Load-bearing structures of frame buildings. Structural schemes of buildings, their advantages and disadvantages - structural schemes of buildings. Foundations. Properties of soil arrays and their types
Residential, public and industrial building... Frameless and frame types buildings. Types of frameworks.
Buildings, except for special ones, are divided into 3 groups: residential, public and industrial. Residential and public buildings are called civil. Residential include apartment buildings, hostels, cottages, hotels, boarding schools, etc. Public buildings include educational, scientific, cultural, educational and treatment-and-prophylactic institutions, trade enterprises, sports and entertainment halls, etc. Industrial buildings include all buildings designed to carry out production processes. Civil buildings subdivided into buildings of mass construction and unique. Industrial buildings are only of mass construction. Buildings of mass construction are erected according to standard designs, they have only minor differences. Unique buildings are erected according to individual projects, as a rule, in a single version. According to the peculiarities of the spatial arrangement of the bearing elements, frameless and frame are distinguished constructive schemes building. Civil buildings can be built according to one or another structural scheme, while industrial buildings, as a rule, are built according to a frame structural scheme. V frameless type outdoor and interior walls take loads from interfloor floors. RICE... The walls of a frameless building can be made of wall panels or small-sized elements (bricks, blocks, etc.).
Seismic behavior of steel buildings with weatherproof perimeter frames. This study examines some of the aspects related to the structural idealization of steel buildings with weatherproof perimeter frames and internal gravity frames. Medium mezzanine offsets are similar for articulated and semi-rigid models. The results also show that the moments that the joints can transfer are close to 30% of the plastic moments of the beams to which they are connected.
The difference between the results is mainly due to the elements that contribute to the strength and stiffness, energy dissipation and dynamic performance of each structural representation. Key words: semi-rigid joints, steel buildings, instant frames, gravity frames, nonlinear seismic analysis.
V wireframe type, the main vertical and horizontal loads are perceived by the load-bearing frames of the building. Frame buildings are divided into multi-storey and one-storey industrial buildings (we will consider later). Building frames are flat and spatial. Depending on the availability of crossbars, frames multi-storey buildings divided into girder and girderless (girderless). Multi-storey girder buildings are available with longitudinal, transverse and cross girders. RICE. 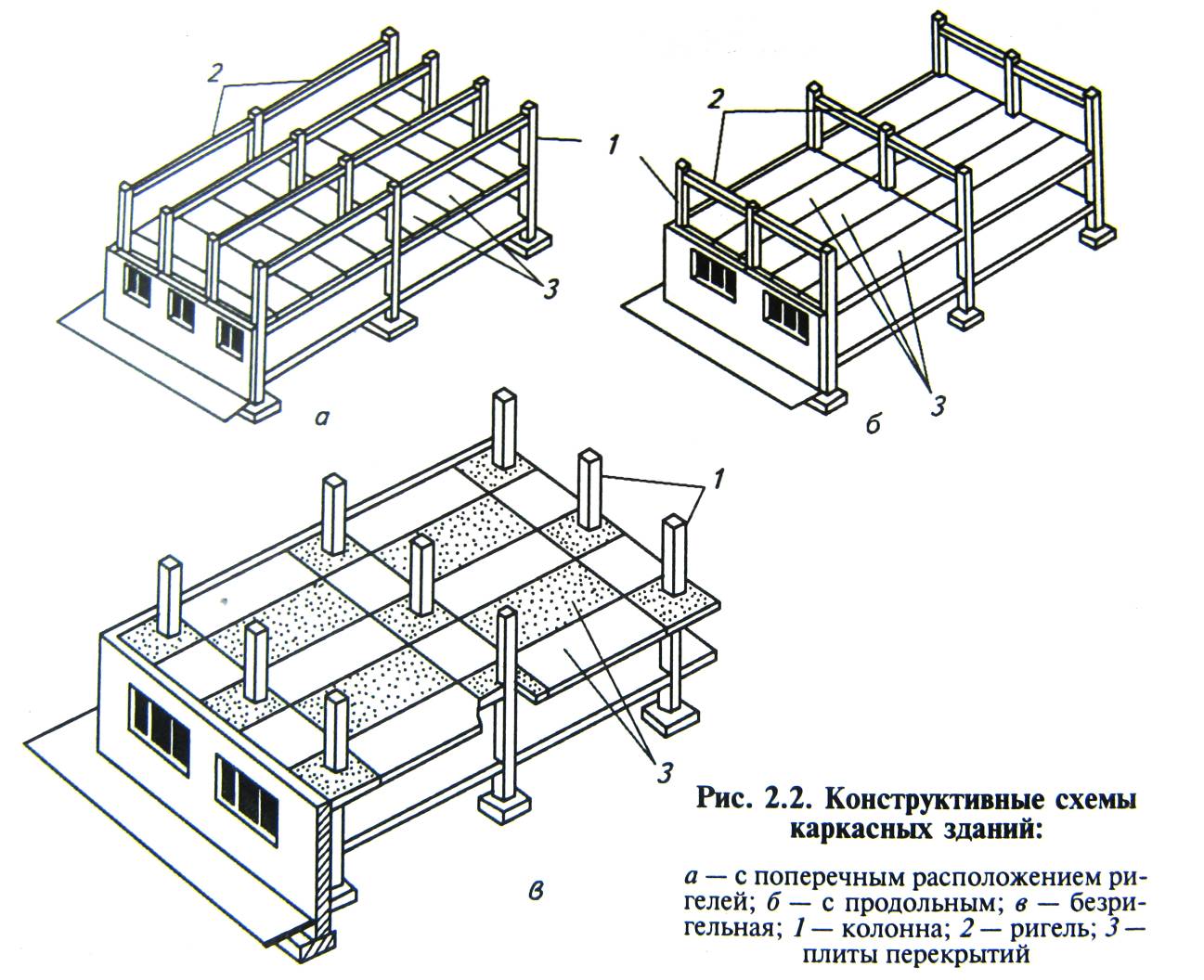 It should be noted that the name "bezel-less" frame is traditional, but not entirely correct. The fact is that the role of the crossbar in it is played by an element that is hidden in the floor level and simultaneously performs two roles: the crossbar and the floor disc. There are buildings incomplete supporting frame, which are a combination of frame and frameless building types. In them, the load from the interfloor ceilings is taken by the internal beams and columns, as well as the external load-bearing walls. RICE.
It should be noted that the name "bezel-less" frame is traditional, but not entirely correct. The fact is that the role of the crossbar in it is played by an element that is hidden in the floor level and simultaneously performs two roles: the crossbar and the floor disc. There are buildings incomplete supporting frame, which are a combination of frame and frameless building types. In them, the load from the interfloor ceilings is taken by the internal beams and columns, as well as the external load-bearing walls. RICE.
This article addresses a number of issues related to the structural idealization of steel buildings with perimeter moment, resisting steel frames, and internal gravity frames. Medium line offsets are the same for fixed and semi-rigid models. The results also show that the maximum moments in the joints can account for up to 30% of the plastic moments of the beams to which they are connected.
Iii "Types of products and services"
Key words: semi-rigid joints, steel buildings, momentarily stable frames, gravity frames, nonlinear seismic analysis. The main goal of the seismic design forecasts specified in the codes is to create structures that have sufficient ability to withstand strong earthquakes without collapsing, albeit with some structural damage. Various structural systems and materials are used to achieve this goal. However, these structural systems have changed significantly over the years, especially in the United States.
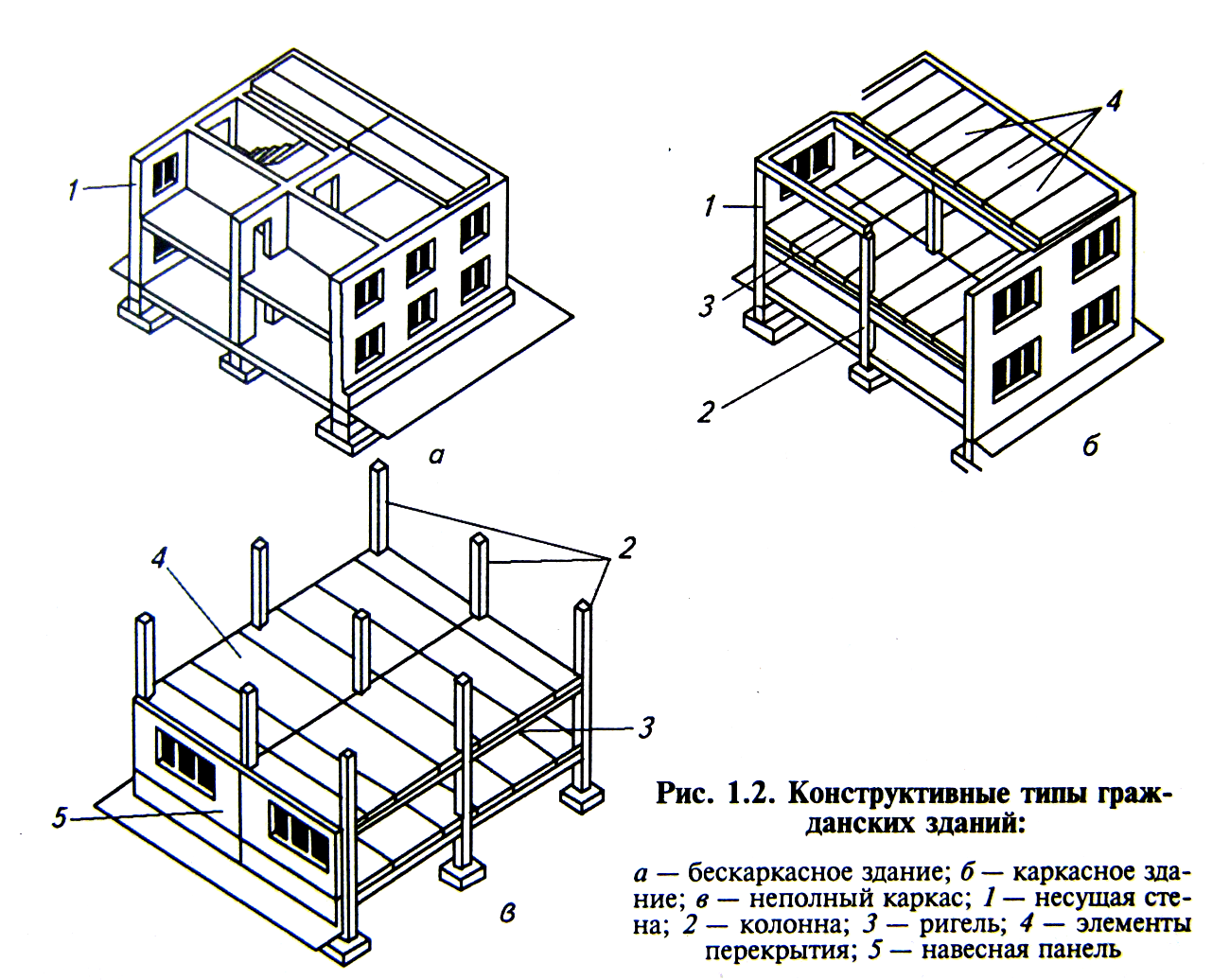
Frame and frameless building types have their own advantages and disadvantages. As a rule, the frame type of the building is cheaper than its frameless counterpart, in addition, frame buildings allow the creation of premises of considerable size, free from internal supports. However, the parts of the columns protruding from the walls and the crossbars protruding from the ceiling frame buildings significantly complicate the layout of the premises and interfere with the use of the internal volume of the building completely.
From the mid 60s to the mid 70s, most joints in steel buildings were time stable joints. Another important advantage is the elimination of flexion about the weak axis. The main disadvantage is the errors that arise when evaluating the answer by simplification. The behavior of the considered structural system subjected to the action of seismic loads is still an "open question" and needs to be studied.
This is, in part, the main focus of this investigation. As mentioned earlier, 3D buildings are modeled as flat frames to simplify the seismic analysis and design process. In addition, modeling buildings as flat frames may not represent the actual behavior of the structure, since, in addition to not considering the participation of some structural elements, the dynamic properties of this model may differ from the dynamic characteristics of the 3D model.
Foundations. Properties of soil massifs and their types.
The base is an array of soil located under the foundation and taking the load from the buildings. The foundations are: natural - soil capable of withstanding the load from the erected building in its natural state, and artificially compacted or hardened soil. The loads acting on the base deform it, causing the building to settle. Precipitation should not exceed the maximum permissible values laid down in regulatory documents. For this, the calculation of the bases for the 2nd group of limit states is performed. In addition, in the case of insufficient bearing capacity of the bearing layer of the soil, the base may lose its bearing capacity and cause a turn in the vertical plane of the building as a whole, or its parts. Serious requirements are imposed on the base soils. Soils must: 1. have sufficient bearing capacity; 2. have low and uniform compressibility; 3. not to be heaving, i.e. an increase in volume when the moisture in its pores freezes; 4. will not be washed out and will not dissolve by groundwater; 5. to prevent drawdowns; 6. prevent landslides; 7. Prevent creep.
Foundations. Properties of soil arrays and their types
Analyzes and conventional constructs steel frames based on the assumption that bell-shaped speaker connections are perfectly rigid or perfectly articulated. Despite these classifications, almost all steel joints used in real frames are essentially semi-rigid with varying degrees of rigidity. It is recognized in the profession both theoretically and experimentally that joints have a semi-rigid non-linear response, even if the amplitude of the applied load is very small. There is evidence that transverse joints can transfer up to 30% of the plastic capacity of the moment of the beams to which they are connected.
Questions for attestation in the architecture of buildings 2011
DocumentThe building is called ground structure, which has an internal space intended and adapted for one or another type of human activity (for example, residential buildings, factory buildings, train stations, etc.)
Iii "Types of products and services"
DocumentAccording to the letter of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation dated June 8, 2, N 4494-ER, this classifier does not need state registration(Information published in the newspaper "Economics and Life", No. 24, June 2
The contribution of these joints to structural strength and rigidity can be even more important when considering the composite action of the slab. This article explores some aspects related to the structural idealization of steel buildings with perimeter frames that are resistant to impulse and internal gravity frames. The responses are scored in terms of global and local parameters. Several models proposed by the United States Federal Emergency Management Agency are used for this purpose.
Models are analyzed in the time domain using 20 seismic records. These seismic records were derived from the United States Geological Databank's National Strong Motion Program datasets and were selected to represent the characteristics of strong earthquakes.
Ministry of economy of the russian federation committee of the russian federation for standardization, metrology and certification all-russian classifier of types of economic activities, products and services russian classification (1)
DocumentMinistry of economy of the russian federation committee of the russian federation for standardization, metrology and certification all-russian classifier of types of economic activities, products and services russian classification (11)
Documentsynthetic fishing line, straw 4303 1 Nylon bristle 4303 Nylon fishing line 4303 9 Synthetic straw 430330 Mixed chemical threads 430331 Viscose chemical threads with nylon 43033 Acetate chemical threads with nylon 430
To achieve the objectives of the study, the seismic response of the models used is estimated as realistically as possible using a finite element analysis procedure based on the stress hypothesis developed by the authors and the research team. An explicit form of the tangential stiffness matrix can be obtained without requiring numerical integration. Large strain configurations can be described using multiple elements without loss of accuracy, and non-linearity can be included without losing their simple simplicity.
This procedure gives very accurate results and is very effective compared to the bias approach. The procedure and algorithm were validated using both theoretical and experimental results available. The results of efforts are transferred between the various elements of the structure through their connections. The bending moment in a joint and its corresponding relative rotation, denoted as a torque curve, are commonly used to represent the flexible behavior of joints.
19 0000 8 products of the electrode and carbide industry
Document01 2 ELECTRICITY, HEAT, WATER, ICE, COLD 02 4 OIL, PETROLEUM PRODUCTS, GAS 03 6 COAL, COAL PROCESSING PRODUCTS, PEAT AND SHALES FUEL OX04 reserved
The structural type of a building is determined by the spatial combination of walls, columns, floors and other load-bearing elements that form its frame. Each structural type of buildings, in turn, can have several structural schemes, which differ in the peculiarities of the location of the load-bearing elements and their interconnection.
Richard's model is used in this study. This model was developed using experimental information and is applied to a wide variety of compounds. Equation 1 represents the stage where the load on the connection increases monotonically. In a typical seismic analysis, at a given point in time, it is expected that some connections will be in the process of charging, while others may be in the process of unloading or recharging. However, it is important to consider this behavior in seismic analysis.
1 - load-bearing walls; 2 - floor slabs; 3 - columns; 4 - crossbar; 5 - curtain walls.
Rice. 6. Constructive diagrams and constructive types buildings.
In the course work, it is necessary to design a frameless two-story residential building. The main carriers structural elements in this case, foundations, ceilings and load-bearing walls will be.
This topic was addressed by Coulson and El Salti. Level 3 and 9 models representing the Los Angeles area and pre-Northridge projects are used in this study to explore the issues mentioned above. In the case of model 2, the perimeter frames are intercepted in the corner; in this case, however, the beam-column connections are hinged to avoid bending about the weak axis. It can be seen from the figures that the frames are practically symmetrical in plan, so no significant torsional moments are expected. The specific elements considered in this study are.
2.3. Apartment and its composition
Apartment – living quarters, consisting of one or more living rooms, a kitchen and other utility rooms, the entrance to which is organized from adjoining territory or from the auxiliary premises of a residential building.
The apartments should provide at least the following premises:
The beam and column sections of the models are shown in Table 1. In all frames, the columns are made of grade 50 steel and the beams are made of steel. For the two models, the gravity columns are assumed to be pivotally connected to the base. Buildings, in this study, are modeled as systems of varying degrees of freedom. All nodes are considered to have six degrees of freedom.
The dynamic response of a structure exposed to different seismic records, even if normalized to its maximum acceleration, will generally be different for each record, reflecting its different frequency content. Thus, an estimate of the structural response using a single seismic record may not correspond to the actual behavior. To study the problems mentioned correctly, the models are fired by twenty time-domain earthquakes recorded at different stations.
1. living rooms (common room, bedroom);
2. utility rooms (entrance hall, kitchen, sanitary unit, pantry or built-in wardrobe, summer room).
According to the design assignment, the composition of the apartments is additionally allowed to include: a dining room, an office, a library, a game room, a room for chores, a cold storage room, a cellar, a drying cabinet for outerwear and shoes, a dressing room, a room for physical education.
As shown in the table, their prevailing periods range from 11 to. The predominant period of these earthquakes is defined as the value of the period corresponding to the largest peak observed in its elastic response spectrum. The attenuation considered in the analyzes is 5% of the critical attenuation; the same one used in design codes. Contribution of gravitational frames.
This ratio is estimated for both directions. Values up to 28% are observed for the 1st floor of the Model. The models did not develop plastic joints when excited by 20 earthquakes. Based on previous experience and for an even comparison, the earthquakes were scaled until the maximum displacement of the middle mezzanine was close to 1%. It was found that about 3-8 plastic joints were formed to displace the desired space. For this case, analogs have also been developed, similar to one, but not shown.
The area and width of the premises of the apartments should be not less given in table 1.
The depth of the living room, as a rule, should not exceed its width by more than two times. The dimensions in terms of the bathroom, lavatory and combined sanitary unit should be selected based on the conditions for the placement of equipment in them (Fig. 4).
The area of the kitchen can be reduced to 5 m 2, provided that there is a separate dining room in the apartment. The length of the corridors without lighting at the ends and adjacent to the staircase should be no more than 12 m.
The statistics are summarized in two models, directions and strain levels. The increase is especially important for the upper floors. Values close to 35% are observed for the 3rd floor in two cases. The answers are expressed in the form of mezzanine shears, mezzanine movements and mechanical elements in some of the basic elements of the models. The mezzanine shift is discussed first.
In general, the above observations are valid for this direction. A parameter similar to the mezzanine shift parameter is estimated for mezzanine displacements. A similar reason for the previous ones is also estimated for the axial load and moment for some columns of the base. The values for the two outer columns are essentially the same. Based on these results, it is concluded that modeling buildings that treat them as flat frames can lead to a significant overestimation of the seismic response.
The width of the outer walls is determined by heat engineering calculations. Internal width not load-bearing walls(partitions) depends on the type of material. Brick partitions are 120mm wide, and gas silicate partitions are 200mm wide. The width of the internal load-bearing walls should be assigned from the conditions of bearing on their floor structures.
The common room should be directly connected to the hallway. It is allowed to enter one of the bedrooms through a common room with an area of at least 16.0 m 2 - in two-room apartments and 18.0 m 2 - in other types of apartments. Bedrooms should be impassable
Figures similar to and also developed for the inelastic case for two models and two directions, but not shown. However, it is noted that since the density is not very significant, the values are very similar for elastic and inelastic behavior. The level of uncertainty in estimating these parameters is similar for the two models. This part of the article discusses the effect of joint stiffness in structural response in terms of shear and displacement of mezzanine and mechanical elements. The results are presented for both averages and individual frames.
Values are observed to be less than 100% in most cases, indicating that the mezzanine shift increases when the stiffness of the joint is considered. Unlike what happens when a lateral static load is applied, where the mezzanine shear is expected to always increase with the stiffness of the joint, the response due to dynamic loading depends on several parameters that are less significant for static analysis.

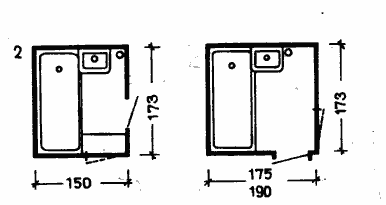
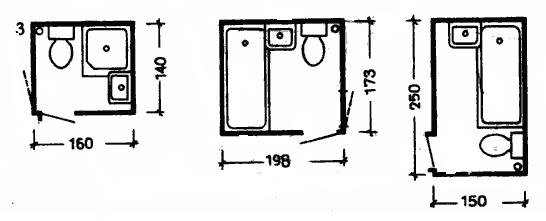
Fig. 7 Dimensions in terms of the toilet (1), bathroom (2) and combined bathroom (3)
2.4. Non-apartment premises
Vestibules should be provided at external entrances to the heated residential part of the building. In single-family and blocked houses, vestibules may not be provided if the entrances to these houses are organized through the verandas.
The width of the vestibules should be taken more than the width of the openings by at least 0.5 m (0.25 m on each side of the opening), and the depth ¾ more than the width of the door or gateway by 0.2 m, but not less than 1.2 m.
The floor mark of the vestibule should exceed the level of the porch floor by 2 cm and be the same amount below the floor mark of the entrance room.
The porch at the main entrance to a residential building must have dimensions in terms of at least 1.4 × 1.4 m and must be protected from atmospheric precipitation by a canopy or other device. All steps of the staircase leading to the porch residential building, must have the same dimensions, the number of steps must be at least three.
When the difference in floor marks is more than 0.45 m from the ground level, the porch, terrace, marches and platforms of external stairs, ramps, entrances must have fences with a height of at least 0.9 m.
The horizontal surfaces of porch, staircase and ramp coverings exposed to weathering must be rough. Facing of these surfaces with glazed tiles and polished (sanded) natural stone slabs is not allowed.
2.5. Ventilation
Ventilation - the exchange of air in rooms to remove excess heat, moisture, harmful and other substances in order to ensure acceptable microclimate parameters and air purity in the serviced or working area. According to the method of air induction, ventilation is divided into natural, artificial, mixed, and in the direction of the air flow into supply, exhaust and supply and exhaust.
Air removal should be provided through the exhaust ducts of kitchens (140x270mm), furnace (140x140 and 140x270) toilets (140x140mm), baths (270x140mm) or combined sanitary facilities (140x270mm).
Compensation of exhaust air for rooms with a standardized hood should be provided for:
· For living rooms - due to the intake of outside air;
For other rooms - both due to the intake of outside air and due to the overflow of air from other rooms of the apartment
Within the limits of one apartment or cell in a dormitory, it is allowed to remove air with one channel with the following rooms connected to it:
· Kitchen, bathroom or shower;
· Restroom, bathroom (shower) and drying cabinet.
It is not allowed to combine ventilation ducts of kitchens, sanitary facilities, storage rooms for food, furnaces and parking spaces.
2.6. Rules for assigning vertical marks for residential low-rise buildings.
The floor elevation of the living rooms located on the ground floor must be at least 0.45 m higher than the planned ground elevation.
The height from the floor to the bottom of the window is usually assigned at least 0.7 m. In apartments for disabled people no less than 0.45m and no more than 0.7m. Sections of the wall under the window with a height from the floor of less than 0.7 m (except for those bordering on summer rooms) must have fences with a height of at least 0.9 m from the floor.
The floor height must be at least 2.8m. The height of the premises of the apartment and the dormitory cell from floor to ceiling must be at least 2.5 m, the height of the intra-apartment corridors must be at least 2.1 m.
In the premises of apartments (living rooms and kitchens) with sloped ceilings, a lower height is allowed in an area not exceeding 50% of the total area of the room.
The height of the walls from the floor to the bottom of the inclined ceiling must be, m, not less:
· 1.2 - at the smallest inclination of the ceiling to the horizon 30 °;
0.8 - the same 45 °,
· And is not limited when the ceiling is tilted to the horizon of 60 ° or more.
For intermediate values of the ceiling slope, the smallest wall height is determined by interpolation.
Height of balconies and loggias fencing is not less than 1.1m from the floor.
External pits of entrances and windows with an elevation of the bottom of the opening below the level of the blind area must be carried out with drainage bumpers with a height of at least 0.15 m from the planning level of the earth. The pit floor must slope away from the door and window openings to a drainage device with a drainage section located outside the enclosing walls of the pit.



