Bunker shelter. Construction and equipment of bunkers. No bureaucracy required
People, as you know, love to be afraid. This weakness is successfully used in their business not only by filmmakers, but also by builders and real estate agents, whose new hit of sales has become comfortable bomb shelters. The range is wide - from minimalist structures, more like a cistern dug into the ground, to luxurious underground mansions.
In 1949, after the Soviet Union conducted its first nuclear test, President Harry S. Truman created the Federal Civil Defense Administration (FCDA), asking Congress for millions of dollars to build a nuclear defense system. At the end of the 50s, funding began for local civil protection departments, whose responsibilities included organizing and supplying air-raid shelters. However, the strongest impetus for their construction was given by the young President John Kennedy (John Fitzgerald “Jack” Kennedy), who in 1961, at the height of the Cuban Missile Crisis, called on his fellow citizens to show consciousness and take care of their own security. Citizens began to build private shelters from the Soviet nuclear bomb. 

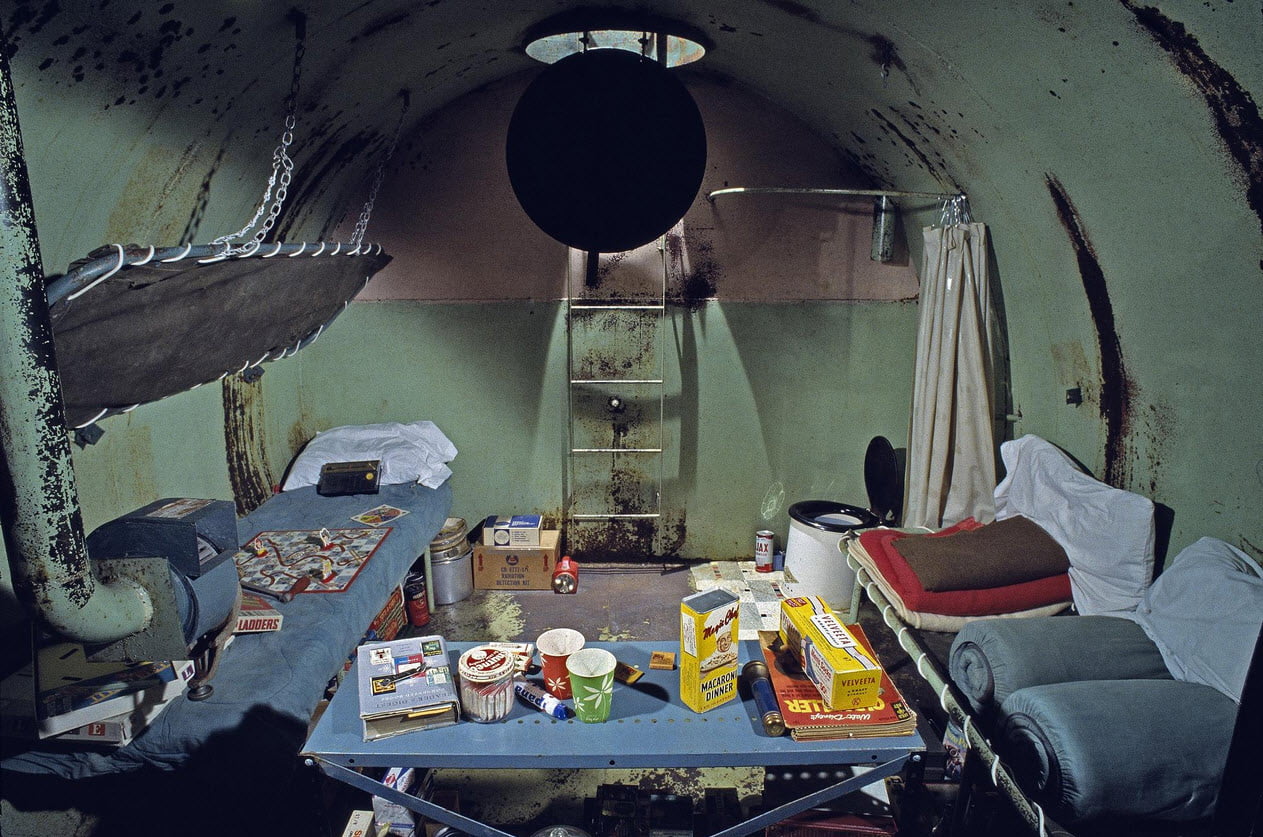
Funded by local and federal authorities, thousands of public shelters were set up across the country, providing shelter for two-thirds of the population. In Washington alone, about 1,300 public shelters have appeared with more than a million beds - enough to accommodate all the city's residents and even some of its guests. However, these were not specialized structures. As a rule, semi-basements of residential buildings, churches, schools and public buildings were used for these purposes, the walls of which were reinforced with concrete to protect against radiation, after which the necessary supplies of food and medicine were stored there. 
In 1965, in the Washington suburb of Bethesda, an experiment was conducted in which 34 Navy officers spent four and a half days in such a basement, eating "shelter" food - cookies, tomato soup, peanut butter and jelly. The subjects lost an average of 2.36 pounds of weight, were in a bad mood and complained of constipation. 
There were much fewer private bomb shelters built - according to some estimates, about 200 thousand of them appeared between 1945 and 1961. On the one hand, it was expensive: in 1961, it cost $2.5 thousand to build a shelter in the backyard of a family home. On the other hand — created the ground for friction with neighbors, since it posed a dilemma: to take them or not to take them into a close family shelter if something happened? The question is all the more difficult because digging a “hole” in the backyard most often became the subject of ridicule from these same neighbors. 

A typical family bomb shelter in the garden, measuring three by four meters in area and accessed through a hatch, took two years to build. In 1961, 38-year-old Charleston, West Virginia resident Michael Preiser, inspired by President Kennedy's call, founded Shelters Inc., which became very successful. The secret of success was that the company sold standardized bomb shelters. It was essentially a set of corrugated metal parts that did not require professional construction skills to assemble. On average, such a shelter cost $685, broken down into monthly payments of $15. 

Some enthusiasts created more powerful structures. A certain head of a family from Washington state built a four-level underground fortress with an area of 130 square meters under his three-story house. m, with several rooms, numerous passages and a three-ton door opened and closed by an electric motor. Life support systems ran on a generator that occupied a separate room. By the way, this house is now on sale for $259 thousand. 
There were also special offers for the rich. In California, Hungarian-born architect Paul László, who built houses for such Hollywood stars as Gary Grant and Barbara Stanwyck, even developed the entire concept of Atomville USA ("Nuclear Village USA"), according to which it was possible to escape the consequences of a nuclear strike in special underground settlements, the structures in which would be connected by a cable car. While the idea was being considered at the Pentagon, the architect built a private bomb shelter in Woodland Hills. In keeping with the architect's signature style, with an emphasis on luxury and comfort, the air raid shelter was a spacious room with telephones and other amenities and could be used as additional living space. Another famous architect at the time, Robert Stacey-Judd, born in London, also designed bomb shelters to order, making them similar to the structures of the ancient Mayan tribe, whose culture he was interested in. 
In the 70-80s, when the anti-nuclear movement tried to convey to everyone that the explosion of even one nuclear bomb would make salvation impossible, bomb shelters began to fall into disrepair. The authorities began to close public shelters, some of the supplies were thrown away, some were distributed to the poor. Their owners converted private bomb shelters into wine cellars and mushroom growing workshops. Local civil defense departments have finally merged with the federal Ministry of Emergency Situations. And if in the 50-60s, programs to protect the population were 90% designed to combat the nuclear threat and only 10% to deal with natural disasters, now the ratio is exactly the opposite, with 10% “reserved” for the nuclear threat. quickly reorient themselves to combating the consequences of terrorist attacks. 
After September 11, there was renewed interest in bomb shelters. In the spring of 2002, the UC Santa Barbara Branch Museum of Art even organized an exhibition entitled “Nuclear Families: The California Nuclear Shelter Movement, 1950-1969.” It featured, among other things, shelter plans designed by Paul László and Robert Stacy-Judd. 

Local branches of the Ministry of Emergency Situations have noted an increase in calls: people are interested in the addresses of bomb shelters and how to build them. Private entrepreneurs, unlike the state, instantly responded to the growing demand. Manufacturers of shelters in the US claim that their sales have increased by 500%. A typical mass-produced shelter resembles a buried tank and costs about $30,000. But you can choose something more fun that preserves your usual lifestyle as much as possible. 
F-5 Storm & Fallout Shelters, based in Baskin, Louisiana, has been making vent units with filters sourced from Switzerland since the '50s and selling them nationwide. Without taking into account installation costs, they cost from $8 thousand to $20 thousand, depending on the configuration. Harden Structures of Virginia Beach, Virginia, sells "survival tents" that purport to protect against chemical, biological and nuclear threats and start at $7,500. For $66,000, Radius Engineering of New Hampshire offers a product called The P10 Disaster Shelter is a ten-person fiberglass structure that fits underground and has bulletproof hatches. 
Kleen Air Technologies Inc. of Frisco, Colorado, works for even more demanding clients: the 18 shelters it has already sold have wood floors, a kitchen and even a laundry room, walls more than half a meter thick, and a minimum area of about 100 square meters. m, although orders mostly come for much larger premises. Mirrors create the effect of expanding space, false illuminated windows create the illusion of a sunny landscape outside the window, and a meditation library should help overcome depression.
In addition to luxurious baths, there are decontamination rooms and a state-of-the-art control room with a generator, internal surveillance cameras, radiation meters, shortwave transmitters, police wave scanners and much more. Starting price: $600 thousand.
20th Century Castles LLC, based in Dover, Kansas, converts closed underground missile bases into bomb shelters for luxury private homes. The former Atlas-F rocket launch base in Adirondack Park, New York, has been converted into a $1.7 million mountain retreat. m with a private landing strip there is a spacious accommodation with three bedrooms. The former Atlas-E rocket launch center in Wamego, Kansas, has been converted into a 1,400-square-foot underground fortress. m for ten people, with a sauna, kitchen and a massive 47-ton garage door (sold for $1.2 million). 
Over the past decades, not only the appearance, but also the concept of shelters has changed. After the films “Panic Room” with Jodie Foster and “Dark Areas” with Bradley Cooper with special rooms, which are increasingly called “panic rooms”, their purpose is to hide a wealthy family from raiders or kidnappers and help them hold out until the police arrive. Such a room could simply be a closet with a reinforced door and a telephone inside.
However, a more typical option is a room separated from the rest of the house by reinforced walls and a hidden magnetic door. It is equipped with a ventilation system and telephone lines, as well as a toilet. For the most demanding clients, we offer Kevlar-armored bulletproof internal walls, indoor television surveillance systems for the house, a generator and other technical support. It is not known how many of these rooms have already been built, but it is known for sure that their owners live mainly in prestigious areas of Manhattan and Hollywood, and it is not surprising - a fully equipped room costs up to $500 thousand. 
Shelters are also being built in Europe. In October last year, the home of well-known realtor Christian Pellerin was demolished for violating planning regulations on the Azur coast in France. In an estate worth $23 million (bought at one time for $100 thousand from an American woman), underground structures with an area of 743 square meters were discovered. m, the construction of which was carried out without permission. This was the reason for the demolition of the house. The underground facility, described by authorities as “a stunning combination of luxury and vulgarity,” included swimming pools, fountains, Jacuzzis, thermal saunas and a bomb shelter.
Programs for the construction of air-raid shelters exist in a number of countries, for example in Switzerland, as well as in Singapore, where a special law in 1998 made their construction mandatory in residential buildings. Since 1983, when the project began, 87 thousand have been built in municipal residential buildings and about 1 thousand in private ones. They can shelter 700 thousand people. 
(2
ratings, average: 3,00
out of 5)
Recent events in different countries indicate that the peaceful situation in the country can change in a matter of hours. Many of us do not think about what weapons the enemy army might use. Accidents at nuclear power plants and other man-made disasters are a direct threat to the lives and future health of people.
To give yourself and your loved ones the opportunity to survive unsafe events, you can build a bomb shelter or bunker with your own hands. This is especially true for land owners.

Preliminary activities
It is not advisable to hire specialists for the construction of this facility - it is expensive, and it is very difficult to find such specialists. It is worth considering that the construction of this structure will require significant material costs for full operation. Before starting construction, you need to determine the type of structure, its purpose, area and necessary equipment.
Then make an estimate. It is advisable to establish whether centralized utilities are located underground at the site of the proposed bunker construction. Permits are not required to build a bomb shelter or bunker on your own site.

Before starting excavation work, it is advisable to determine at what depth the groundwater flows. You can do this yourself. Pay attention to nearby bodies of water and the water level in your neighbors' wells. Your bunker should be at least half a meter above the groundwater level. The optimal depth for building a bunker is at least four meters. If the waters in your area lie closer to the surface, then the construction of an underground shelter in this area is not advisable.
Basic requirements for bunkers and underground shelters
A bunker is necessary to protect people from the destructive effects of the elements, nuclear explosions, and artillery shelling. What are the requirements for a bunker:
- the shelter must provide reliable protection from adverse impacts;
- the facility must be equipped with several exits;
- be resistant to increasing amounts of moisture in the soil;
- provide conditions for the full functioning of people during the period of placement in the shelter;
- comply with the necessary sanitary and hygienic standards.
The characteristics of a shelter depend on many factors:
- level of protection from external influences;
- location relative to a residential building;
- spaciousness;
- duration of stay in shelter;
- speed of construction of the structure;
- the presence of a ventilation system and its power.
In the case of a structure for short-term use, it reduces costs and facilitates the construction process.
Let's start construction work
Foundation and floor
After completing the preparatory work, you can begin marking the area for the future underground shelter. A pit of the required size is dug along the marked boundaries. It is advisable to make it larger than the planned dimensions of the bunker for the convenience of working with the walls by treating them with waterproofing materials. Afterwards we prepare the basis of the future structure:
- it is necessary to level the bottom;
- backfill with clay, fine gravel, and sand on top;
- if desired, lay a vapor barrier film;
- Fill the floor with cement mortar using reinforcing metal mesh.
When pouring, it is necessary to leave cavities for future utilities and highways. The reinforcement frame used to fill the floor must be tied to the overall structure. After pouring, the screed should dry for two weeks.

Walls
For the construction of walls, it is optimal to use concrete or expanded clay blocks, but the best option would be monolithic concrete walls. To increase the strength of the structure, it is recommended to fill the walls and internal partitions of the shelter with concrete mortar. When building an underground shelter, concrete must be of the highest quality with the addition of moisture-repellent additives. The height of the walls must be at least 2.2 m. The outer side of the walls must be treated with moisture-resistant impregnations, resins or slabs.



Roof
After erecting walls and partitions, take care of the installation of utility lines. Route electrical cables to the structure. After that, proceed to the roof. For a bunker, the strength characteristics of the roof are checked by hitting a projectile. It is optimal to start work by laying the metal I-beam on which the roof frame is built. Next, lay a sheet of metal 40mm thick. Next, you need to lay a vapor barrier.
The next layer can be made of concrete screeds followed by pouring concrete mortar. For entry, leave a hole necessary for unimpeded entry into the bunker if necessary. A hatch or door is selected to ensure maximum tightness. To descend, build a reliable ladder.


Before starting interior decoration, it is necessary to carry out moisture-proofing treatment indoors. To do this, use waterproofing or liquid glass. Afterwards, if necessary, partitions are erected to zone the space.
Engineering Communication
To extend the period of stay in a shelter, it is necessary to take care of an uninterruptible power supply and ensure high-quality ventilation of the room using air filtration systems. To save space, sleeping places are arranged in the form of beds in two tiers. If it is possible to install a sewer system, this will solve many sanitary and hygienic problems. If water supply and sewer pipes are located nearby, it is worthwhile to provide for the supply of mains to the shelter.
Strategic reserve
To ensure life in extreme conditions, it is necessary to leave a reserve in the shelter:
- drinking water, at least 300 liters, technical water, at least 100;
- shelf-stable canned foods, cereals and spices in sealed packaging;
- The first aid kit should contain dressings, antiseptics, antibacterial agents, a thermometer, water disinfectants, adhesive plaster, scissors, a tourniquet, gauze bandages, and a set of medications as needed;
- protective clothing, shoes;
- lanterns;
- gas mask, respirator;
- means of communication with the outside world.
The bunker is covered with soil from above, masked around the entire perimeter of the roof, leaving a hatch on the surface for entry.
- If you're not aware of the soil conditions in your area, it's a good idea to take this into account before you decide to put up a shelter, because the soil can be very thick in the wet season and as thin as feathers in the dry season. The hole should be dug at an outward angle to prevent it from collapsing on you. Some areas have soil as strong as dry clay, while other areas have calcium carbonate, which is something comparable to good strong clay soil. This type of soil will allow you to dig the hole straight down with less chance of collapse. Here you can save on framing material. You can use mud as a backup base for cement. Areas where the soil is softer and more dangerous to work in need high cover unless you have another place for the hole. Another problem in small areas when working with very soft soil is if you are digging too close to your neighbors' property. Their house may begin to crack, and you may be punished for it. Masonry underground or a block of concrete is a big project considering the cost of materials and finding a solid plan. Millions were spent developing such plans during the Cold War, and they were tested in specific terrain, making them the #1 choice. Unfortunately, many of them are no longer in print, but they can be found in e-books at www. firstpatriotpress.com. You don't have to go into debt to build a shelter. Using a list of materials and an old pickup truck with a few bags of cement, you can gradually gather the materials you need, piling them next to your house over a short period of time. It's always a good idea to buy minus 10% of your list so you don't end up with a bunch of unnecessary materials. If you hire a contractor to do some work, buy 100% of what you need so that contractors don't run around and buy more materials and demand money for it. So that you don't pay for the work of three men, not one. If the contractor needs something, he will have to break off from work and go buy him something. Labor is the most expensive commodity on a job site, so if you're missing a few pieces of plywood, always head to your local store to buy the supplies you need. Three or four people standing around while you drive across town to save a few bucks is just stupid. You can build the shelter yourself, but it's a hefty project. Buy plastic rebar in case you trip and fall, because a piece of protruding rebar can kill you if you fall on it. The bending of the reinforcement is done by bending the rigid pipe on the crossbar by 5 cm. Press down on the base with your foot, lift the pipe and you will have a fairly right angle. Cutting rebar is easier than cutting with a saw, but you can also do it with a hacksaw. Make the cut half way and put your foot on the side of the cut and it will break as you lift. This will save you from cutting the entire length of the plank.
- Be sure to stock up on food, water, and preferably omega-3 supplements, calcium, and multivitamin tablets. Make sure that there are no windows or holes in the piece of plywood and that most of your shelter is underground. Existing basements or cellars will require additional shielding. Here are the minimums to stick to: 10 cm of concrete, 12-15 cm of brick, 15 cm of sand (bags or boxes, it doesn't matter) can be filled with earth as a side support, 17 cm of earth, 20 cm of hollow cinder blocks filled with earth or sand if nothing else is available (12 cm if with sand), 25 cm of water, 35 cm of books/magazines or 45 cm of wood. Make sure you have plenty of food and water, canned food or any other food that won't spoil. Ready-to-eat foods are also recommended.
- First aid kit. It is imperative to have a wide range of medications, and not just a set of emergency medications. Here's what a first aid kit should contain, as recommended by the Ministry of Defense:
- Sterile gauze dressings 10x17 cm
- Compress and bandage 5x5 cm 4 strips
- Gauze bandage compress type 7 cm x 6 m
- 3 five-meter rolls of 2 cm and 5 cm wide gauze bandage
- Compressed bandage 93x93x132 cm
- Gauze, petrolatum 7x66 cm 3 stripes
- Scotch tape 2 cm x 1 m 100 strips
- Adhesive plaster 1x7 cm 100 strips
- Eye wash
- Ammonia solution for inhalation, aromatic ampoules (1/3cc, 10 units)
- Povidone-iodine without iron, 10% 1.4cl
- Sodium chloride bicarbonate mixture (salt)
- Surgical razors/scalpels
- Instructions for use and maintenance.
- The following are particularly recommended medications that should be included in your kit, although some may need your doctor's approval (many can be used to treat symptoms of radiation sickness):
- Tweezers
- Compazine suppositories (for nausea and vomiting)
- Opium tincture (for diarrhea)
- Antacid tablets (for upset stomach)
- Bottle of aspirin (minor pain)
- Narcotic (severe pain)
- Other non-essential items you should have:
- Sleeping bags
- Lots of warm clothing and blankets (when you are outside the shelter) and light ones when you are inside
- Sunscreen and lotion
- Toiletries
- Sunglasses
- Flashlights and batteries
- Radios and walkie-talkies (not cell phones, the EMP (electromagnetic pulse) from the explosion will be useless for a while so you won't receive any signals)
- Self-powered flashlights and radios that are sealed in aluminum foil or other metal so that EMI will not damage them. Batteries will be very difficult to find after a nuclear attack, for obvious reasons, so make sure the power is self-sufficient.
- Torches
- Candles. Use only if there is no gas leak nearby; explosive gas.
- Glowing sticks
- Waterproof matches
- Smokefuckers
- Compass
- Chalazone tablets for water purification (they will not filter out radiation, only pathogens!)
- Needles and threads
- Canvas
- Weapon for self-defense, preferably a pistol.
- Axe/cutter, handsaw, crowbar, leather knife, combat knife and cutlery. (Remember to bring a whetstone or grinder to sharpen sharp objects.)
- Pencil, paper and anything else that will help pass the time
- Copy of this article
The house is considered a protective fortress for every person. Within the framework of this conventional concept, many began to think about more reliable buildings. The question arises of how to build a bunker. It is located underground, nothing better can be imagined. If a person is afraid of natural disasters and simply tries to stay in a protective place, there are special projects for such a structure.
You can build it on your own site, often this is done at the dacha. There are a number of advantages to this shelter, although it does not always save. If you decide to build, you will have to take useful instructions as a basis and implement the project according to it. There are no difficulties, just prepare all the tools and materials, because the house underground has its own construction features. What exactly are the features, we will consider further.
There will be no paperwork
When thinking about how to build a bunker, many take this issue into account. Is there any paperwork required? The first advantage, according to experts, is that there is no need to prepare documentation or obtain permission for such a structure. But this is provided that everything is done on a personal plot. Although there is an exception. If there are communications of central importance under the soil, it is more difficult to make a bunker. The structure may be damaged, and this is a serious violation.
Before building a bunker, all these issues should be clarified. This is the first step towards constructing protective housing. It will not be possible to do it alone, so an assistant must be present, or better yet more than one. Only after this the main work begins. It is important to take into account the proximity of groundwater during construction.
Proximity of groundwater
Before building a bunker, you will have to understand at what level the groundwater is. If you ignore this, you will end up with not a living space, but a large swimming pool. To do this, it is important to know at what depth the waters are. But can such procedures be performed independently? According to experts, the process is not so complicated: attention is directed to the nearest wells and any bodies of water. The difference between the ground and water levels will become the principle of occurrence of ground flows. It is not difficult to make accurate calculations; it is important to take your time at this stage. The instructions for performing the work are elementary - everyone who creates their own in-depth home must come to this goal with certain knowledge.
Opinion of experienced architects
Another assistant is deep-water wells. In the process of their creation, it becomes more clear at what level the ground flows occur.

The house underground should be formed above the streams, the minimum distance is 50 centimeters. The bigger, the better. Here is the calculation: if the groundwater is at a level of 5 meters, then the foundation pit for a new building is made at 4.5 meters. Although when groundwater lies above 4 meters, it will not be possible to create a full-fledged house underground. Because attention is paid to comfort, protection, ease of existence for a long time. Reliability is not the last thing, so every little detail will have to be calculated.
How to choose a place?
Many people think about how to choose a base and calculate the depth of the bunker. Sometimes ideas arise to build a shelter under the house, in the basement. Architects believe that this is a bad idea and should not be implemented. And all because disasters occur - hurricanes, winds, flooding. The main structure will collapse, and the entrance to the shelter underground will be showered with fragments. We'll have to look for something more suitable. If the size of the plot allows, construction begins.
Although such a structure is allowed if there is an additional entrance to the bunker, at a distance of up to 10 meters from the house. Communication is essential for a fulfilling life. If they are autonomous, this is the best solution. Communications should not be connected to the house; in the event of a collapse, there will be no electricity supply to the bunker. This is emphasized by all architects and specialists in the construction of residential premises.

In addition, you will have to hide the entrance area. It is located in the place of outbuildings on the site. Often the construction of a bunker with your own hands is carried out from the entrance. Let him be in the garden among the trees and bushes. It will not be visible to anyone - only the owners will know how to get into their
What area?
An important point in every home is to check the dimensions. The basis is that people will stay in it for a short period of time. During a natural disaster, a hurricane, the following calculation of the area is made - 4 m 2 per resident. In these conditions, it will be comfortable to wait out unfavorable conditions on the surface of the earth.
If there are three people in a family, then it turns out to be 12 m2, it is not difficult to implement such a project. The calculation is carried out by multiplication. If the area around the house is large, then the area increases, but not to the detriment of comfort. Bunkers are built for temporary and long-term stays. The choice of some parameters depends on this.
Short period
Architects believe that in order to stay inside the shelter for a short period of time, a septic tank made of durable material may well be suitable. What is being done:
- Purchase a durable container.
- It is buried in the ground at a certain distance.
- The size is calculated based on arrivals.

You can wait out hurricanes and tornadoes in it, and it also does not require additional care for many years. There is no need to invest in this building, install ventilation and heating. To exhaust the air, two natural ventilation pipes going to the surface are enough. There is no need to supplement the structure with special cleaning devices.
You will need to install a standard filter for cleaning. Sometimes it is done with your own hands. You buy gauze and glass wool - they are fixed to the pipes. Electricity is connected to the main system. It is worth making batteries so that there is a supply for a long period.
Heating
This is an open question. Because the ground does not freeze more than one and a half meters. Maximum heat is not required for temporary stays. Experts advise having a reserve:
- Warm things.
- Blankets.
- Blankets.
- Thermal underwear.
The price of such a shelter is around 400 thousand rubles. The required volume of the septic tank is 19 m3; preparing the pit will not take long, and everyone can handle it quickly. It’s easy to hire workers for about 30 thousand rubles.
For a long stay inside
Before building a long-term underground bunker, it is worth considering each room. Its total area is no less than 15 m2. A separate room is provided for the location of generators and other necessary components.

For such a structure, drainage is made under the foundation. It must be at least 25 centimeters, and the wall - 27. To prevent the soil from creeping, it is strengthened using accessible, inexpensive material. The bottom of the pit is leveled before construction begins. After the foundation dries, the walls begin to be erected after 30 days. For reliability, the reinforcement should be fixed every three rows. The size of the drainage under the foundation is created arbitrary.
The roof must be reliable. Durable metal is used. We must not forget about heat and waterproofing. A ladder for descent and a tightly closing door are installed. In order not to call such a shelter a trap, an emergency exit is made. Before you begin interior decoration, it is worth creating durable, high-quality waterproofing for the walls. There are many materials for this. Next, a partition is made between the main housing and the engine room. The cost will be around 150 thousand if you do it yourself.
To stay in such a protective shelter for several days, it is worth considering:
- Autonomous electricity. A generator running on diesel or gasoline is suitable. For fuel storage, two-tier installations are made.
- Ventilation with air filtration.
- Conditioning. Thanks to this, air is supplied with purification; the installation cost is high.
Reserves
If your stay involves several days, then you cannot do without supplies. One of the important components is water (at least 300 liters). The number of people matters. It is important to have canned food, cereals, and other products that are packaged and have a long shelf life.

You can't do without a first aid kit. It includes:
- Bandage, adhesive plaster.
- Cotton wool.
- Thermometer, tonometer.
- Scissors, tourniquet.
- Masks, heating pad.
A set of tablets is inserted individually. Painkillers and antipyretics are a must. If you have chronic health problems, you need to take more auxiliary medications. Since nutrition will deviate from the norm, digestive tablets are required.
What else is taken into account?
In addition to food and a first aid kit, it is necessary to create conditions for comfortable rest and sleep. Clothing is changeable, but the main thing is that you can go out into the light. If chemical exposure is implied, then you cannot do without personal protective equipment - gas masks, protective clothing, a flashlight. The last item on the list of important things is quite useful for internal moving in order to save electricity.

Conclusion
To fully be in the bunker, you need to individually create conditions for yourself. Each person gets used to his own - food, warmth, general atmosphere. Today, such buildings are in great demand. It’s not difficult to build them, even without experience. But if you do everything alone, this process will drag on for a long time.
Here is a design for a bunker for 4-8 people. Well, approximate data on the equipment.
To protect against the action of a shock wave, durable metal protective and hermetic doors are installed at the entrances. The entrance structure is designed for a load exceeding 1.5-2 times the standard for floors. This is not accidental, since the entrances are the most vulnerable place in a protective structure: a shock wave penetrating through stairwells, corridors and other routes due to repeated reflection and compaction can sharply increase excess pressure. The life of those being sheltered depends on their ability to withstand external influences.
At the entrance to the shelter, expansion chambers should be provided to reduce the impact of the blast wave on the protective-sealed doors. The entrance to the expansion chamber from the premises within the sealing loop must be equipped with two hermetic shutters - closed under the influence of a shock wave. The width of the vestibule-gateway, the width and length of the vestibule and vestibule for swing doors should be 0.6 m greater than the width of the door leaf. Structural and planning solutions for entrances, elevated and built into the first floors of shelters, must provide the necessary protection from penetrating radiation and exclude the possibility of direct radiation entering the protected premises. The simplest method is to provide 90° turns or screens at the entrances opposite the doorways with overlaps between the screens and shelters. Protective thicknesses of screens and ceilings are taken based on radiation exposure.
For shelters, a device should be provided at one of the entrances of the airlock vestibule. A single-chamber airlock is installed for shelters. In the outer and inner walls of the airlock vestibule, protective and hermetic doors should be provided that correspond to the calculated impacts and protection class of the shelter. Security-hermetic doors must open outward during the evacuation of those being sheltered.
All entrances to shelters, except those equipped with airlock vestibules, must be equipped with vestibules. Doors in vestibules should be provided: in the outer wall - protective-hermetic, corresponding to the calculated impacts, shelter protection class and type of entrance, in the inner wall - hermetic. The doors must open as the sheltered persons are being evacuated.
Entrances to built-in shelters should be located closer to the corners of buildings and in walls located parallel to the direction of prevailing winds (in the direction of winter winds).
An emergency exit tunnel combined with the entrance to the shelter may be provided to accommodate a single-chamber airlock vestibule. In free-standing shelters, it is allowed to design one of the entrances, located outside the area of possible rubble, as an emergency exit. Emergency exits should be located, as a rule, above the groundwater level. The excess of the groundwater level relative to the floor of the emergency exit is allowed to be no more than 0.2 m, and in an emergency exit combined with the entrance - no more than 1.0 m.
In conditions of high groundwater levels, it is possible to design an emergency exit through the coating in the form of a protected shaft without an approach tunnel. When combining the mine emergency exit with the entrance, a staircase descent should be provided. The exit from the shelter to the tunnel must be equipped with protective-hermetic and hermetic shutters, installed respectively on the outer and inner sides of the wall. Removal of emergency exit depending on the height and type of buildings is taken according to table. 4 SNiP II-11-77
The dimensions of openings and passages to the premises must meet the requirements of SNiP II-11-77 and other regulatory documents. The number of entrances should be at least two, while the second entrance should be an emergency (evacuation) exit in the form of a tunnel with an internal size of at least 1.2x2 m and a doorway measuring 0.8x1.8 m.
Entrances and emergency exits must be protected from precipitation and surface water. Structures protecting entrances must be made of lightweight, non-combustible materials.
________________________________________
Let's look a little at the technical content of life support systems.
For shelter:
1. Inputs and outputs:
DZG I-IV - 1 pc.
DG - 1 pc. (with DES -3 pcs.)
LZG I-IV - 1 pc.
LG - 1 pc.
UZS 8/25 - 2 pcs. (used if the door or hatch does not correspond to the class)
2. Protection of engineering heads:
MZS - 2 pcs. (with DES -3 pcs.)
3. Filtration:
FVK 1/2 - 1 set.
4. Power units:
DES - 1 pc. (power depends on the number of consumers)
1. Inputs and outputs:
DG/SU - 2-4 pcs.
2. Filtration:
Special filter-ventilation equipment includes:
filter-ventilation unit;
air intake and protective device;
means of sealing entrances and exits, consisting of hermetic doors and sealing material for partitions and curtains.
Air purification in shelters from chemical agents, RP and BS is carried out using absorbent filters of filter-ventilation units, which are supplied to the troops by the NBC protection service, and installed by the units of the engineering troops equipping the shelters. In addition to absorbent filters, other protective devices of the units purify the air from large particles of ordinary or radioactive dust.
The main parts of the FVA 50/25 and FVA 100/50 filter and ventilation units are:
filter-absorber FP-50/25 or FPU-200, which serves to purify the air supplied to shelters from OM, BA and RV;
electric manual fan MGV or VAP-1, which is designed for intake and movement of outside air through a ventilation protective device, air duct and absorber filter, supplying purified air into the structure and creating pressurization in it;
ventilation protective device VZU-50 or VZU-100, which serves to protect against the penetration of excess pressure into a structure at the shock wave front through an air intake device, as well as to clean the air entering the structure from large particles of radioactive or other dust. It protects the air intake device from atmospheric precipitation entering it;
air intake device (air duct), which is used to supply outside air to the absorber filter;
set of mounting parts and tools.
In addition, the filter-ventilation unit kit includes sealing and waterproofing means: lightweight sliding hermetic doors, waterproof paper and rubberized fabric panels.
The FVA 100/50 unit also includes an air flow indicator URV-2.
A sheet of rubberized fabric is used to make a curtain that separates the covered part of the entrance from the outside atmosphere in front of the protective hermetic door to form a second vestibule in buildings that have one vestibule.
The procedure for installing filter-ventilation units, the sequence of checking the correct installation and serviceability of the units:
when installing ventilation protective devices, the cover of VZU-100 or VZU-50 should not protrude above the level of the shelter cover;
a drainage ditch is torn off from the pit with the VSU;
The nipple rings of the filter-absorbers must be turned counterclockwise and against the stop to ensure the tightness of the connections of the component parts of the unit;
free space is provided for rotating the fan handle;
the air flow indicator URV-2 is installed horizontally so that the arrow coincides with the scale zero;
to ground the fan electric motor, one end of the grounding wire is clamped with a bolt securing the electric motor to the fan, and the other end, if the unit is mounted in a metal structure, is connected to the frame of the structure, in a structure made of non-metallic elements - to a metal rod or pin driven into the ground between the frame elements ;
panels of hermetic doors must move freely along the segments, providing the ability to open (close);
after closing there should be no gap between them;
Before entering a structure with one vestibule, a curtain will be installed.
Units FVA-100/50 and FVA-50/25 must supply the building with 100 and 50 m3/h of purified outdoor air, respectively.
The protective properties of the aggregates are tested using chloropicrin.
To do this, a rag moistened with 5 - 7 ml of chloropicrin is brought to the air intake device of a working filter-ventilation unit. The absence of the irritating odor of chloropicrin in the inhabited area, determined organoleptically by the personnel located inside the object, indicates the reliable protective properties of the unit.
The tightness of the structure is checked by measuring the deviation value of the valve flaps for air flow in the upper segments of the hermetic doors (with the protective hermetic door or hatch open). At the nominal air supply of the units, the valve flaps should deviate from their bodies by a distance of 1 -1.5 cm. For smaller deviations of the valve flaps, measures should be taken to increase the tightness of the structure.
The procedure for starting filter-ventilation units for operation from an electric drive:
insert the plug of the electric motor cable into the socket;
smoothly, without jerking, turn the fan manual drive handle at least three to four turns;
press the electric motor start relay button for no more than 3 s. Pressing the start relay button for a longer time may result in burnout of the motor winding.
3. Power units:
UPS - 1 set. (provision for at least 2 days)
1. Good explosion-proof doors are not cheap, domestic ones cost about 100 thousand rubles, but passing a blast wave through a shelter is suicidal. It will knock out all internal non-sealed doors, destroying both people and equipment. The best option in the case of a power supply is to simply concrete the entrance; in any case, after exposure to a shock wave it will be impossible to use it. You can, of course, reproduce the design of the subway passage, but this is an additional unmasking - 2 exits.
2. San. the node is located this way due to the position of the sewer chamber, the drain comes from the sanitary unit, kitchen, vestibule and steam generator. This is a communication issue. It is worth considering the issue of using diesel exhaust gases and wastewater for heating and water heating (possibly a heat pump, but the price tag is high).
3.The FVU must be located near the emergency exit, and there must be easy access to the emergency exit from living quarters. Regarding the used air, this is not a very good idea, read the book “Steel Coffins” (author Herbert Werner), it describes well what happened on board when the snorkel was clogged - the diesel engines instantly burned all the oxygen. This can also happen in a shelter when ventilation fails.
4. A single-tier system is more promising due to the ability to disguise the construction of a bunker, for example, as the construction of a swimming pool. Drainage as such is not needed, and at a depth of 7 meters it is useless. External waterproofing - pasted in 2-4 layers, hydrophobic concrete M400 (used for the construction of swimming pools), internal waterproofing painted in 2 layers on metal (if using containers). Next is 50-100 mm of insulation, vapor barrier and interior finishing.