How to convert an uninterruptible power supply into a power supply. We make a powerful inverter from a UPS. Step-by-step algorithm of actions
Front panel of the unit
Back panel

The transformer itself

Its dimensions are 100 X 80 X 80 mm. Weight 2.2 kg. On inspection, no visible damage was found. One winding is visible under the insulation, a fairly thick wire of about 1.5 square meters. mm maybe thicker. I found the winding with the highest resistance in this transformer, it turned out to be 12.6 Ohm. The color of the wires is white + black, on one side of the core. I applied 220 V to them for a short time - nothing - no hum, no smoke - it's already good. I found a secondary on the other side of the iron with a maximum voltage of about 15 V. The color of the wires is white + yellow.

I had a 50 A diode bridge. I connected it through my native connectors, this is clearly visible in the figure. Then I connected a 12 Volt 35 Watt halogen lamp to the diode bridge.

The voltage under load dropped to 13 volts. The voltage at the output of the diode bridge is 14 V, without load.

Current under load - 3.3 Amps. The lamp was on for about an hour. After that, I checked the temperature of the transformer winding with my hand - it was completely cold. I think he will pull more current, but it was already too lazy to check. So it is quite possible to make quite powerful and high-quality power supplies or chargers from uninterruptible transformers. Author: Volodya (skrl)
The UPS is a very profitable device. While it works, the user has no problems with the power supply. But the functionality of this device does not end there. The simplest refinement of an uninterruptible power supply makes it possible to create on its basis such devices as a converter, power supply and charging.
How to convert an uninterruptible power supply into a 12/220 V voltage converter
A voltage converter (inverter) converts a 12-volt direct current into an alternating current, simultaneously increasing the voltage to 220 volts. The average cost of such a device is 60-70 US dollars. However, even owners of worn-out uninterruptible power supplies with a battery start function have a very real chance of getting a working converter for nothing. To do this, do the following:
Open the UPS case.
Dismantle the battery by removing two wires from the drive terminals - red (to plus) and black (to minus).
Dismantle the speaker - an audible alarm device that looks like a centimeter washer.
Solder the fuse to the red wire. Most designers advise using 5 amp fuses.
Connect the fuse to the "input" contact of the UPS - the socket where the cable was inserted connecting the uninterruptible power supply to the outlet.
Connect the black wire to the free contact of the “input” socket.
Take a regular cable to connect the UPS to the outlet, cut off the plug. Connect the connector to the input jack and determine the colors of the wires corresponding to the red and black contacts.
Connect the wire from the red terminal to the positive of the battery, and from the black terminal to the negative.
Turn on the UPS.
Eaton 5P 1150i UPS internals
Such a transformation is only allowed by uninterruptible power supplies with a battery start function. That is, the UPS must initially be able to turn on from, without being connected to a power outlet.
If the UPS has a regular outlet, 220 volts can be removed from its contacts. If there is no such outlet, it will be replaced by an extension cord connected to the “output” socket of the uninterruptible power supply. The extension plug is removed, after which the wires are soldered to the contacts of the “output” socket.
The main disadvantages of such converters:
- The recommended operating time for such an inverter is up to 20 minutes, since the UPS is not designed for long-term battery operation. However, this disadvantage can be eliminated by inserting a 12 V computer fan into the UPS case.
- No battery charge controller. The user will have to periodically check the voltage at the drive terminals. To eliminate this drawback, you can embed a conventional automotive relay into the design of the converter by soldering the red wire behind the fuse to pin 87. When properly connected, such a relay will open the power supply when the battery voltage drops below 12 volts.
How to make a power supply from an uninterruptible power supply
In this case, only an uninterruptible power supply will be needed from the entire design. Therefore, the user who decides on such a remake of the UPS will either have to gut the entire UPS, leaving only the case and transformer, or remove this part, preparing a separate case for it. Then proceed according to the following plan:
Using an ohmmeter, the winding with the highest resistance is determined. Typical colors are black and white. These wires will be the input to the power supply. If the transformer remains in the UPS, then this step can be skipped - the input to the home-made power supply in this case will be the "input" socket on the end of the UPS, connecting the device with the outlet.
Next, the transformer is supplied with alternating current at 220 volts. After that, voltage is removed from the remaining contacts, looking for a pair with a potential difference of up to 15 volts. Typical colors are white and yellow. These wires will be the output from the power supply.
The input to the power supply is formed from wires, on one side of the core. The output from the block is formed from wires located on the opposite side.
A diode bridge is placed at the output of the power supply.
Consumers are connected to the contacts of the diode bridge.

Transformer
The typical voltage at the output of the transformer is up to 15 V, however, it will drop after connecting to a self-made load power supply. The output voltage of the designer of such a device will have to be selected through experiments. Therefore, the practice of using a UPS transformer as the basis of a computer power supply is far from the best idea.
Alteration of an uninterruptible power supply for charging
In this case, a minimal transformation similar to the one described in the paragraph above is not needed. After all, the uninterruptible power supply has its own battery, which is charged as needed. As a result, to turn the UPS into a charger, you need to do the following:
Locate the primary and secondary circuit of the transformer. This process is described in the paragraph above.
Apply 220 volts to the primary circuit by inserting a voltage regulator into the circuit - as such, you can use a rheostat for light bulbs that replaces the traditional switch.
The regulator will help calibrate the voltage at the output winding in the range from 0 to 14-15 volts. The insertion point of the regulator is in front of the primary winding.
Connect a 40-50 ampere diode bridge to the secondary winding of the transformer.
Connect the terminals of the diode bridge to the corresponding poles of the battery.
The battery charge level is monitored by its indicator or voltmeter.
Write a letter
For any question, you can use this form.
Uninterruptable power source - irreplaceable thing. Moreover, it and its components can be used in very different ways. From the old uninterruptible power supply or its parts, you can easily get:
- inverter;
- Charger;
- power unit.
As for the power supply, using an old uninterruptible power supply you can make both a simple block and a laboratory one. Naturally, a laboratory power supply is much more difficult to assemble, install, install and configure, and will also require more additional parts and tools. However, they are based on the same principle, and the same problems arise when using them.
Initially, we will begin to consider a simple power supply and a scheme for its manufacture from an old UPS from a computer.What will be required?
To make a simple do-it-yourself power supply from an uninterruptible power supply will be required:
- transformer from uninterruptible power supply;
- case - the old case from the UPS is also suitable, and it is independently made to create a power supply;
- diode bridge.
When performing work, it is necessary to have basic knowledge in physics and electromechanics, as well as observe safety regulations, use protective clothing and use dielectrics.
When it comes to a simple power supply, most are faced with the same difficulty: the outputs from standard transformers are typically 15 V.
When a load is connected to the resulting power supply, it “sags”, so that the desired voltage is selected experimentally.Step-by-step algorithm of actions
Action algorithm for self-production of a power supply from an old UPS will be as follows:
- the transformer is disconnected from the UPS, the future case of the device is being prepared;
- using an ohmmeter, the winding with the highest resistance value is determined: black and white wires, which in the future will serve as an input to the device (if the old case from the UPS is used for manufacturing, then the input will be the corresponding socket located at the end of the uninterruptible power supply and serving for connection of the device and socket);
- from the wires located on one side of the location of the core, an "input" is formed, from the wires located on the opposite side, the "output" of the device is equipped;
- the transformer is supplied with alternating current with a voltage of 220 volts;
- voltage is removed from unused contacts;
- a pair is determined that has a potential difference of 15 volts (white and yellow wires - “output”);
- a diode bridge is installed on the "output";
- consumers are connected to its contacts.
Almost for free I bought myself a 350W uninterruptible power supply from a computer. I always wanted to make a powerful 10A 12V power supply from it, all the same, the transformer is more reliable than the impulse switch. When the opportunity presents itself, why not take advantage of it?
The assembly process took about five hours, and the entire assembly lasted two months. I bought an uninterruptible power supply two months ago.
The first step was to remove the transformer. And the resistance of the network windings was checked. The black wire is the beginning of the winding, the blue wire is the end of the winding, the red wire is the outlet. 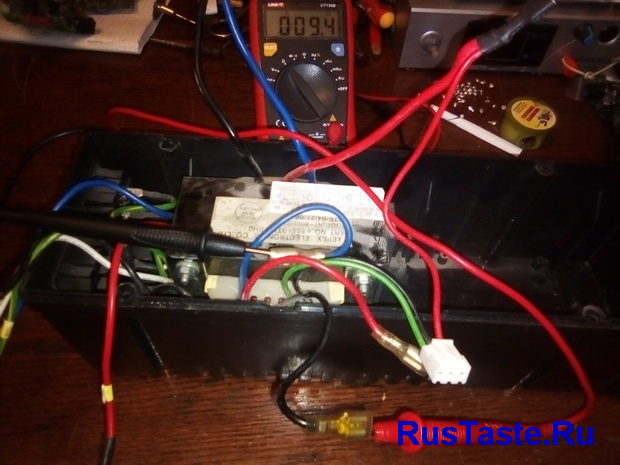

When I decided on the network winding, I decided to supply power between black and red, then the output power will be slightly higher, and the no-load current will be higher. Naturally, this will lead to additional heating of the windings, but I will have forced cooling.
Having considered all possible options for the future power supply, I ordered the necessary components from China and, in order not to waste time, prepared the case. I moved the transformer from its original place and fixed it to the bottom with four M4 screws, where the trance stood. installed a radiator for the future diode bridge. I also cut a hole for the fan in the back of the case.  Somewhere in a month, a pulse-down converter came to XL4016 12A 0-32V, here is a link to it. Che, I stopped to take a photo before reworking the converter, so I'll explain what I did.
Somewhere in a month, a pulse-down converter came to XL4016 12A 0-32V, here is a link to it. Che, I stopped to take a photo before reworking the converter, so I'll explain what I did. 

Instead of native tuning resistors, Soviet resistors were installed. For the voltage regulator, a 4.7 kΩ resistor is installed, I will bring it out with two wires to the front panel. This rating makes it possible to regulate the voltage in the range of 1.2V-18.5V. For the current regulator, I installed a variable resistor of 1 kOhm, added a 25 kOhm resistor along the positive wire, which makes it possible to regulate the current within 0-10A.
Also, instead of the block, I soldered wires, wires 0.75 mm square. twisted in pairs to increase the cross section.
A month later, literally yesterday, the rest of the components arrived and I set to work. There are no photos of the process again, so I'll go through the finished device.
Two regulators were displayed on the front panel: current and voltage. Installed ammeter type 91C4 10A, electronic voltmeter and terminal blocks left over from the previous one. I also removed the voltage stabilization indicator LED from the board. 

In the rear part, an XL4016 converter board is installed on the partition, a KBPC5010 diode bridge was installed on the radiator, and a 35V 4700 uF capacitor was glued to the case. The capacitor is needed to filter the mains voltage, after the bridge it turned out to be 22V.
To power the fan and voltmeter, I used an additional winding from the transformer, installed a diode bridge with a 2200 uF capacitor. After the 25V diode bridge, this voltage is suitable for powering a voltmeter, but there is a lot of this for powering a fan, so the fan will be powered through two 470 Ohm 2 W resistors in parallel. The bridge with the capacitor was fixed with a canopy.
By the way, to protect against all sorts of cases, I installed a fuse on the side panel. 
 This whole assembly took only 5 hours, we can say that everything was assembled in the evening.
This whole assembly took only 5 hours, we can say that everything was assembled in the evening.
Now it's time to move on to testing this device, well, first I'll look at how accurate the voltmeter is.
I chose the main voltages as for charging different Batteries, the first will be the voltage for LI-ION 4.18 V. The voltmeter showed 4.16 V, which is quite normal for a Chinese voltmeter. 
I chose the next voltage for three lithium batteries, here the voltmeter showed 0.1V more, which is also not so scary.  The last voltage is 14.4V for lead batteries. Also an error of 0.1 V, but again it is acceptable.
The last voltage is 14.4V for lead batteries. Also an error of 0.1 V, but again it is acceptable.  Well, I'll check the ammeter, although it pleased me much more than the voltmeter.
Well, I'll check the ammeter, although it pleased me much more than the voltmeter.  Enough messing around, it's time to load up. What will happen to the block if there is a short circuit?
Enough messing around, it's time to load up. What will happen to the block if there is a short circuit?  Well, now I’ll load everything with nichrome, it turned out to load 6A at 15 V
Well, now I’ll load everything with nichrome, it turned out to load 6A at 15 V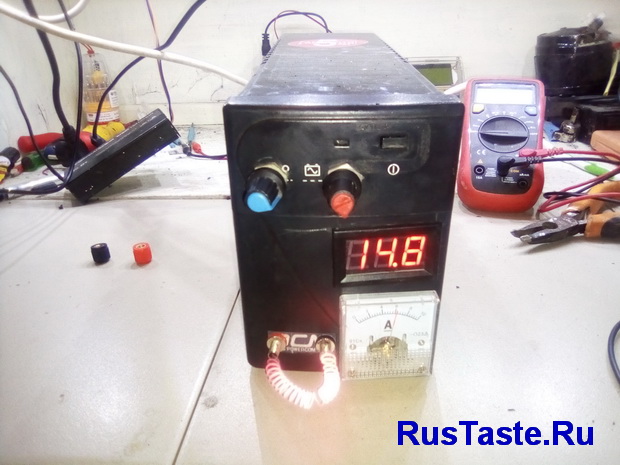  I will not load for a long time, because I will melt the case. But for about 10 minutes everything warmed up without problems for the case
I will not load for a long time, because I will melt the case. But for about 10 minutes everything warmed up without problems for the case
The last thing left to do for this power supply is to connect the wires with the terminals. I bought such a wire once for 300 rubles.  This completes the assembly and the last thing I need to do is draw a power supply circuit for you
This completes the assembly and the last thing I need to do is draw a power supply circuit for you 
And also add links to all used components
Converter on XL4016 12A 30V worth 290 rubles
Diode bridge 50A 1000V for 100 rubles
Voltmeter 100V for 60 rubles
Ammeter 10A for 130 rubles
Terminal block 4 pieces for 100 rubles
Considering that the uninterruptible power supply itself cost 500 rubles, plus additional parts and so on, my power supply unit from an uninterruptible power supply cost me 1,500 rubles
Well, that’s all for now, if you like my homemade products and don’t want to miss new ones, subscribe to updates in In contact with or Odnoklassniki
Do not want to delve into the routine of radio electronics? I recommend paying attention to the proposals of our Chinese friends. For a very reasonable price, you can buy pretty high-quality chargers

Simple charger with LED charging indicator, green battery is charging, red battery is charged.
There is short circuit protection and reverse polarity protection. Perfect for charging Moto batteries with a capacity of up to 20A\h, a 9A\h battery will charge in 7 hours, 20A\h in 16 hours. Price for this charger 403 rubles, delivery is free

This type of charger is able to automatically charge almost any type of car and motorcycle batteries 12V up to 80Ah. It has a unique charging method in three stages: 1. Constant current charging, 2. Constant voltage charging, 3. Trickle charging up to 100%.
There are two indicators on the front panel, the first indicates the voltage and percentage of charge, the second indicates the charging current.
Pretty high-quality device for home use, the price of everything 781.96 rubles, delivery is free. At the time of this writing number of orders 1392, grade 4.8 out of 5. When ordering, do not forget to specify europlug
Before every car owner someday the question arises of how to charge a dead battery. He appeared in front of me once too. And it happened, as always, unexpectedly, on a day off, in the village, and as luck would have it, no one nearby found anything resembling exercise. I had to strain my brains and quickly make a simple but powerful charger from improvised means. And the burnt UPS helped me in this - an uninterruptible power supply for computers. Without going into deep details, I'll just note that this device powers the computer from the built-in 12-volt battery when the power goes out.
The most important thing is taken from a broken uninterruptible power supply - a powerful transformer, which usually remains intact, we do not need all the other spare parts from it.

So, to make a simple charger you will need:
1. Transformer from a burned-out uninterruptible power supply
2. Diode bridge (rectifier) 2-4 pcs.
3. Capacitor 100 ... 1000 microfarads with a voltage of at least 25 V
4. Medium size radiator
5. Plank, plywood, plastic
6. Thermal grease KPT-8
7. Tester
8. Soldering iron, pieces of wire






With the help of a tester, we determine the winding leads, which have a higher resistance (from 10 to 50 Ohms), this will be a 220 V network winding. The leads of the secondary winding are 12V thicker, it is wound with a thicker wire, so the resistance of the secondary winding is almost zero.

The conclusions that went to the output connectors of the uninterruptible power supply will now be connected to the network, and the wires through which 12V was supplied from the board will be connected to the rectifier.
You will also need several rectifier diode bridges GBU406, GBU 605, GBU606, and a filter capacitance, a capacitor from 100 to 1000 microfarads for a voltage of at least 25V (from a burned-out computer power supply). A small heatsink for the diodes will also come in handy. Of course, you can make a rectifier using ordinary diodes with a maximum current of at least 10 A and a reverse voltage of at least 25 V, but at that moment they were not at hand, and later I also used ready-made rectifier bridges, because it is convenient to mount them on a radiator . Rectifier bridges are stacked, smeared with heat-conducting paste and pressed against the radiator with a long bolt. All pins of the same name are connected in parallel. Pluses with pluses, minuses with minuses, etc.

A transformer, a radiator with diodes are attached to a suitable wooden board, plywood, or a piece of plastic, the entire circuit is mounted, a cord with a plug from an old soldering iron is connected - and charging is ready!
Mounting options and layout of the charger nodes can be any, based on what is at hand.


With a rectified output voltage of about 18 V, the charger freely gives a current of up to 5 A. A conventional battery is charged in an hour, a strongly planted one in 3 ... 4 hours. Many motorists in our village now have such charging.
Moreover, for a better charge of the batteries, I came up with the idea of connecting the charger in a pulsed mode. Pulse, of course, is said loudly, it only means that it is connected to the outlet through an electromechanical time relay.
This is a simple daily electromechanical relay, it comes from China, they sell in the store for 150 rubles.