Finnish technology for pouring underfloor heating on the ground. Insulated Finnish foundation: do it yourself
Do you want to know how our neighbors, who are only 300 kilometers from St. Petersburg, make strip foundations for a private house? I'm talking about the finns. Highly interesting technology... Fast and convenient. I think it’s not expensive. At the expense of pacticity, it's up to you to judge!
The strip foundation technology is optimized to reduce manual labor. All earthworks are done by machinery, the excavator is used not only for digging a foundation pit! The excavator works as a bucket and does that job. some Tajiks do with shovels and wheelbarrows. It dilutes, pours in, transfers rubble from the heap and spreads it around the site.



They do almost nothing with their hands .. unless they break the axles for the future foundation or connect pipes. That is, they only do with their hands what cannot be done otherwise. When it becomes difficult for an excavator to work, due to its size, a small excavator is brought in instead!


This pile of yellow and incomprehensible rubbish will soon become the foundation! You will be surprised. this is a permanent formwork. It looks very practical, the reinforcement cage is covered with a thick film. at one time, the most it.
In literally half a day, a strip foundation is assembled from this fixed formwork for sluggish finna. The fragments of the formwork are connected to each other with special equipment, the metal rings are pressed. This is three times faster than we are used to doing here - to twist the reinforcement cage with wire and a hook. I don't think they know this technology at all.



Thanks to the cunning shape of the reinforcement, you can freely do without foundation and other tweaks. In fact, external reinforcement. very good, sorry. that we do not produce anything of the kind.
Pay attention to how clean and colorful their builders are. It would be funny if our Tajiks are dressed like that!


Literally in a day, they assemble a strip foundation for a very rather big house. Black pipes that stick out of the ground are for storm sewers, for water drainage. A roof drain will be installed into these pipes. Isn't it a good idea?


The foundation is poured using a concrete pump and a vibrator, everything is as usual. It is interesting that a mixer combined with a concrete pump has arrived! Then, when the mixer ran out of solution, a second one was attached to it from behind. Very practical!




Like everything, flooded, smoothed, beautiful ... but no! Now we begin to lay the foundation strip itself. Or the base ... see for yourself.

All manufacturers are familiar to us. The blocks will be placed on the usual Vetonit for us. And they stir the solution in our way, with a shovel and a concrete mixer.

We place the solution, and we begin to lay a number of blocks, it would seem that everything is quite normal. Figs there!


After the first row of blocks, two thick reinforcement rods are placed on them and a yellow trough is placed - a solution dispenser. We roll it until the reinforcement is filled and put the second row of blocks. It turns out very quickly and accurately. We use something similar for laying Hebel gas blocks. More precisely, they are trying to use ... the technology does not take root, everything is put in the old fashioned way.



I've been waiting. that for the corner they will get some kind of special lotion. But no, they smeared the cake of the solution with a trowel, and the whole business.


That's the whole "tape" of the foundation. There are no vertical ties, not even vertical grout seams. Then this tape is pasted over on both sides with foam board. This is instead of the usual waterproofing of the financial institution. Then they fall asleep with a layer of rubble, both outside and inside. Mandatory, with the help of mechanization. The crushed stone was brought by a mixer with a conveyor belt. The most common crushed stone is transported with a mixer! But it's convenient ...

What kind of rods are sticking out, I still do not understand, these are pieces of reinforcement placed under the foam plastic on the glue. Mysterious ... In general, an interesting design has turned out, how to calculate such a strip foundation is not clear to me. It is unambiguously clear that the structure turned out to be plastic and only a frame structure can be placed on it. However, it is these houses that the Finns build in 90% of cases.

On our website there is a large section on foundations, where belt, pile and slab foundations, technologies for their construction and reports from our visitors, who built it themselves and sent us an article.
The foundation is the basis of the future home and therefore special attention should be paid to its arrangement. The most modern, reliable and fast is the installation of a monolithic foundation slab. The difference between the foundation slab is a rigid spatial reinforcement along the entire zero surface, which allows it to perceive the loads arising from seasonal uneven movements of the soil without internal deformations.
A monolithic reinforced slab is one of the most reliable foundations. On moving (heaving) soils, such foundations, in contrast to conventional stationary ones, resting on a fixed base, have seasonal vertical displacements together with the soil and are called "floating". Their design is solid reinforced concrete slab... Due to the enormous bearing capacity of the foundation slab, it can be used on weak, bulk and heaving soils, in cold regions with seasonal soil freezing and the potential for frost heaving, with any indicators of the chemical aggressiveness of the soil, since the foundation slab is protected from all sides by inert to chemical influences material - extruded polystyrene foam.
One of the most common types of foundation slabs in Europe is “ swedish plate". More than a million houses have been built using this technology in Europe. Its reliability has been confirmed by many years of operation in such "winter" countries as Sweden, Finland, where the weather conditions are very similar to those in Russia.
The Swedish stove is insulated monolithic foundation low depth. The main feature of this technology is that the entire base of the house is enclosed in a thick layer of insulation for the foundation, including the bottom. Thus, freezing of the soil under the house and all its movement is excluded. Under warm home the soil does not freeze or heave. Such a foundation is suitable for any soil at any depth of groundwater.
Advantages:
It is a universal foundation for all types of soil.
Serves as a heat accumulator at home. Prevents heat loss through the foundation to the ground and atmosphere.
Does not allow the soil under the base of the house to freeze through.
Allows you to install such heavy devices and structures in the house as a boiler or fireplace.
Installation technology
After removing the surface soil layer, the slab base cushion is backfilled with quarry sand. The sand cushion is compacted. Next, the laying of pipes for engineering communications is carried out. This is followed by leveling and laying of the side elements, and then 2 layers of extruded polystyrene foam plates are laid layer by layer.
Next, a reinforcing cage made of steel reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm is mounted in two layers with a cell of 200 mm. Pouring is carried out with concrete of the M300 brand (class B 22.5), the thickness of the slab is 250 mm.
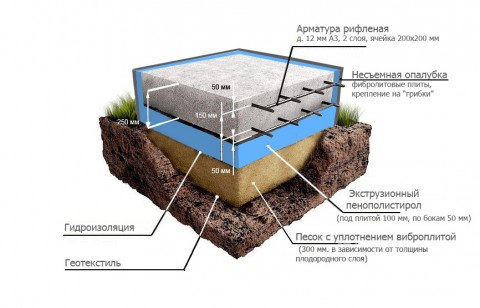
Technological complete set of the foundation:
Geotextile laying.
Installation of mortgages for entering engineering communications into the house - electricity, water supply, sewerage.
Sand cushion device with compaction with vibrating plate thickness 300 mm.
Permanent formwork made of GB-600 fiberboard plates.
Laying waterproofing.
Laying insulation - extruded polystyrene foam URSA or PENOPLEX under a foundation slab 100 mm, on the sides of the foundation - thickness 50 mm.
Mounting reinforcement cage in two layers with a cell 200 * 200mm from steel corrugated reinforcement (A3) with a diameter 12 mm.
Pouring a monolithic slab with a thickness 250 mm certified concrete grade M300(class B 22.5) with leveling and grout sealing.
Normative base: The normative base for this type of foundation is established in SNiP 3.03.01-87 and VSN 29-85, for the Moscow region in TSN MF-97 MO.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frame structures on shallow strip foundations(MZLF) are today one of the most promising areas of development low-rise construction... Significant weight loss, single or two-storey house allows the use of effective engineering solutions, characterized by low labor intensity. The insulated Finnish foundation (UFF) appeared in domestic practice 8-10 years ago. The technology widespread in the Scandinavian countries was initially perceived with distrust. Any innovation associated with a reduction in the volume of work is met with rejection by a large part of the construction community. But for several years, buildings built using UVF technology have proven themselves well in terms of energy saving and comfort. At the same time, no problems with the strength and rigidity of the supporting structures were noticed.
The term became famous thanks to construction forums, but is not official. In accordance with the SNiP categories, we are talking about a combination of MZLF and a floor on the ground, for the construction of which external thermal insulation is used.
The increasingly popular foundation scheme in the Russian Federation from the Finnish construction company Omatalo provides:
- Shallow tape foundation, consisting of a concrete base with a section of 600 x 200 and foundation blocks 200 mm thick, making up the base of the required height. Thorough compaction of backfill soil is mandatory.
- Reinforced cement-sand screed, 80 mm thick, cast over a 150 mm layer of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). Before pouring, the wiring of the pipes of the water heated floor is laid. The insulating plates rest on fine-grained anti-capillary rubble. Sand filling is located under the rubble.
- Structural separation of the plinth and floor slab with an EPPS layer. A slab with a thickness of 50 - 70 mm adjoins the inner side of the plinth and is located at its entire height, resting against the bottom of the foundation cushion.
- Arrangement of the insulated scaffold using 120 mm EPS plates installed along the outer perimeter of the basement at the depth of the top of the foundation cushion.
Schematic diagram of the UFF device - insulated Finnish foundation
Developers vary this scheme by varying the thickness of the layers, thermal insulation materials and some other components. For example, instead of EPSS, PSB-S plates (the most durable types of foam plastic) can be installed under the screed, and when installing a warm floor, in some cases, preference is given to electrical systems. In climatic zones with a frost index of more than 70,000, the plinth is preferred to be cast into a fixed formwork made of extruded polystyrene. The common thing for all modifications of uff is the observance of three principles:
- MZLF is located in a trench with compacted backfill soil;
- thermal insulation layers are located under the floor screed, as well as between the plinth and the screed;
- it is obligatory to install an insulated scaffold adjacent to the base of the foundation tape.
In European and North American practice, this scheme is not allocated to a special category, but is included in the group of antifreeze or insulated MZLF. Basically, there are two terms:
- Frost Protected Shallow footing / foundations (FPSF) and
- Insulated Shallow footing.
Range of application and features of the scheme
Each project requires an individual calculation of the foundation, depending on the characteristics of the soil, the weight of the house, the ratio of the building area to the length of the perimeter, the characteristics of the climatic zone and other factors.
If to generalize as much as possible, then the Finnish foundation of the considered structure can be recommended for use in all climatic zones of the Russian Federation for all categories of soils with an approximate load of 1 - 3 tons per linear meter of MZLF.
The specified load range is suitable for most projects frame houses with number of storeys 1 - 2 and one-storey cottages without limiting the type of their design. However, the adaptation of UVF for more heavy houses no problem: the design change in this case goes the way increasing the cross-sections of the pillow and the basement of the strip foundation.

Typical design of MZLF - shallow strip foundation
In economic terms, the scheme is suitable only for buildings without basements.
Among the advantages of UVF are:
- Sleek and simple anti-frost protection solution
- High energy efficiency indicators, only slightly inferior to the scheme of the type of insulated Swedish plate (USHP).
- Good adaptive ability to change projects in terms of loads, basement height, sequence of implementation of individual stages, maintainability of laid communications.
- Opportunities to carry out work with small forces and small funds, taking significant breaks in time (for example, you can do without formwork, and it is permissible to engage in heating distribution and cast the floor slab after the roof has been installed).
- The option better than the UWB adapts to the slopes of the site.
- The scheme can be used with a high level of groundwater
Disadvantages (in many respects, conditional) of a foundation of this type are associated with insufficient energy efficiency in relation to the concept of a "passive house" and a significant amount of earthworks... The cost of the cycle for the implementation of schemes close to the Omatalo technology is 100 - 120 $ / m² of the construction plan.
The option is more expensive than the standard zero cycle. However, if we take into account the insulation and wiring of communications, the Finnish scheme comes out a little cheaper.
A technical and economic comparison with the USHP gives the following results: with a basement height of 80 cm and higher, the option is 10% - 15% more expensive than the insulated Swedish plate. The height of the basement has a significant impact on costs, as it is directly proportional to the volume of backfill materials delivered to the facility.
It should be noted that the replacement of extruded polystyrene foam with foam (while maintaining the thickness of the insulating layer) does not give a tangible reduction in the cost of the project (the total amount is reduced by no more than 2% - 3%). If we proceed from the same level of energy efficiency, taking into account moisture absorption, then floor insulation with PSB-S plates is more expensive than with EPS.
UVF device technology
Let us consider step by step a set of works, based on the optimization (reduction) of the time for their implementation.

Conclusion
The most impressive result of the installation of a foundation with thermal insulation according to this scheme can be considered the double benefit from performing one manipulation. Namely: the insulating layer, on the one hand, is an obstacle on the way of heat from the room to the ground, on the other- accumulates geothermal heat rising from the bowels, protecting concrete and soil from freezing.
The second important bonus of the technology is the comparative simplicity and popularity of all work methods for the overwhelming majority of domestic construction teams.
Related video: the process of constructing the Finnish UFF foundation
The construction of any home begins with laying the foundation. Its strength, stability, quality of materials and work performed affect the service life of the entire structure. From modern ways device foundations for the house, the Finnish slab is very popular.
This technology was invented in Germany, but it is called Finnish because she found wide distribution in Norway, Sweden, Finland. And, according to its capabilities, it is excellent for the Russian climate.
Technology features
- Depending on the type of building, it can have a different functional load;
- Differs in a rather high reliability and strength in case of soil instability (heaving, sandy, swampy soil), due to the large support area and relative lightness;
- It has proven itself well at a high level of groundwater;
- High construction speed (7-10 days).
Step-by-step technology for arranging the foundation Finnish slab

- Work is underway to prepare and clear the construction site; ring drainage is installed (if necessary).
To do this, first, using a level, it is necessary to calculate the height difference between the extreme points of the surface where the house will be located. This provides a more accurate construction project and select a point relative to which the surface will be leveled;
- The marking of the future foundation is made with the help of pegs, which are driven in along the perimeter of the construction site and the fishing line stretched between them;
- The soil layer is removed;
Advice! The removed soil layer can then be used to create a garden.
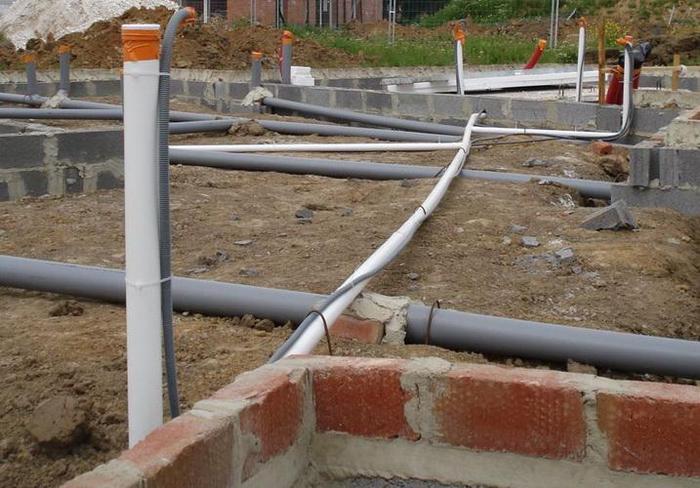

Attention! When building on soil with high level groundwater drainage system is installed on initial stage construction.
Advice! If a circular drainage system is still provided, then each layer of the slab (gravel, sand) is laid with a layer of geotextile.
The result is a flat slab of relatively small thickness with good strength and excellent thermal performance. The floor does not directly touch the slab, thanks to the insulation layer. All communication systems are laid in a screed, including a heating system that can be laid in the floor throughout the entire area of \ u200b \ u200bthe living quarters.
Depending on the load, the depth and location of the stiffeners can vary. The heavier the building is planned to be built, the more rigid the structure is supposed to be at the stage of laying the foundation.
Calculation of materials for the foundation Finnish slab
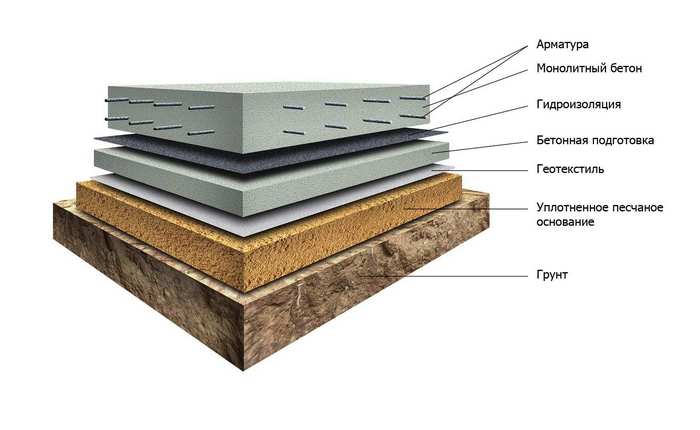
The calculation should take into account the following parameters:
- Ground water level;
- The general condition of the soil on the building site;
- Temperature and climatic conditions;
- Number of storeys of the future building;
- The exact plan of the location of the walls (for summing up communications).
Advice! This view foundation provides for many preliminary stages and a large preparatory front of work. And since the pouring of concrete is carried out at the same time, therefore it is better to trust the professionals.
The Finnish slab foundation is chosen if:
- Construction is required as soon as possible;
- Construction is carried out on difficult terrain;
- The presence of a high level of groundwater;
- The building will be carried out on the ground with strong frost penetration;
- A durable and solid construction of the base for the house is required;
- This implies the installation of a floor heating system;
- The project requires the creation of a high basement of the building;
- There is no way to dig a deep pit;
- Need high energy efficiency;
- There is no need for a sub-floor.
Upon completion of the work, you can begin finishing.
Building a house starts with installing the foundation. The quality of its implementation, stability and strength will affect the life of the structure. It is important to choose the right type of foundation for your home. Among its many types, the Finnish slab is popular.
The Finnish slab was invented by Finnish engineers. Slabs of relatively small thickness are obtained. They are characterized by durability and good thermal performance. This type of foundation is recommended for buildings where it is planned to equip a floor heating system. This system widespread in Finland, Sweden, Norway. Houses are often built in these countries frame type, this foundation can be used not only for frame houses.

The Finnish plate is considered a type of Swedish plate and has some differences. It is adapted to the climatic conditions of Russia and was developed taking into account the individual needs of developers in the region. This type of slab differs from the Swedish one by the presence of additional stiffeners around the perimeter, as well as by the peculiarities of laying the insulation.
The Finnish slab is laid over the entire area of the building, while the pressure on the ground is significantly reduced. The structure is a complete platform for the home. Strongly heaving soils, which are characterized by the raising of the base during freezing of the soil, are not terrible for such a foundation. Due to the peculiarities of its construction, the load on it from the soil is reduced to almost a minimum.
Stiffeners allow to increase the section height in places where heavy loads are expected. The location of the stiffeners depends on the structure. For example, the larger the size of the building, the more rigid the structure must be made.
To summarize what a Finnish slab is: it is a type of foundation installed on various types of soil for building a house in which it is planned to equip a system of underfloor heating. This foundation can be used for the construction of a building without a warm floor system. The outer walls of the future structure are supported by additional stiffeners. Insulation is laid on top of the slab, after which a screed is made.
Insulation protects the floor heat from dissipation, since the floor does not directly touch the slab. The screed is made after the underfloor heating system and the sewer pipe system have been installed. Therefore, such a foundation is recommended to be made for a building where the construction of underfloor heating is provided. Thus, a flat floor with a heating system is created.

The slab has a relatively small thickness, which allows it to be used in places where there is a high level of groundwater. However, when building a foundation, it is necessary to create a drainage system. Most often it is recommended to create a circular drainage and sand cushion, while these layers should be separated by geotextiles. However, with low groundwater levels, such drainage may not be suitable. Since for the installation of this foundation there is no need to prepare a very deep pit, therefore all work on preparation for pouring this foundation is reduced to a minimum.
Design features
The design is a cold loop. The insulation must be laid on foundation slab, while the thickness of the insulation must be at least 150 mm. When using insulation, the warm floor on the ground floor does not touch the cold contour of the fundamental slab. The warm floor is laid in a reinforced screed, which should be 80 mm.
A feature of the arrangement of this foundation is its quick installation, since the slab is poured in one sitting. However, the cost of this design is more than other types. When arranging this foundation, it is necessary to use a reinforced screed. The insulated Finnish slab is suitable for the construction of almost any house. It can also be frame houses.
You can choose the type of Finnish slab for the foundation in the following cases:
- if you need a foundation for a house that needs to be built quickly;
- if you need a durable foundation;
- if a warm floor system is installed in the house;
- if the building will be erected on a ground with severe freezing.
Advantages and disadvantages
This foundation has its pros and cons of using, like any other type of foundation.
There are the following advantages of the Finnish slab:
- the possibility of creating a high base;
- a small amount of earthwork is required, since a deep pit is not needed under the Finnish slab;
- high energy efficiency;
- no subfloor arrangement is required;
- the ability to install a system of underfloor heating;
- can be installed on difficult terrain;
- suitable for installations with high groundwater levels;
- possibility of holding fine finishing upon completion of installation.
The foundation of this type is excellent for the construction of buildings on difficult types of soil. It can be land with deep soil freezing, sandy, swampy and heaving soils.
Main disadvantages:
- relatively expensive construction;
- the installation of a Finnish slab can take up to 2 weeks, depending on the characteristics of the soil and the speed of the main work.
Installation technology

Foundation technology "Finnish slab" includes the following stages of the device:
- preparatory work
- sand cushion installation
- installation of a waterproofing layer
- device of mortgages. Engineering communications are being arranged
- slab pouring
- creating a layer of insulation
- installation of a stove with a system of underfloor heating and the necessary communications.
First, the difference in height between the points on the surface where the house will stand is calculated. To do this, you need to use a level. This will help you create an accurate home construction project and align the site with the selected point. Next, the foundation is marked. The top layer of soil is removed from the site (as a rule, it can be useful for creating a garden, since this layer is most often fertile). If the soil is homogeneous, then the settlement of the structure will be uniform and without distortions. One of the hardest types of soil to work with is rocky soil.
You can mark the territory using pegs and fishing line. The pegs must be driven around the perimeter of the construction site. A fishing line is pulled between the pegs. To create the foundation, a Finnish slab must be dug. The depth will depend on the main features of the soil, including the level of freezing and the level of groundwater. However, the Finnish slab does not require a deep excavation.
The pit is covered with geotextile, which has a density of 350. The geotextile is covered with crushed stone. The main water pipes and special pipes are being installed, through which the electric cables will run. The design of these communications should be clear and carefully planned, since then it will not be possible to change the location.
The crushed stone is carefully compacted, trenches are pulled out from above, where the main sewer pipes are installed. After that, the layer of crushed stone is covered with geotextile and sand is poured onto it, thus creating a sand cushion. It is important that these layers are separated by geotextiles. The sand layer should be even and its thickness should be at least 20 cm. After that, it is carefully compacted. Next, the formwork is built, and the surface is poured with concrete.
This type of foundation, as well as the type "Swedish slab", is insulated, but unlike the Swedish, Finnish slab is not insulated on the ground. A layer of insulation is created between monolithic slab and a coupler. After the layer of insulation has been installed, the final stage of work is performed: creating a screed with a warm floor system. All the necessary pipes are installed: under the floor heating system, sewerage dilution. After laying pipes for the underfloor heating system, it is laid reinforcing mesh... Can be poured with concrete or semi-dry screed. The recommended screed thickness is up to 10 cm.
Thus, a high foundation is created, which has good insulation with a warm floor system and communications. The big advantage of using a Finnish slab foundation is that immediately after the screed has dried, a fine finish can be carried out.









