Calculation of lumber in a cube. Standard sizes and types of timber
A building material that has been widely used since ancient times to this day. A striking example of this is the superbly preserved monuments of ancient architecture throughout Russia. If previously a wooden beam was a log processed (planed) on four sides to obtain the same cross-section along the entire length, then the modern production of this building material has long been no longer limited to its classic look and shape.
What will we talk about:
Types and forms
There are three main types wooden beam:
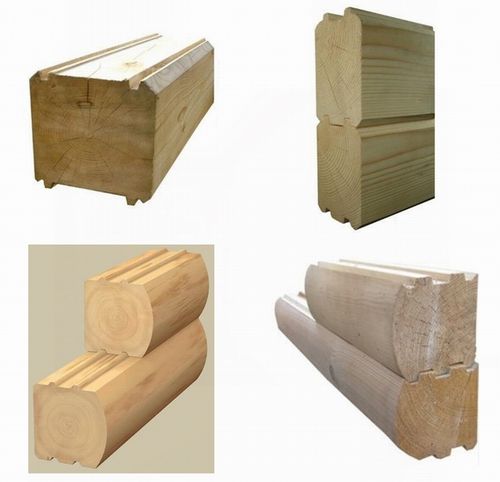
- solid (classic, smooth) timber;
- profiled timber;
- glued wooden beams.
Their shape is only square and rectangular for all three types of timber, with a flat surface of all four ribs. So it is with grooves and protrusions of different shapes and sizes on two (opposite) sides of the profiled beam. Photo. Glued laminated timber can be either solid or processed with a profile plane.

Wood
Due to its natural properties and characteristics, not every tree can serve as a basis for obtaining construction timber from its trunk. The main types of wood for construction timber are:
- pine;
- fir;
- larch;
- cedar.
Much less commonly used are aspen and birch. The wood of these species, despite their low cost, is used only for auxiliary elements.
Dimensions, GOST section
Along its length wooden beams(timber) range from three to nine meters, but the main lengths are considered to be 300 - 600 cm. As the most optimal dimensions for transportation, storage and construction. In some cases, timber can be made to individual sizes (up to 9 m). This mainly applies to standard typical structures made of profiled timber.

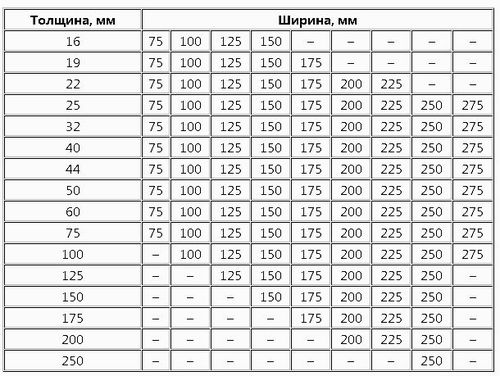
The cross-sectional dimensions of wooden beams start from 100 mm (10 cm) and reach 300 mm. With a square cross-section it is:
- 100 X 100 mm;
- 150 X 150 mm;
- 200 X 200 mm;
- 300 X 300 mm.
And correspondingly:
- 100 X 150 mm;
- 150 X 200 mm;
- 250 X 300 mm;
- Or a different size (100 X 200 mm, etc.).
Standard sizes wooden beams state standards(GOST) are mandatory for all enterprises producing such products and are listed in the following table:
- GOST 8486-86 “Softwood lumber”;
- GOST 2695-83 “Lumber hardwood»;
- GOST 23431-79 “Wood. Structure and physical and mechanical properties. Terms and Definitions";
- GOST 18288-87 “Sawmill production. Terms and Definitions";
- GOST 24454-80 “Softwood lumber. Dimensions".
In addition to the size of wooden beams according to GOST, there are a number of tables with standards for its grade, humidity, properties, and so on.
Technologies for the production of wooden and construction timber
Solid timber
Today, due to the low cost, the most popular type of product. The low (relatively) price is due to the fairly cheap and simple equipment used for its production. Availability and a wide range of applications not only in the construction of houses (baths, pavilions, etc.) make this material a bestseller.
Wooden profile beam (profiled)
Like the classic (solid) one, it is made from whole logs, according to the same dimensions and sections of wooden beams indicated in the table above. With one but significant difference. The two sides, the lateral ones, of such a beam are even. And 2 (top, bottom) respectively have a groove and a protrusion (ridge) for tight alignment with each other. The number and shape of grooves (ridges) depend on the width of the beam and design features general construction from it. Thus, at a higher cost compared to solid timber, profiled timber is an order of magnitude more economical. When working with it, there is no need to additionally seal (caulk) the walls. The adhesion of the beams to each other increases. And what is not unimportant is the construction process itself is significantly reduced in time.
Glued laminated timber
A modern technological method for manufacturing timber, which appeared a little over 30 years ago. Home distinctive feature The advantage of laminated veneer lumber is that it does not require solid tree trunks to produce it. Depending on the required thickness, N number of boards glued under pressure are used. An example is the production of plywood. Glued laminated timber not only does not lose any quality characteristics in comparison with the analogue (solid), on the contrary, it receives a number of differences. Such as increased resistance to deformation and strength. Due to the additional cost of production (glue, press), laminated wood beams are usually produced in profiled forms.
Advantages of building with timber beams
What are the advantages of building houses from wooden beams? various types First of all, it should be noted that it belongs to the so-called green construction technologies. Technologies that cause minimal harm to the environment, both during the construction of the building, its operation, and in the case of its dismantling and disposal. It takes three to four weeks to build a house once the foundation is ready.

When using profiled or laminated timber there is no need for external and internal finishing. The heat-insulating and noise-absorbing properties of wood have been known for centuries and do not require additional descriptions. The main problem of the past - the danger of fire, mold and various bugs - wood borers, today can be easily eliminated with the help of modern fire-resistant and biological impregnations.
The service life of wooden buildings is not inferior to stone houses, and in many respects economic indicators surpasses them. Natural wood creates its own microclimate indoors, which has a beneficial effect on physical health residents.
Almost everyone relies on standardized dimensions, particularly standard timber dimensions, in the design and construction of timber structures and industrial products. Why is standardization so important in an industry like woodworking?
The need for standardization
Humanity has long come to understand that it is necessary to voluntarily comply with certain rules and requirements in the process of its production activities, because this:
- simplifies the exchange of information necessary in the development, design and manufacture of final structures and structures;
- makes it possible to use standard measuring equipment;
- allows the use of the same type of processing equipment in the process of wood preparation, pre-processing, storage and transportation;
- allows the use of unified methods for calculations during design;
- allows for preliminary calculations of storage areas and the use of rolling stock;
- standardized dimensions of lumber make it possible to easily calculate volume and weight, which is extremely necessary for planning deliveries and storage;
- statistical data grouped by type of wood in accordance with standards allows for long-term and strategic planning related to the production of individual grades of lumber.
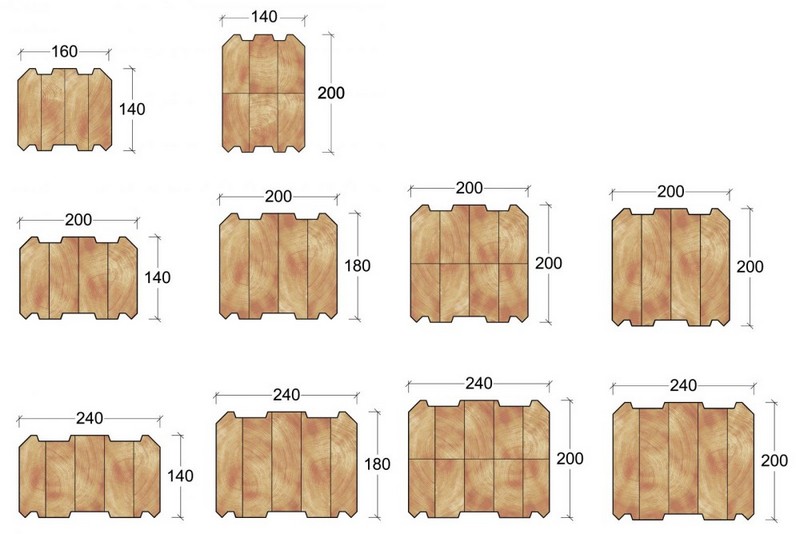
Lumber, depending on the type of tree from which it is made, is divided into coniferous and deciduous.
The quality of wood is determined by the presence of knots, inclusions, rottenness, etc. Coniferous wood is divided into 5 grades based on quality, and deciduous wood is divided into 3 grades.
The quality of wood is determined by the worst element and marked at the ends. The letter “O” denotes products of the highest quality.
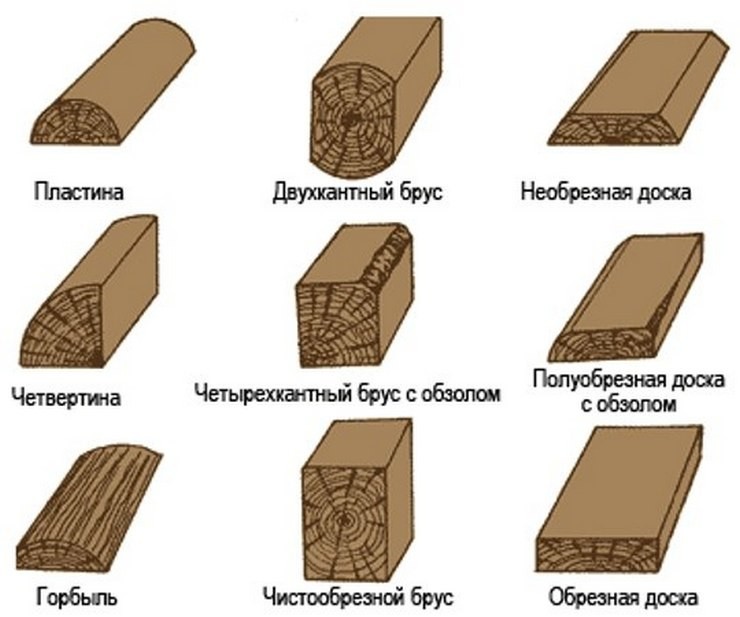
Depending on the cross-sectional shape, all lumber is divided into several large groups:
- Gorbyl. It is made from the side part of the log, and, accordingly, has 1 sawn side.
- Sleeper. A type of lumber obtained by trimming all 4 side surfaces, but without forming edges.
- Beam. It is made from the central part of the log, and, accordingly, has all 4 sawn sides. The cross section of the beam is determined by the ratio of width and height less than 2.
- Board. It differs from timber in the ratio of width to height greater than 2. In accordance with the classification methodology, according to the processing method, it is divided into one-sided edged, unedged and edged.
In accordance with existing standards for our country (similar standards exist throughout the world), all lumber is divided according to the processing method into the following:
- single-sided sawn timber - wooden blanks in which 3 surfaces were formed by sawing, and the fourth has retained its natural shape;
- edged lumber - these are wooden blanks in which all 4 sides are formed by sawing;
- unedged are blanks in which 2 sides were formed by sawing, and 2 sides retained their natural shape.
Types of timber
Timber as an element building structure, is characterized by a ratio of width and height of the cross section of less than 2. Standard timber in accordance with GOST has a width selected from the following size range: 50, 60, 75, 100, 130, 150, 180, 200, 220, 250 mm. But the following standard sizes are most in demand in construction: 100x100 mm, 150x150 mm, 200x200 mm. It is to these standards that metal fasteners are manufactured and cutting tools are designed.
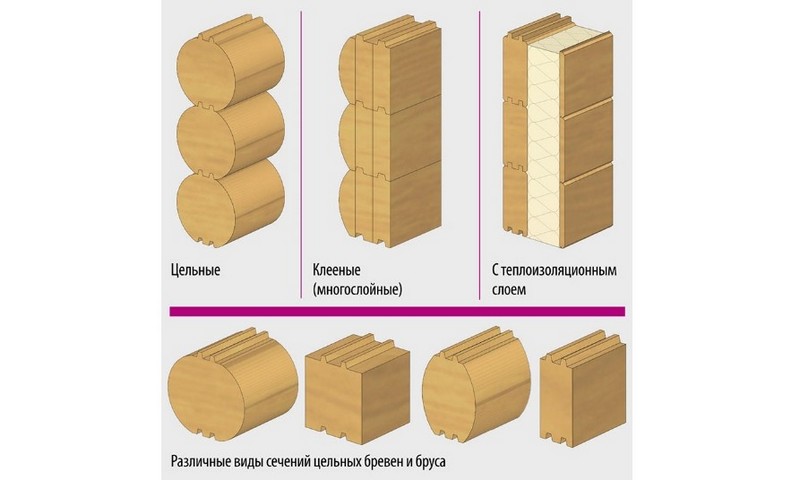
Based on the manufacturing method, the following types of timber are currently distinguished:
- Solid timber. Made from the central part of the tree. Most traditional technology manufacturing by longitudinal sawing of a wooden blank, which produces 4 unedged boards: a slab and a central part.
- Rounded timber. It is produced in a similar way, but the cross-section of such a product is not rectangular. By appearance the rounded beam resembles a sleeper, but is longer. Rounded beams are used as load-bearing elements of wooden structures.
- Glued laminated timber. Modern technology manufacturing, first used by Finnish woodworking specialists. The wooden blank is dissolved into several thin boards - lamellas. These lamellas unfold relative to each other in such a way as to minimize warping during the drying process. After which everything is glued under pressure. Such laminated veneer lumber is practically not subject to temperature changes; the opposite direction of the boards compensates for this.
- Thermobeam. A modern high-tech solution that combines thermal insulation and mechanical properties. Structurally, the thermal beam consists of 2 boards connected to each other with a polyurethane-based filler. To ensure mechanical strength, a special insert is glued through a certain space between the sidewalls.
- Packet timber. It is a wooden structure assembled from thermal timber. The connection is made using special polyurethane ties, which for a long time retain the ability to compensate for temperature expansion.

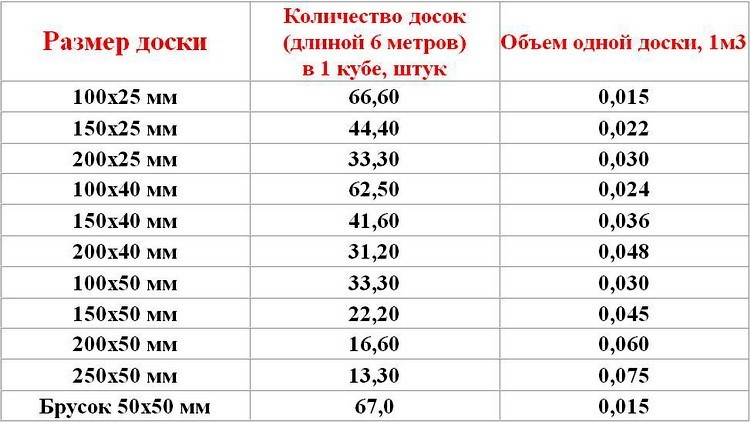
When building a house from timber, first of all it is necessary to calculate the amount of material that we will need. For accurate calculations, it would be good to know the standard sizes of timber and edged boards - the most commonly used lumber in country house construction.
Typically, construction timber has the following dimensions:
- 150×150 mm;
- 100×150 mm;
- 100×100 mm;
Small timber has dimensions of 40×40 mm and 50×50 mm.
The standard length of the beam is 6 meters, and the beam can only be longer if you ordered it specifically at the sawmill. When ordering timber more than six meters in length, you should take into account possible difficulties during its transportation, since not all types of transport can provide the necessary capacity.
Standard sizes of edged boards are 100 and 150 mm wide and 50, 40 and 25 mm thick. Like timber, the standard board length is 6 meters.
Timber and edged boards are made mainly from coniferous trees growing in this region, due to economic feasibility. The most commonly used lumber in construction is pine and spruce, as well as aspen and birch, as they are the cheapest. Fir and larch timber and boards are slightly more expensive. Cheap lumber is mainly used for the base of construction, frames and load-bearing walls.
For interior decoration lumber from mahogany, beech, ash, oak and linden is used. Of course, these materials are already noticeably more expensive, but they look much more presentable, they are more interesting and more difficult to process, and they have an attractive texture.