard usually produces a sufficient yield, so it is possible to apply heavy pruning to either side of the canopy of one or more trees. For this, perennial skeletal branches are removed with a saw almost at their base or transferred to a side branch. Sometimes heavy pruning is necessary on one side of the crown of a tall tree, which obscures a less tall but more valuable one.
It also happens this way: the gardener sees that one of the paths in the garden is well lit by the sun, and decides to use it for planting any light-loving crops, naturally, adding a sufficient amount of nutrient soil to this place. He lays a new path under the crowns of mature trees, cutting off individual branches that are under shading and do not give a good quality crop.
It is necessary to remove part of the crown or the whole tree not in early spring and not in late autumn, when the plants are without leaves, but during the period when they give the greatest shade. This is usually done in the fall, after harvest.
An amateur gardener should also remember the need to periodically change the places where berry bushes are grown. So, after 10 - 12 years, blackcurrant bushes are uprooted and, after thorough fertilization of the soil, new plants are planted in the intervals between the old planting. Old plantings of raspberries are also replaced with new ones, but new places are already allocated for them. In one place, raspberries can be grown for no more than 12 years.
These were the advice of the country-famous gardener B. A. Popov.
There is another remarkable person, a scientist with extensive experience in horticulture, known to many gardeners, a researcher at the selection department of the All-Russian Selection and Technical Institute of Horticulture and Nursery of the Russian Academy of Agricultural Sciences - Anatoly Mikheev, whose recommendations in rejuvenating gardens must be heeded.
So, an experienced scientist does not advise immediately getting rid of everything unnecessary in the old garden. It is necessary to carefully observe the life of the garden and only then proceed to its reconstruction. First of all, it is necessary to carefully examine each tree. The reasons why trees need to be uprooted are as follows: if they have hollows, the bark dies off, cracks heavily and lags behind, annual growths are weak (no more than 10 cm).
A single tree is easiest to cut down at a level of 40–50 cm from the ground. If it is surrounded by other trees, shrubs, then you should first cut down the skeletal branches (starting from the bottom), and then the remaining bare trunk, but not at the surface of the earth, but at a height of about 1.5 m: it will be easier to swing it when uprooting.
It is also recommended to use such a simplified method of uprooting trees using ammonium nitrate: cut the tree as low as possible, gouge a recess in the stump (it is better to drill several holes with a drill), pour two handfuls of ammonium nitrate into it, cover it with a plastic bag and tie it with twine. In a month, saltpeter will corrode the wood and turn it into dust. In the vacated space, if it is not shaded by other trees, you can plant a new plant. At the same time, it is important to remember about the cultural turnover and self-fertility of varieties (these are varieties that can set fruits without the presence of pollinating varieties nearby):
- you can not plant an apple tree after an apple tree, a pear after a pear, and a plum after a plum;
- in place of the uprooted apple tree, cherry, plum, pear should grow - and the same with other trees.
Rejuvenating pruning.
If 20-25-year-old apple and pear trees have healthy trunks and main branches, they can grow and produce crops for a long time, although the fruits will become small over time. Such trees needrejuvenating pruning. In the first year, the crown must be subjected to strong thinning - to remove perennial branches. This will give impetus to the awakening of dormant buds on the trunk and at the base of the skeletal branches. From them grow long vertical shoots, the so-called tops.
The following year, tops that thicken the crown are cut into a ring, and the remaining ones are shortened, leaving two or three lateral buds. Trimming into a ring means that no stumps are left during trimming, and the cut itself is even and without breaking the surrounding bark. From the growing shoots and form a crown. In two or three years it will be possible to collect large fruits.
Promising varieties can be grown in an old garden by regrafting part of the skeletal branches on an old tree. Tops are also suitable for this. True, a lot of grafting will have to be done so that new varieties make up a significant part of the crop. The benefits of regrafting are obvious: thanks to the mutual pollination of several varieties, fruits are better tied and their quality is improved.
If in the old garden you inherited grow irga, chokeberry (chokeberry), wild-growing hawthorn and mountain ash, you should not get rid of them. Pear varieties can be grafted onto these plants ('Velesa', 'Chizhovskaya', 'Thumbelina', 'Vidnaya'). They will not be as durable as those grafted onto a wild pear - they will live for 15-20 years, but in the third year they will give a good harvest.
In case of planting only one cherry or plum tree, it is recommended to choose a self-fertile variety that does not require cross-pollination (cherries - 'Molodezhnaya', 'Bulatnikovskaya', 'Rastorguevskaya', 'Memory of Enikeev', 'Rusinka'; plums - 'Morning', 'Egg blue', 'Blue gift', 'Alexy'). Or, in the crown of a self-fertile variety, say 'Skoroplodnaya', plant a pollinator variety - for example, 'Red Ball' or one of the varieties of cherry plum (for the Moscow region, 'Kuban Comet', 'Traveler', 'Cleopatra', 'Golden Fleece' are recommended ).
It must be remembered that all cherries are self-fertile, and in order for a single tree to bear fruit, two or three other varieties must be grafted onto it. In this case, the tree will look very beautiful if it is possible to select varieties with different fruit colors for grafting, for example, dark red ('Fatezh'), pink ('Bryansk pink') or yellow ('Chermashnaya'). Note that cuttings or seedlings of the varieties listed above can be bought without problems in nurseries or in stores.
Berry bushes in the old garden also require rejuvenation. This work is best done in the fall. For example, currants and gooseberries can grow and bear fruit in one place for 10-12 years. With age, annual growth weakens, yield and quality of berries decrease. It is recommended to uproot and burn bushes older than 12-15 years. In the vacated places, it is best to plant other crops - raspberries, vegetables, ornamental shrubs.
But you can do it differently: remove the entire above-ground part of the berry bushes, and form a new young crown from the growing branches, shortening 1-2-year-old growths by 4-8 buds. Or like this: cut old 5-7-year-old branches to the base, shorten 3-4-year-old branches to the side branch and thin out the bushes, removing weak and thickening branches. After rejuvenating pruning, currants and gooseberries will yield another 5-6 years.
We wish you a successful rejuvenation of your old garden! published