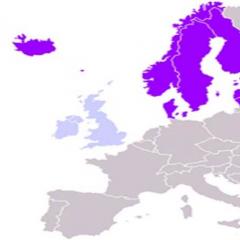
Sowing countries of Europe. Countries of Northern Europe. Geographical position. Materials on the Internet
Nordic countries - these are, first of all, Finland and the Scandinavian countries. The Scandinavian countries include European states, Denmark, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. Below is thelist of countries in Western Europe:
V Nordic countries the main industry is mechanical engineering and shipbuilding.
Square Northern Europe is ≈ 3.5 million km². North population Europe - about 26 million people.Throughout Northern Europe, 52% of men live and 48% of women. In these parts, the population density is considered the lowest in Europe and in the densely populated southern regions is no more than 22 people per 1 m2 (in Iceland - 3 people / m2). This is facilitated by the harsh northern climatic zone. The territory of Denmark is more evenly populated. The urban part of the North European population is mainly concentrated in the metropolitan areas. The natural growth rate of this area is considered to be low at approximately 4%. Most of the residents are Christian - Catholic or Protestant.
Norway- the main treasure of the country is its nature. Thousands of secluded bays and fjords encircle its coast, low mountains covered with forests and meadows create a unique flavor. Thousands of clean lakes and rivers provide a unique opportunity to enjoy fishing and water sports. In the fjords, the rocks rise tens of meters up like a sheer wall, and the water is so quiet that it resembles the polished surface of an emerald.
Sweden- a country of contrasts. Snow and sun, mountains and archipelagos, cold climate and warmth, millennial traditions and modern technologies ... Fantastic skerries and wonderful shores stretching for 2,700 km among undulating spaces, deep forests and thousands of lakes.
Finlandfamous for its lakes, the Northern Lights, the magical Lapland of Santa Claus, clear starry skies and white snow.
Denmark- these are fjords and bays, dunes and cliffs, cool shady beech forests, beautiful lakes and wide wooded plains. These are old estates, picturesque villages and towns, castles and monuments of the past centuries. But, most importantly, no city in the world will tell you as many fairy tales as Copenhagen, the city of chimney sweeps, the Snow Queen and the Princess and the Pea, tells its guests ...
Iceland- in any corner of the country you will feel the extraordinary energy emanating from the majestic mountains and mesmerizing fjords, the energy of the dazzling sun in summer and the northern lights in winter; the attractive force of the cold beauty of glaciers and lava, frozen in a bizarre shape at the bottom of deep canyons.
Geographical position
Northern Europe occupies the northwestern part of Eurasia. It covers countries located on Scandinavian Peninsula (Norway, Sweden) Adjacent to them Finland, As well as Denmark and island Iceland... When the Vikings lived in these territories, they made the peoples of Europe fearful. Sailing to the coasts, they suddenly attacked settlements, leaving behind ashes and dead, and quickly disappeared into the open sea. As brave sailors, the Vikings served as the discovery of Iceland and Greenland, as you know.
A feature of the geographical position of the Nordic countries is their coastal location. The seas have a great influence on both the climate and the economic activities of the population. The capitals of states and large cities are located on the coasts, where the majority of the population lives.
Features of nature
ReliefNorthern Europe is mostly mountainous. OldScandinavian mountainsstretched on the Scandinavian Peninsula along the coastNorwegian Sea. The rest of the territory is occupied by plains, lie onBaltic crystal shieldancient platform. Within its framework, igneous and metamorphic basement rocks - granites, quartzites and gneisses - come to the surface. Therefore, everywhere from under a thin layer of soil, numerous rocks and boulders protrude. Iceland, the "Land of Fire and Ice", has a peculiar relief. The island is a young area of the earth's crust, where numerous geysers and volcanoes operate. Especially activeHekla volcano... Iceland is considered the active volcanic region of our planet.
In the past, as a result of the cooling of the climate, a glacier sheltered northern Europe. Moving, huge masses of ice polished rocks, smoothed the earth's surface, formed glacial deposits - moraines. The glacier brought huge boulders to the plains. The fjords are also a consequence of long-standing glaciation - Narrow, winding, deep sea bays with high steep shores, which cut the shores of the Scandinavian Peninsula. They were formed as a result of the flooding by the sea of river valleys and depressions deepened by the glacier.
Climate of the Nordic countries
Climate Northern Europe, despite its northern location in the temperate and subarctic zones, is not so harsh. It is softened by the warmth of the North Atlantic Current. Winters are surprisingly warm enough there, while summers, on the contrary, are cool. Wet winds from the Atlantic Ocean cause cloudy, cloudy weather with rain and fog.
Due to the large amount of precipitation (over 1,000 mm / year) Northern Europe is rich in inland waters. The rivers, although not always full-flowing, are very short. There are many rapids and waterfalls in their channels, and the current is very stormy. Such rivers cannot be used for navigation. But their rapid currents are a source of cheap electricity, so hydroelectric power plants are being built on the rivers. There are numerous small and large lakes that occupy the Glacier-Plowed Basins.
Northern Europe is a land of forests. Although part of it is occupied by tundra, however, taiga is widespread over large areas - pine and spruce forests with an admixture of birch.
The natural features of Northern Europe have left their mark on the cultural traditions of the population. And now popular folk songs, dances and fairy tales, where the heroes are trolls - supernatural beings in the form of little men. Hand-made folk costumes can often be seen at various festivals.
Resource availability
Northern European countries have large reserves of natural resources. On the territory of the Scandinavian Peninsula, iron, copper, molybdenum ores are mined, in the Norwegian and North Seas - natural gas and oil, on the Spitsbergen archipelago - coal. The Scandinavian countries have rich water resources. Nuclear and hydroelectric power plants play an important role here. Iceland uses thermal waters as a source of electricity.
Agricultural complex
The agro-industrial complex of the Northern European countries is fishing, agriculture and animal husbandry. Mainly meat - dairy direction (in Iceland - sheep breeding) prevails. Grain crops are grown among the crops - rye, potatoes, wheat, sugar beets, barley.
Economy
Many indicators of economic development prove that the Nordic countries are leading the entire world economy. Unemployment and inflation rates, public finances and growth dynamics differ significantly from other European regions. It is not without reason that the North European model of economic growth is recognized as the most attractive in the world community. Many indicators were influenced by the efficiency of the use of national resources and foreign policy. The economy of this model is built on quality exported products. This applies to the production of metal products and goods of the pulp and paper, timber processing industry, machine-building industry, as well as ore deposits. The main trading partners of the Nordic countries in foreign trade are Western European countries and the United States. The fishing industry accounts for three quarters of Iceland's export structure.
State and national symbols
On the state flags of all the Nordic countries, a characteristic cross is depicted, shifted from the center to the left. The very first flag on which such a cross appeared is the flag of Denmark.
Passport and Labor Union of the Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (with the exception of Greenland) form a passport union, created in 1954. Citizens of the member states of the union can freely cross the borders within the union without presenting or even having a passport (however, it is still necessary to have identity documents), as well as to find a job without obtaining a work permit. It is noteworthy that Norway, unlike Denmark, Sweden and Finland, is not a member of the European Union.
The video tutorial allows you to get interesting and detailed information about Northern Europe. From the lesson you will learn about the Nordic countries, their characteristics, geographical location, nature, climate, place in this sub-region. The teacher will tell you in detail about one of the Nordic countries - Great Britain.
Topic: Regional characteristics of the world. Overseas Europe
Lesson: Northern Europe
Subregions of Europe:
1. Northern Europe.
2. Southern Europe.
3. Western Europe.
4. Eastern Europe.
Rice. 1. Map of subregions of Europe ()
Northern Europe- a cultural and geographical region that includes the states of the Scandinavian Peninsula and adjacent territories, the Baltic states, Iceland and the British Isles.

Rice. 2. Map of Northern Europe ()
Share (value) of Northern Europe
According to the UN division, the following states belong to Northern Europe:
1. United Kingdom - London
Guernsey Island
Jersey Island
Isle Of Man
2. Denmark - Copenhagen
Faroe islands
3. Ireland - Dublin
4. Iceland - Reykjavik
5. Latvia - Riga
6. Lithuania - Vilnius
7. Norway - Oslo
Svalbard and Jan Mayen
8. Finland - Helsinki
Åland Islands
9.Sweden - Stockholm
The region has one of the highest life expectancy rates.
The Nordic countries are characterized by high rates of urbanization - up to 80%, in Sweden - 85%, in Iceland - 94%.
Largest cities: London, Copenhagen, Stockholm.
Most believers in Northern Europe are Protestants.
The largest economies in Northern Europe: Great Britain, Sweden, Norway. The highest indicators of GDP per person are in Norway: almost $ 60,000.
Almost all the Nordic countries are characterized by high indicators of the standard of living of the population. These countries are standards of living standards of the population and the development of society. Norway ranks first in the HDI ranking. Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Denmark are among the top ten countries leading in HDI.
Great Britain- an island state in the north of Europe, located in the British Isles. The full name of the state is the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Great Britain includes Northern Ireland, Scotland, England, Wales, as well as some small overseas territories. Capital London. Great Britain has an amazing history: originally inhabited by Celtic tribes, it went from a remote Roman province to the mighty British Empire, shrinking in the middle of the twentieth century to almost its original size, without losing either its influence on the world stage or the respect of the world community.
English is now essentially an international language of communication. English is one of the six official and working languages of the United Nations.
The culture of Great Britain is rich and varied, it greatly influences the culture of the world community on a global scale. Great Britain has strong cultural ties with its former colonies, especially with those states where English is the official language. Immigrants from the Indian subcontinent and the Caribbean have made significant contributions to British culture over the past half century. During the formation of Great Britain, it included former independent states with different cultures.
Great Britain is a democratic country, according to its political structure - a parliamentary monarchy headed by the queen. The UK legislature is a bicameral parliament. Parliament is the highest authority throughout the territory, although Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have their own governing administrative structures. The government is headed by the monarch, direct control is exercised by the prime minister, appointed by the monarch, who is thus the chairman of His (Her) Majesty's government.

Rice. 4. Map of Great Britain ()
The main sectors of the UK economy: mechanical engineering (especially the automotive industry), the chemical industry (especially organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals), light industry, agriculture, transport, services and many others.
Great Britain is a member of NATO and the European Union, however, the country is not included in the Euro zone, keeping its traditional national currency - the pound sterling. Great Britain is one of the leaders of the modern world. The country possesses nuclear weapons, is one of the ten countries in terms of GDP, is a permanent member of the UN Security Council, a member of the G7.
For more than 50 years, the head of state has been Elizabeth II, who heads the Commonwealth.

Rice. 5. Elizabeth II - Queen of Great Britain ()
Homework
Topic 6, p. 3
1. What are the features of the geographical location of Northern Europe?
2. What are the features of the geographic location of Great Britain?
Bibliography
The main
1. Geography. A basic level of. 10-11 grades: Textbook for educational institutions / A.P. Kuznetsov, E.V. Kim. - 3rd ed., Stereotype. - M .: Bustard, 2012 .-- 367 p.
2. Economic and social geography of the world: Textbook. for 10 cl. educational institutions / V.P. Maksakovsky. - 13th ed. - M .: Education, JSC "Moscow textbooks", 2005. - 400 p.
3. Atlas with a set of contour maps for grade 10. Economic and social geography of the world. - Omsk: FSUE "Omsk Cartographic Factory", 2012. - 76 p.
Additional
1. Economic and social geography of Russia: Textbook for universities / Ed. prof. A.T. Khrushchev. - M .: Bustard, 2001 .-- 672 p .: ill., Maps .: color. incl.
Encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books and statistical compilations
1. Geography: a reference book for high school students and those entering universities. - 2nd ed., Rev. and finished. - M .: AST-PRESS SHKOLA, 2008 .-- 656 p.
Literature for preparing for the State Examination and the Unified State Exam
1. Thematic control in geography. Economic and social geography of the world. Grade 10 / E.M. Ambartsumov. - M .: Intellect-Center, 2009 .-- 80 p.
2. The most complete edition of typical options for real assignments of the Unified State Exam: 2010. Geography / Comp. Yu.A. Solovyov. - M .: Astrel, 2010 .-- 221 p.
3. The optimal bank of tasks for preparing students. Unified State Exam 2012. Geography. Study guide / Comp. EM. Ambartsumova, S.E. Dyukov. - M .: Intellect-Center, 2012 .-- 256 p.
4. The most complete edition of typical versions of real USE assignments: 2010. Geography / Comp. Yu.A. Solovyov. - M .: AST: Astrel, 2010 .-- 223 p.
5. Geography. Diagnostic work in the format of the Unified State Examination 2011. - M .: MCNMO, 2011. - 72 p.
6. USE 2010. Geography. Collection of tasks / Yu.A. Solovyov. - M .: Eksmo, 2009 .-- 272 p.
7. Tests in geography: grade 10: to the textbook of V.P. Maksakovsky “Economic and social geography of the world. Grade 10 "/ E.V. Baranchikov. - 2nd ed., Stereotype. - M .: Publishing house "Exam", 2009. - 94 p.
8. Textbook on geography. Geography Tests and Practical Tasks / I.A. Rodionova. - M .: Moscow Lyceum, 1996 .-- 48 p.
9. The most complete edition of typical options for real assignments of the Unified State Exam: 2009. Geography / Comp. Yu.A. Solovyov. - M .: AST: Astrel, 2009 .-- 250 p.
10. Unified State Exam 2009. Geography. Universal materials for training students / FIPI - M .: Intellect-Center, 2009. - 240 p.
11. Geography. Answers on questions. Oral exam, theory and practice / V.P. Bondarev. - M .: Publishing house "Exam", 2003. - 160 p.
12. Unified State Exam 2010. Geography: thematic training tasks / O.V. Chicherina, Yu.A. Solovyov. - M .: Eksmo, 2009 .-- 144 p.
13. USE 2012. Geography: Typical exam options: 31 options / Ed. V.V. Barabanova. - M .: National education, 2011 .-- 288 p.
14. USE 2011. Geography: Typical exam options: 31 options / Ed. V.V. Barabanova. - M .: National education, 2010 .-- 280 p.
Materials on the Internet
1. Federal Institute for Pedagogical Measurements ().
2. Federal portal Russian Education ().
The article briefly talks about the Nordic countries. Indicates the distinguishing features that distinguish the states of the region from other European states. The main indicators by which the Scandinavian countries are recognized and absolute leaders are considered.
Where are the Nordic countries located?
The area of the region occupies about 20% of the total Europe, and the population of the region is equal to almost 4% of the total European population.

Rice. 1. Northern Europe on the map.
The states of Scandinavia include:
- two European states - Sweden and Norway;
- Iceland;
- Denmark;
- self-governing region - Faroe Islands.
The first two countries on the list occupy the Scandinavian Peninsula, which is the largest in Europe. Denmark is located on the Jutland Peninsula and neighboring islands. It is geographically close to the Scandinavian Peninsula and is separated from it by the narrow Oresund Strait. Iceland is located on the island of the same name in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is separated from the Scandinavian Peninsula by a significant area of ocean water, which is a difference of almost a thousand kilometers.
TOP-4 articleswho read along with this
The northernmost point of the Scandinavian territory is the Svalbard archipelago, which is located in the Arctic Ocean.

Rice. 2. Spitsbergen Archipelago.
List of northern European countries and their capitals
The following small states are now included in the list of Northern Europe:
- Denmark - Copenhagen;
- Latvia, Riga;
- Iceland - Reykjavik;
- Lithuania - Vilnius;
- Finland - Helsinki;
- Norway - Oslo;
- Estonia - Tallinn;
- Sweden - Stockholm.

Rice. 3. Skyscraper Turning Torso in Malne. Sweden..
The largest of the states of the Northern European region, which are part of Scandinavia, is Sweden, whose population is 9.1 million people, and Iceland is recognized as the smallest state. Its population does not exceed 300 thousand people. About 48% of women and 52% of men live in Northern Europe.
According to the UN gradation, Great Britain also belongs to Northern Europe, along with part of its island territories.
The development of the Nordic countries is such that today these states are becoming leaders in the world economy. States stand out significantly from other European regions in terms of inflation and unemployment.
The economic growth model of the Scandinavian countries is considered the most attractive in the world. This primarily concerns the level of efficiency of exploitation of external and national resources.
The main characteristic of the Northern European economy is that it is focused not on quantity, but on the quality of the product produced.
Virtually all parts of Northern Europe are characterized by high living standards. Countries represent benchmarks in this area including the development of society. It is known from the report of international organizations that Norway is in first place in the world in terms of the human development index.
What have we learned?
We found out that the Scandinavian countries have the highest life rates in comparison with other European powers. We learned that the model of economic development of the northern region of Europe today is one of the most effective in the world. Complemented the existing knowledge on the subject of geography (grade 7). Received background information on the states that are part of the region.
Test by topic
Assessment of the report
Average rating: 4.3. Total ratings received: 200.
These include: Denmark, Norway, Iceland, Faroe Islands, Finland, Sweden. The total area of the region is 1.3 million square meters. km, the population is about 23 million people. The main direction of agriculture is animal husbandry. The share of livestock products in about ... World sheep breeding
Northern part of the territory of Western Europe; the concept has a historical and geographical character. Usually in North. Europe includes the Scandinavian countries (Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Denmark) as well as Finland. Sometimes to the North. Europe also includes sowing. part… … Geographical encyclopedia
Vi. NORTHERN EUROPE- Great Britain and Ireland. 9000 3000 BC Mesolithic. 3000 1800 BC Windmill Hill culture (Neolithic). 1800 1600 BC Peterborough and Scara Bre (Neolithic) cultures. 1900 1200 BC Bell goblet culture (bronze). 1600 BC 1100 ... ... Rulers of the World
Vi. NORTHERN EUROPE - complete- ... Rulers of the World
Europe- (Europe) Europe is a densely populated highly urbanized part of the world named after the mythological goddess, which together with Asia forms the continent of Eurasia and has an area of about 10.5 million km² (about 2% of the total area of the Earth) and ... Investor encyclopedia
This term has other meanings, see Europe (disambiguation). Political map of Europe ... Wikipedia
This article contains an unfinished translation from the French language. You can help the project by translating it to the end ... Wikipedia
On the map of the hemisphere, North America (English North America, French ... Wikipedia
Europe (Greek Europe, from Assyrian erebus - west; in ancient Greece, this was the name for the territories lying to the west of the Aegean Sea), part of the world, the western part of the continent of Eurasia. I. General information In the north, Europe is washed by the Arctic Ocean and ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
North Star Service ... Wikipedia
Books
- , Chernysheva O.V., Komarov A.A. (Ed.). The collection chronologically covers the period from the early Middle Ages to the present day. Of particular interest are materials on modern and recent history: political events in Sweden - elections in ...
- Northern Europe. History problems. Issue 8,. The collection chronologically covers the period from the early Middle Ages to the present day. Of particular interest are materials on modern and recent history: political events in Sweden - elections in ...
Undoubtedly, a very important article for understanding both the reasons for the emergence of the greatest cultures and civilizations on earth, and the reasons for the difference in mentality and, accordingly, the different psychology of nations within even one white race.
About the Romans and Germans.
Continuing the controversy about the relationship between the Romanesque and Germanic principles in Europe.
A very important question is touched upon - the question of the relationship in a particular civilization of racial and cultural principles. Assuming the real superiority of the Romanesque culture over the Germanic, we are simultaneously talking about the dominance of the cultural component over the racial one. Which, of course, is not entirely true. But the attitude to the culture of the people is also wrong from the point of view of its racial composition, according to the principle "the more Nordids, the more perfect the culture." Both approaches lead to idiocy. The first approach, in its utmost idiocy, asserts that genetics is completely unimportant; yesterday's cannibalistic negro, who went through education in a developed culture, will be equal to a European. The second approach, while not lagging behind in idiocy, will elevate the culture of Norwegian fishermen above the Italian Renaissance and French classicism.
Obviously, the truth lies somewhere in between. Man is a complex creature in which both cultural and biological components are difficult to correlate. The easiest way to understand the question of this relationship is to use a computer analogy.
The biological in man can be compared to the factory hardware in a computer. The frequency of the processor, the RAM, the power of the video card, the quality of the workmanship of the parts and their reliability, etc., etc. are human genetics. True, unlike a computer, it is impossible to take and replace individual parts in a person. The "system unit" is tightly sealed and cannot be changed.
In turn, culture and upbringing are a set of programs that are installed on top of the factory hardware.
It is clear that not every hardware can be equipped with the same set of programs. Some programs have high demands on the power of iron, and weak hardware does not pull them. In turn, poorly written, crooked programs can leave most of the excellent hardware unused, or even harm it. And also, good programs may be incompatible with this particular, also good hardware.
It is also difficult to say what is more important than the hardware or more important than the program. Just as the most perfect computer without programs is a pile of silicon, so the most perfect person without cultural firmware is an animal. It is absolutely impossible to install convenient, modern programs on a bad, weak computer.
Among Europeans, it is the North Europeans who have the most perfect "iron". The skull of the North European is on average larger, the brain is larger than that of the South European. Late puberty of North Europeans provides them with a longer period of learning (with the onset of a riot of sex hormones, both the animal and the person become dull, become poorly trained, conflict-oriented, focused on executing instinctive programs). The peoples of the Nordic-Cromanid composition - the Germans of Hanover, the Danes, the Scots - have the highest average brain mass in the world. In addition to the intellectual advantages, the North Europeans are not deprived of physical parameters. They, unlike also very large-headed Mongoloids, do not have a reduced level of male hormones, which is expressed in a decrease in body size and weight, decreased libido, decreased aggressiveness and self-esteem. Smart and strong, it was not by chance that the North Europeans conquered and populated vast areas, forming the ruling class everywhere. The original habitat of the North Europeans is harsh enough to ensure natural selection, to allow only the smartest and strongest to survive and reproduce.
(note: the colossal difference in the structure of the Nordic-Cromanid and Mongoloid skulls shows that with comparable sizes of the brains of the North-European and the Mongoloid, the development of different lobes of the brain will be very different. That is, with the same weight of 1600 grams, the brain of a German will be heavier due to completely different areas than the Chinese brain)
However, the same harsh environment until recently has not been conducive to the development of rich and strong cultures. This was hampered by two factors:
1. Natural. In the harsh northern conditions, most of the strength and energy had to be spent on fighting the environment. When the question of survival is at stake, there is no time for art and philosophy.
2. Racial and social. Even the smartest person needs a lot of time to create high standards of culture. Excess time, in the technological conditions of the ancient world, is created using hierarchy. When a dependent person - a slave, a trill, a slave - does the rough work for the master, helping him to free up time for something else. But the Germanic tribe, surrounded by other Germanic tribes (consisting of smart and strong North Europeans) simply did not have a constant source of slave power.
But in the south, where the climate allowed the northerners to breathe out and significantly increase their numbers, and all the rough work fell on the shoulders of the conquered population, the descendants of the northern invaders created great civilizations and amazed the world with the splendor of their cultures. Such cultures flourished until the northern blood dried up in them, after which they became the prey of the next wave from the north. Actually, these are the Romanesque cultures, which are completely wrong to consider, especially in retrospect, as an exclusively South European product.
(note: The process of creation and fall of ancient cultures was brilliantly revealed by Hans Gunther in his work "The Racial History of the Hellenic and Roman Peoples")
European history is a history of constant interchange. The best human material went from north to south, and the high culture created with the active participation of this material returned home centuries later, from south to north, where it created purely Germanic cultures. That is, the Germanic cultures in the historical sense are really later than the Romanesque, and are often secondary in relation to them.
When comparing the Germanic and Romanesque cultures proper, the following is striking. German culture is always a culture of clear hierarchy and order. German ordnung, Roman Legem et Ordinis. German society is a society of harsh but fair laws, a rigid but obvious hierarchy. In German culture, valor, straightforwardness, honesty, decency, restraint and practicality are extolled, they cause disapproval - cunning, cunning, talkativeness, intemperance, explosive emotionality.
The Romanesque society is a booth and brothel, where behind the outward appearance of chaos, nevertheless, a certain order is hidden, maintained through all kinds of secret societies, diasporas, mafias, sects, lodges. In the Romanesque culture, intelligence, cunning, money-grubbing, enterprise, eloquence, masks, situational morality are extolled, they cause disapproval and ridicule - straightforwardness, inflexibility, stiffness. Decency is perceived as a lack of intelligence and cunning.
A significant drawback of Germanic culture is that it is suitable only for peoples who are predominantly North-Caucasian in racial terms. Formed by northern Europeans to communicate with northern Europeans, the entire Germanic culture is based on education and upbringing, which are addressed primarily to the minds of students. By default, a German assumes in any person the same qualities that are inherent in himself. Rationality, consistency, restraint in emotions, the ability to see and understand one's interest and relate it to someone else's, the ability to make reasonable compromises and concessions, the ability to correct instinctive behavior with the head are necessary conditions for a full-fledged perception of German culture.
When faced with other peoples demonstrating behavior illogical from the point of view of a North European, a German always tries to act as a teacher appealing to reason, explaining to his students that they are wrong. For obvious reasons, to no avail. Then the German moves from moralizing to punishment, and again with a negative result.
On the other hand, Romanesque culture demonstrates a very good understanding of people of other ethnic groups and races. It was born as a product of the interaction of northern and southern Europeans, and was originally built on an understanding of how different people are. Romance cultures easily find a common language with any natives, never aiming at their re-education. Therefore, it was the Romanesque nations that became famous for their colonial successes - the colonizer always sees the native as he is, uses his strengths and takes his weaknesses into account. Where the German sees a non-European native as a threat, the Roman always sees an opportunity to profit from him.
Actually, even racial theories can be roughly divided into 2 branches:
- The first - the Romanesque - asserts the non-white world as the world of people slightly deprived of God. The attitude to the natives of the Romanesque nations is as to inferior, but very useful assistants who require a certain subtlety in the development and management, but they do not pose any danger at all. The idea of the total superiority of Europeans over non-Europeans among the Romanic peoples is adjacent to a condescending and benevolent attitude towards the natives, like children or pets, completely incapacitated without an owner.
- The second - the German one - perceives non-Europeans as a threat. Incomprehensible in their thoughts and illogical in their actions, not amenable to re-education, colored for a German is a threat that requires constant monitoring and periodic military suppression. The inability to manage the population of color is a huge headache for the people of German culture. Colored people are not people for a German. The ideal option for a German is to resolve the color issue through the destruction of the colored population, but this option is in view of the fact that the meaning of the existence of colonies is in the removal of valuable resources, and the North Europeans are not adapted to live in a hot tropical climate. The same Nazism is a purely German phenomenon if only because the Nazis perceived non-Europeans, especially half-blood Semites, as a real threat and enemy. A thought that would never have found a response in a person of Roman culture.
The conclusions from the above are very simple. European cultures - both Romanesque and Germanic - have both their own strengths and significant disadvantages. Living at the beginning of the post-national era, modern Europeans are able to analyze the merits and demerits of each culture, forming the correct views and guidelines. Moreover, there is one culture in the world that has demonstrated a successful synthesis of the Romanesque and Germanic cultures.
The domination of the Anglo-Saxons in the modern world is not at all accidental. Having retained a significant Nordic component, especially in the middle and upper strata of society, the British have created a fairly transparent and stable legal system for a comfortable life for Europeans. At the same time, mastering the Romanesque techniques of fine control, the British received a serious weapon in the fight against other nations and maintaining control over the colonies. By combining the Romanesque and Germanic understanding of non-European races, the British rationally used and continue to use the natives where necessary, and destroyed where they presented a problem or were useless (that is, in those climatic conditions where Europeans could live peacefully).