Assortment of welded mesh reinforcement. Reinforcing construction mesh: description and application
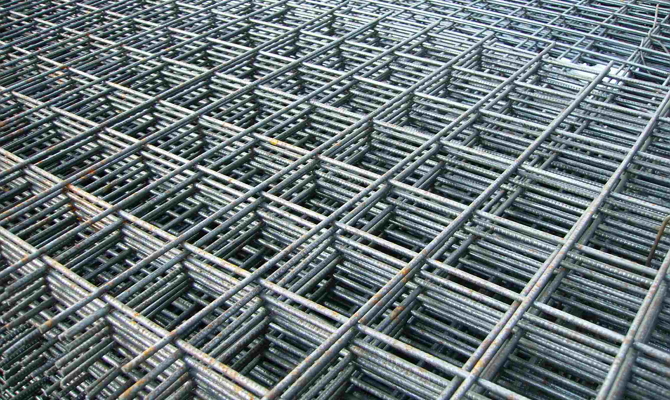
GOST 23279-2012 (85) regulates the production of welded meshes (flat or rolled), which are manufactured at factories that produce products for construction organizations. Meshes are used to reinforce prefabricated or monolithic concrete products or reinforced concrete structures. They can also be used for the construction of various small structures, such as greenhouses, outbuildings, gazebos, and so on.
Welded meshes are made using reinforcing steel (rods or wire), with a thickness of 3 to 40 mm. The most popular are products with mesh sizes of 50 × 50 and 100 × 100 mm.
1 Classification
Reinforcement meshes are divided according to GOST 23279-2012 (85) in accordance with the following characteristics:
- diameter (section) of rods or wire;
- constructive arrangement of fittings.
From what diameter of the reinforcement is used in production, this parameter is split:
- light - have transverse and longitudinal rods from 3 to 10 mm;
- heavy - rods located in one direction and having a diameter of 12 mm.
Another subgroup, which is determined by the direction of the reinforcement:
- working fittings located in one direction (transverse or longitudinal), and distribution fittings in the other;
- working fittings are located in both directions.
1.1 Features
Reinforcement mesh in accordance with GOST 23279-2012 (85) has the following types:
- type 1 (heavy) - the diameter of the working fittings is larger than that of the distribution fittings;
- type 2 (heavy) - there is a working valve in both directions;
- type 3 (heavy) - the working armature is located in the transverse direction and its diameter is larger than that of the distribution armature;
- type 4 (light) - cross bars are located across the entire width of the mesh;
- type 5 (light) - has offset transverse bars.
The nets are produced in accordance with GOST 23279-2012 (85), in flat or rolled form.
2 Parameters
The step of the rods of the same direction is the distance between them and it should be the same over the entire area. For heavy meshes of the first type, it is allowed to have an additional step of transverse bars at the edge of the product, which can be equal to 100, 200 and 300 mm.
Lightweight reinforcing meshes can have an additional step in the longitudinal direction at the edges or cutting places (cutting is carried out using special scissors, which can be read separately). The additional spacing of rods located longitudinally can have dimensions from 50 mm to a given cell size (50 × 50, 100 × 100 mm), while at the edge it should be a multiple of 10 mm, and at the cutting points 50 mm.
The transverse components of the reinforcing mesh can have an additional step from 50 to 250 mm, with the condition of a multiplicity of 10 (50 × 50, 100 × 100 mm).
Lightweight reinforcement made in one strip, can be with the release of longitudinal rods from 25 to 250 mm (divisible by 5). For transverse, values of 15, 20 and 30 mm are allowed, or from 25 to 100 mm (with a multiplicity of 25). Such outlets are suitable for cells with dimensions of 50 × 50, 100 × 100, 100 × 250 mm.
2.1 Dimensions
These parameters are presented in the following form: 50 × 50x4, 100 × 100x5. By the numbers, you can determine that the cell is a square, the sides of which are 5 (10) cm, and the diameter of the rod is 4 (5) mm, according to the above examples.
2.2 Weight
2.3 Technical requirements
Welded metal meshes made of reinforcing steel are manufactured in accordance with GOST 23279-2012 (85) and specific working drawings, as well as accompanying technological documentation.
Working fittings in heavy nets is made of steel of class A-III with a bar section of 10-40 mm. In some cases, the use of steel is allowed A-I diameter 10-32 mm.
Distribution fittings of heavy mesh (type 1) are made of steel A-I II (6-16 mm), and in type 3 - steel A-III (10-16 mm) and steel A-I (6-16 mm).
For light meshes, steel grade B500C (4-5 mm), reinforcing wire made of steel grade Br-1 (3-5 mm) and reinforcement made of steel grades A-III and A-I (6-10 mm) are used.
Distribution fittings can be B500S steel with a diameter of 4-5 mm and wire B-l with a diameter of 3-5 mm.
The connection of the rods at the points of their intersection is carried out using resistance spot welding, the operating modes of which must comply with regulatory documents.
In products made with the use of steel grades A-I, without fail, all intersections of the rods must be fastened. When assembling a product from rods and wires, welding of intersections is allowed through one or two staggered. In this case, two rods running along the edges of the product must be fastened without fail.
A maximum of two non-welded intersections (with the help of clamps) are allowed on an area of 1 m² out of the number of joints required to be fastened.
2.4 Marking, transport and storage
The data on the product packed in bags or rolls must be indicated on two metal or plywood tags, which are attached on two different sides.
The total weight of one packed unit should not exceed three tons. The nets in bags are tied with soft wire in four places, and rolls in three places.
The information on the tags indicates the following:
- name (trademark) of the company that manufactured the products;
- a type ( symbol) products;
- the number of units in the package;
- package (roll) weight in tons;
- production date and batch number.
During transportation and handling, it is necessary to adhere to the rules for safety precautions, and also observe precautions aimed at protecting the product from mechanical damage.
Storage is permissible in covered rooms with distribution by brands and stacks, the height of which does not exceed 2 meters. Rolls can be stacked in tiers, the number of which does not exceed 3. When forming a large number of stacks, a free passage must be left between them, the width of which is at least 0.5 m.
2.5 How is reinforcement mesh produced? (video)
Welded mesh reinforcement (SAS) is used in a number of important construction activities. It is indispensable for reinforcing reinforcement of monolithic reinforced concrete structures and in other works.
1 Reinforcement mesh - and wherever it is not used!
SAS is a cold-drawn steel mesh made of low-carbon wire. Its cells are connected by welding. The profile of the finished product can be periodic or ordinary smooth.
A variety of protective coatings may be applied to the mesh surface. They, firstly, increase the technical performance of the mesh structure, and secondly, significantly expand the scope of its application.
Reinforcing mesh made of steel, which is also called reinforced, is very reliable and durable. It is most often used in the following areas:
- Building. SAS is used in the construction and arrangement of walls, guaranteeing them unique strength characteristics. If we take a mesh with rods of increased thickness, it can be used to create foundations of different orientation and complexity in structures and buildings. Also, reinforced mesh products are suitable for performing other restoration and repair activities in the field of modern construction.
- Road works. The use of steel mesh for reinforcement guarantees the highest quality paving slabs. Their installation becomes faster and easier, and the strength of the resulting structure is very high level... It is also considered expedient to use meshes for reinforcement when carrying out planned road repairs.
- Household. Low-carbon wire structures can now be seen on many backyards and garden plots... In this case, the reinforced SAS makes it possible to build any frame structures, be it large greenhouses or small greenhouses, as well as all kinds of fences.
- Finishing work. The described wire mesh products have proven themselves well when interior decoration premises. Light types of SAS provide high-quality leveling of irregularities on wall and ceiling surfaces and at the same time optimize and accelerate plastering activities.
In addition, the reinforcement mesh is currently very actively exploited by bridge builders. It is used to strengthen bridges, their supports and other elements of such structures.
2 Advantages of grids - competitors, envy!
SAS has a truly unique combination of excellent performance and technical indicators(weight, strength and so on). Due to this, it can be used on the most difficult industrial and construction sites, always getting an impeccable work result.
Reinforced mesh is described by the following advantages of use:
- Multifunctionality - there is no such branch of modern industrial production where SAS is not used. And every day the areas of its application are expanding.
- Acceptable cost of material made of wire with a low carbon content - competing meshes lose to SAS in terms of their production cost. The increase in the production costs of steel products naturally increases their selling price.
- Efficiency of work performance - reducing the time for construction and other activities, as well as simplifying the technological process.
- Low specific weight, ease of fastening, safe operation and ease of installation

It is also worth noting a large selection of geometrical dimensions of reinforced meshes allowed by GOST 23279–2012. This Gosstandart, which describes all the requirements for the CAS, we will consider in more detail below. In addition, finished mesh products can be transported without any problems and can be stored in almost any conditions.
All these advantages are achieved due to the fact that SAS is manufactured on innovative equipment for the latest technology, which are accepted throughout the civilized world. In the production of wire mesh with a small amount of carbon, it is used, it can also be used. Due to this, the finished mesh structures become highly resistant to mechanical external influences and receive an excellent indicator of strength.

To increase the anti-corrosion protection of the SAS, a special layer (most often zinc) can be applied to its surface. Such processing is carried out using electrolytic technology or by hot application of a protective coating. Both techniques have worked well. Usually, the choice is made of the technology that allows you to obtain, in each specific case, a layer of a given thickness and a certain appearance.
3 GOST 23279 - what should be the mesh for reinforcement?
This standard describes rolled and flat CAS with a cross section of 3–40 mm, in which the rods, which are elements of the mesh structure, are located perpendicular to each other. The considered products according to GOST 23279 are divided into different types by the method of reinforcement placement (working) and by the section of the rods.
Reinforcement in welded mesh made of low-carbon wire can be located in the transverse and longitudinal directions, only in the transverse or only in the longitudinal direction. According to the cross-section of the rod, the products are divided into light and heavy. Under the latter, GOST means SAS, in which the rods in one direction have a cross section of more than 12 mm. Structures with transverse and longitudinal rods not exceeding 10 mm in diameter are called light.

There are five types of welded steel mesh:
- With longitudinal reinforcement (working), the section of which is greater than the section of the distribution armature. Such products are classified as heavy.
- Armature in both directions, heavy.
- With transverse reinforcement of large cross-section, heavy.
- With displaced rods located transversely, the lungs.
- With rods (transverse) for the entire available width of the CAC.
GOST allows the production of wire structures with rectangular and square cells, in rolls or in a flat form. Please note that in rolls it is allowed to produce only 3–5 mm lightweight SAS from the weight of which does not exceed the values specified in the standard.
The sections of the working reinforcement of products for reinforcement are determined taking into account the cross-sectional area of the (transverse) reinforcing elements (a calculation should be performed, in which not only the diameter, but also the weight of the latter should be taken into account). The ratio of the section of the smaller bar to the larger one must be 0.25. CAC must have (required!) Rods of the same diameter in one direction.
The weight of the mesh is determined by its type (light, heavy), length, width and section of the rods used. If the structure is made, for example, from rods with a diameter of 4 mm, with dimensions of 200 by 600 cm and with cells of 20 by 20 cm, the mass of one square meter will be equal to 0.99 kg. But the weight of the meshes with the same parameters, but made of rods with a cross section of 8 mm, will already be 3.95 kg.
4 Other Gosstandart requirements are important!
According to GOST 23279 for heavy meshes for reinforcement, working reinforcement is reinforcing steel (rod) with a section of 10-40 mm of classes A600C, A500C, A400. It is allowed to use rods of hot-rolled A240 alloys. Light CACs are made from wire with a cross section of up to 5 mm ( type B-I, Вр-I) or from reinforcing steel 6-10 mm of classes А240, А500С, А400, В500С.
GOST clearly stipulates that the intersections of rods in wire and bar periodic reinforcement can be welded staggered through two or one position. In this case, at all intersections, the last two rods in the mesh structure should be connected. If the CAC is made from steel A240, all intersections are welded without exception.
Cross-shaped joints in the described products are welded point technology according to GOST 14098. Welding modes for this operation are selected based on the requirements of the existing regulatory documentation at the enterprise.

The tensile strength and breaking force of the mesh rods in the places of their welding is checked according to standard 10922. The shear strength must comply with the provisions of the same GOST.
Acceptance of SAS is carried out in rolls or in batches. In addition to all standard analyzes, the products undergo additional checks for the indicator of the slump of the rods and for the value of their straightness.
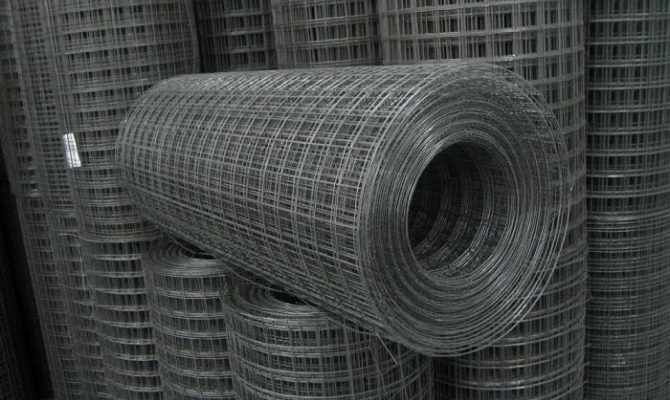

Reinforced mesh is tied in packages weighing no more than three tons. Without fail, the packages are tied in four sections using soft metal wire. If the product is supplied in rolls, the bundling is done in three or more places.
The meshes are transported horizontally. In this case, it is necessary that the packages rest on 3-centimeter spacers or on wooden blocks of similar thickness. The storage of the CAS is carried out in the same way.
GOST 23279-2012
INTERSTATE STANDARD
WELDED REINFORCEMENT NET FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES AND PRODUCTS
Are common technical conditions
Welded reinforcing meshes for reinforced concrete structures and products. General specifications
ISS 91.190
Introduction date 2013-07-01
Foreword
The goals, basic principles and basic procedure for carrying out work on interstate standardization are established by GOST 1.0-92 "Interstate standardization system. Basic provisions" and GOST 1.2-2009 "Interstate standardization system. Interstate standards, rules, recommendations for interstate standardization. Rules for development, adoption, application, renewal and cancellation ".
Information about the standard
1 DEVELOPED by the Russian Engineering Academy
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 "Construction"
3 ACCEPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Conformity Assessment in Construction (Appendix B to the Protocol of June 4, 2012 N 40)
Voted for the adoption of the standard:
Short name of the country according to MK (ISO 3166) 004-97 | Abbreviated name of the national authority government controlled construction |
|
Azerbaijan | State Committee for Urban Development and Architecture |
|
Ministry of Urban Development |
||
Kyrgyzstan | Gosstroy |
|
Ministry of Construction and Regional Development |
||
Ministry of Regional Development |
||
Tajikistan | Agency for Construction and Architecture under the Government |
|
Uzbekistan | Gosarkhitektstroy |
4 By order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology of November 29, 2012 N 1306-st, the interstate standard GOST 23279-2012 was put into effect as a national standard Russian Federation from July 1, 2013
5 REPLACE GOST 23279-85
Information on changes to this standard is published in the annual information index "National Standards", and the text of changes and amendments is published in the monthly information index "National Standards". In case of revision (replacement) or cancellation of this standard, a corresponding notice will be published in the monthly information index "National Standards". Relevant information, notice and texts are also posted in information system common use- on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet
1 area of use
1 area of use
This standard applies to welded flat and rolled meshes (hereinafter referred to as meshes) manufactured at enterprises of the construction industry from reinforcing steel with diameters from 3 to 40 mm inclusive, with the arrangement of rods in two mutually perpendicular directions, and intended for reinforcing prefabricated and monolithic reinforced concrete structures and products.
2 Normative references
This standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST 427-75 Measuring metal rulers. Technical conditions
GOST 5781-82 Hot-rolled steel for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures. Technical conditions
GOST 6727-80 Cold-drawn low-carbon steel wire for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures. Technical conditions
GOST 7502-98 Metal measuring tapes. Technical conditions
GOST 10922-90 * Welded reinforcement and embedded products, welded joints of reinforcement and embedded products of reinforced concrete structures. General specifications
________________
* The document is not valid on the territory of the Russian Federation. GOST 10922-2012 applies, hereinafter in the text. - Note from the manufacturer of the database.
GOST 14098-91 Welded joints of reinforcement and embedded products of reinforced concrete structures. Types, designs and sizes
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or according to the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year, and for the respective issues of the monthly information index "National Standards" for the current year. If the reference standard is replaced (changed), then when using this standard, the replacing (modified) standard should be followed. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which the reference to it is given applies to the extent not affecting this reference.
3 Classification
3.1 Grids are subdivided:
- by the diameters of the rods;
- by the location of the working fittings.
3.2 Depending on the diameter of the rods, the meshes are divided into heavy and light.
3.2.1 Heavy meshes are those that have rods with a diameter of 12 mm or more in one direction.
3.2.2 Light nets are nets with longitudinal and transverse rods with a diameter of 3 to 10 mm inclusive.
3.3 According to the location of the working reinforcement, the meshes are subdivided into:
- with working fittings in one direction (longitudinal or transverse) and distribution fittings in the other direction;
- with working fittings in both directions.
4 Types, main parameters and dimensions
4.1 The nets are made of the following types (see Figures 1 and 2):
- type 1 - heavy with working fittings in the longitudinal direction, the diameter of which is greater than the diameter of the distribution fittings;
- type 2 - heavy with working fittings in both directions;
- type 3 - heavy with working fittings in the transverse direction, the diameter of which is greater than the diameter of the distribution fittings;
- type 4 - lightweight with transverse rods for the entire width of the mesh;
- type 5 - lightweight with offset transverse rods.
Figure 1 - Heavy nets
Type 2
Type 3
Figure 1 - Heavy nets
Figure 2 - Light meshes
Type 5
Figure 2 - Light meshes
4.2 The nets are made flat or rolled.
Light mesh with longitudinal rods made of reinforcing steel with diameters from 3 to 5 mm inclusive is made in rolls.
4.3 The nets should have rods of the same diameter in one direction.
4.4 Grids are made with square or rectangular cells.
4.5 The diameters of the working reinforcement of the meshes are assigned on the basis of the required cross-sectional area of the reinforcement required for the calculation.
4.6 The ratio of the smaller diameter of the rod to the larger one should be at least 0.25.
4.7 The main parameters of the meshes are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 - Mesh parameters
In millimeters
Mesh view | Mesh type | Mesh width | Mesh length | Bar diameters | Distance between bars (in axes) - bar spacing | Bar release sizes |
||
longitudinal | transverse | transverse | longitudinal and |
|||||
650 to 3050 | 850 to 9000 | Multiples of 25 |
||||||
850 to 5950 | Multiples of 25 |
|||||||
850 to 3050 | 850 to 6250 | |||||||
650 to 3800 | 850 to 9000 or up to roll length | 100 (150) | 100 (75) | |||||
3950 to 9000 or up to roll length | ||||||||
* It is allowed to use a rod spacing of 100 and 300 mm in the grids of standard design documentation for reinforced concrete structures. Notes (edit) 1 Heavy meshes of type 1 with a width of 1500 to 3050 mm with longitudinal rods with diameters of 36 and 40 mm and type 3 with a length of 3050 to 6250 mm, prior to the development of the production of automated equipment, are made using single-point machines and hanging welding tongs. 2 By agreement with the manufacturer, it is allowed to use heavy meshes of type 1 and light flat meshes up to 11500 mm long. 3 In light meshes of type 5, the length of the transverse rods ranges from 0.85 to 0.90 of the mesh width. 4 The distances between the longitudinal and transverse rods of light meshes, indicated in brackets, are allowed to be taken in the feasibility study. |
||||||||
________________
Probably a mistake in the original. Should read: See 4.9 (letter from Rosstandart TK 465 "Construction" dated December 27, 2016 N TK-736/2016). - Note from the manufacturer of the database.
4.8 The distance between the rods - the main pitch of the rods in one direction - should be taken the same.
4.8.1 In heavy nets of type 1 for transverse bars at the edge of the net, an additional step of 100 is allowed; 200 and 300 mm.
4.8.2 In light meshes, in addition to the main pitch of the rods in the longitudinal direction, it is allowed to use an additional pitch at the edges of the mesh, as well as in the place of its cutting.
The additional step of the longitudinal rods is taken from 50 mm to the size of the main step, which is a multiple of 10 mm at the edge of the mesh and a multiple of 50 mm at the point of cutting the mesh.
The additional step of the transverse rods is taken from 50 to 250 mm, divisible by 10 mm.
4.9 The dimensions of the outlets of the longitudinal and transverse rods should be taken equal to or multiples of 25 mm in accordance with those indicated in Table 1.
In light grids made in one strip, the dimensions of the longitudinal rods outlets are allowed to be taken from 25 to 200 mm, multiples of 5 mm, and the dimensions of the transverse rods outlets - equal to 15; 20 and 30 mm, as well as from 25 to 100 mm, multiples of 25 mm.
4.10 Grids are designated with marks of the following structure
where - designation of the mesh type (see 2.1);
- designation of the name of the welded mesh (with the addition of an index for rolled mesh);
, - diameters of longitudinal and transverse bars, respectively, indicating the class of reinforcing steel;
, - the width and length of the mesh, cm, respectively.
In the designation of the mesh brand, the following are additionally given:
- for light meshes, as well as heavy meshes of type 3 with the main pitch of longitudinal rods 400 mm after the diameter of the rods (through a dash) - the value of the pitch of the rods in millimeters;
- for grids with an additional step - above the line or below the line, respectively, the values of the additional step of longitudinal or transverse bars in millimeters (in brackets).
For grids with the dimensions of the outlets of the transverse and longitudinal rods differing from 25 mm, the designation of the mesh grade after the designation of the mesh length is supplemented with the following designation:
where, - the values of the longitudinal bar releases (when only one value is given), mm;
- value of transverse rod releases, mm.
Examples of symbols:
- heavy mesh type 1 with longitudinal bars made of reinforcing steel of the A500C class with a diameter of 25 mm, with a pitch of 200 mm and with transverse bars made of reinforcing steel of the A500C class with a diameter of 10 mm, with a pitch of 600 mm, a width of 2050 mm and a length of 6650 mm, with longitudinal outlets and cross bars 25 mm:
Flat light mesh type 4 with longitudinal bars made of A500C class reinforcing steel with a diameter of 10 mm and transverse bars made of B500C reinforcing steel with a diameter of 5 mm, with a pitch of longitudinal and transverse bars of 100 mm, a width of 2550 mm and a length of 6050 mm, with outlets of longitudinal and transverse bars 25 mm:
Roll mesh type 5 with longitudinal and transverse rods made of B500C class reinforcing steel with a diameter of 5 mm, with a main pitch of longitudinal rods of 200 mm and an additional one - 100 mm, with a pitch of transverse rods of 150 mm, a width of 2340 mm and a length of 120,000 mm, with longitudinal rods outlets 125 and 175 mm, with 20 mm transverse rod outlets:
5 Technical requirements
5.1 Grids should be made in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to working drawings and technological documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
5.2 As working reinforcement in heavy meshes, rod reinforcing steel of classes A500C, A600C and A400 (A-III) with a diameter of 10-40 mm should be used.
In the course of feasibility studies, it is allowed to use rod hot-rolled reinforcing steel of class A240 (A-l), with a diameter of 10-32 mm, as working reinforcement.
5.3 Reinforcing steel of classes A400 (A-III), A500C, B500C and A600C with diameters of 6-16 mm is used as distribution reinforcement in heavy meshes of type 1, reinforcing steel of classes A400 (A-III), A500C, B500C in type 3 meshes and А600С with a diameter of 10-16 mm and А240 (А-l) with a diameter of 6-16 mm.
5.4 Light meshes should be made of reinforcing steel of class B500C with a diameter of 4-5 mm, reinforcing wire of class Bp-I with a diameter of 3-5 mm and bar reinforcing steel of classes A400 (A-III), A500C, B500C and A240 (AI) with a diameter of 6- 10 mm.
As distribution fittings, it is allowed to use reinforcing steel of class B500C with a diameter of 4-5 mm and reinforcing wire class B-l with a diameter of 3-5 mm.
5.5 Grades of reinforcing steel for the manufacture of meshes must correspond to the grades established project documentation(in accordance with the requirements of building codes and regulations for the design of concrete and reinforced concrete structures, depending on the operating conditions of the structures) specified in the order for the manufacture of meshes.
5.6 Reinforcing steel must meet the requirements:
- bar reinforcing steel of classes A400 (A-III) and A240 (A-I) - GOST 5781;
- rod reinforcing steel of classes A500C and B500C - current regulatory documents *;
_______________
* In the Russian Federation, GOST R 52544 applies to reinforcing steel of classes A500C and B500C.
- rod reinforcing steel of class A600C - current regulatory documents;
- reinforcing wire of classes Bp-I and B-l - GOST 6727.
5.7 Cross-shaped connections of bars in grids should be carried out by resistance spot welding in accordance with GOST 14098.
Welding modes must comply with the requirements of the current regulatory documents.
5.8 In meshes with working reinforcement made of smooth bar reinforcing steel of class A240 (A-l), all crossings of bars must be welded.
In meshes with working reinforcement of a periodic profile (rod and wire), it is allowed to weld intersections of rods through one or two intersections in a checkerboard pattern, if there are no special instructions in the working drawings. The two outermost rods in the meshes must be welded at all intersections
In the reinforcing mesh, no more than two non-welded intersections of bars are allowed on an area of 1 m of the mesh from among the intersections to be welded.
5.9 The breaking force or temporary resistance to breaking of the rods at the welded points during tensile testing (weakened at the points of intersections and joints) should not be lower than that required by GOST 10922.
5.10 Requirements for shear strength of welded joints of bars - in accordance with GOST 10922.
If the welded joints of rebars made of reinforcing steel of a periodic profile, located in two or one direction, do not impose requirements for equal strength in accordance with GOST 10922, then the rejection load during the shear test should be at least 30% of the breaking strength of the reinforcing wire or the ultimate tensile strength of the reinforcing steel of a smaller diameter.
5.11 Cross-shaped connections of the rods of the nets should not be destroyed by impact effects when the nets are freely dropped from a height of 1 m.
5.12 Butt joints of reinforcing steel should be carried out by resistance butt welding in accordance with GOST 14098.
Welding modes - according to the current regulatory documents.
Working reinforcement on a rod length of 6 m should not have more than two, and on a rod length of 12 m - more than three butt joints.
Butt joints of bars of one direction within the reinforcement spacing in the other direction are allowed at least through three bars.
5.13 The values of the relative settlement in the cross-shaped joints of the rods (in fractions of the smaller diameter of the welded rods) should be for reinforcing steel of classes А240 (А-l), А400 (A-III), В500С, А500С and А600С from 0.2 to 0.5.
5.14 Values of actual deviations geometric parameters nets should not exceed the limit specified in GOST 10922.
5.15 Longitudinal and transverse bars in meshes should be straight.
Values of actual deviations from the straightness of rods should not exceed 6 mm over a rod length of 1 m.
6 Acceptance rules
6.1 The nets are accepted in batches in accordance with the requirements of GOST 10922 and this standard.
6.2 In each mesh or roll selected from the lot, the following is additionally checked:
- the size of the issues;
- straightness of the rods;
- the amount of upsetting of the rods.
6.3 Upon receipt of unsatisfactory test results for at least one of the indicators, a second test is carried out on a double sample. The retest results are valid for the entire batch.
If, upon re-checking, at least one mesh does not meet the requirements of GOST 10922 and this standard, all meshes are subject to piece-by-piece acceptance.
7 Control methods
7.1 Methods of control and testing of meshes must comply with the established GOST 10922 and this standard.
7.2 The width and length of flat meshes, the pitch of the longitudinal and transverse rods, the dimensions of the outlets, the straightness of the rod and the difference in the length of the diagonals, as well as the width of the rolled net, the pitch of its longitudinal and transverse rods, the dimensions of the outlets and the straightness of the transverse rods are checked with a tape measure in accordance with GOST 7502 or a metal ruler in accordance with GOST 427.
7.3 Cross-shaped connections for impact action are checked at the posts of production and packing of nets by free dropping of nets from a height of 1 m to concrete base or metal linings.
8 Labeling, transport and storage
8.1 Flat meshes should be bundled. Package weight should not exceed 3 tons.
8.2 A package of nets should be tied with soft wire in at least four places, and a roll of nets at at least three places.
8.3 Each package and roll of nets must be attached at least two metal or plywood tags, which indicate:
- name or trademark of the manufacturer;
- conventional designation of grids according to 4.10;
- the number of meshes in the package;
- weight of the package or roll, t;
- batch number and date of manufacture.
Tags should be affixed to different sides of the bag and roll.
8.4 Each batch of meshes supplied by specialized enterprises of reinforcement products must be accompanied by a quality document, which indicates:
- name and address of the manufacturer;
- number and date of issue of the document;
- batch number;
- name of products with indication of their brands and number in the batch;
- date of manufacture.
The document must be signed by the employee responsible for the technical control of the manufacturer.
8.5 The nets should be transported in a horizontal position.
When loading, transporting and unloading the nets, measures must be taken to ensure their safety from damage. Methods for carrying out loading and unloading operations must comply with the safety rules provided for in the construction.
8.6 The nets should be stored indoors. Packages of nets should be stored separately by brands in stacks of no more than 2 m in height. Rolls of nets should be stored in no more than three tiers. When storing the nets between the stacks, a free passage of at least 0.5 m must be ensured.
8.7 During storage and transportation, each package must be supported by wooden lining and spacers with a thickness of at least 30 mm.
Mesh pads should be laid on a dense, carefully leveled base. When storing the nets in stacks, the spacers between the bags must be stacked vertically one above the other in the height of the stack.
Electronic text of the document
prepared by JSC "Kodeks" and verified by:
official publication
M .: Standartinform, 2013
Welded mesh is one of the most popular types of metal products today. Among these meshes, the most common are welded reinforcing meshes. The wire in them is welded by resistance spot welding in accordance with the requirements of GOST 14098 at right angles at the intersection points. An anti-corrosion coating is applied to the mesh to increase its service life.
Welded mesh reinforcement is classified into two broad classes:
- masonry (armpoyas) and road;
- for glass reinforcement and thermal insulation.
Requirements for the range of reinforcing meshes are defined by the standards:
- GOST 8478-81 “Welded meshes for reinforced concrete structures. Technical conditions ";
- GOST 23279-85 “Welded reinforcing meshes for reinforced concrete structures and products. General technical conditions ".
These meshes are intended for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures in construction and roadways.
They are made of low-carbon reinforcing wire of Br-1 and B-1 classes in accordance with GOST 6727-80 and are supplied in rolls or cards.
To increase the corrosion resistance of the mesh, one of the types of zinc coating is used:
- galvanized, then welded (electrolytic zinc coating with a layer of about 10 g / m2);
- welded, then galvanized (electrolytic zinc coating with a layer of about 20 g / m2);
- hot-dip galvanized, then welded (hot zinc about 50 g / sq. m.);
- cooked, then hot-dip galvanized (hot zinc about 130 g / m2).
The amount of zinc on the mesh is directly proportional to the service life of such a product.
Assortment of welded mesh for glass reinforcement and thermal insulation
This type of mesh is intended for glass reinforcement and thermal insulation. The material is low-carbon wire. A feature of such a mesh is the presence of transverse threads of the mesh fabric, which have double corrugation (No. 25) or single corrugation (No. 125) in each cell. The range and technical requirements for this mesh are determined by TU 14-4-713-97 and TU 14-4-714-97. The mesh is produced from wire with a diameter of about 5 mm and 0.6 mm, with a pitch of 12.5 mm and 25 mm, web widths from 600 mm to 2000 mm.
Technical characteristics of wire of variable cross-section VR-1
To increase the adhesion of the mesh to the reinforced material, ribbed wire of variable diameter VR1 according to GOST 6727-80 is used. It is made from wire rod made according to OST 14-15-193-86. After appropriate machining, the wire takes on the following appearance:
An example of the ratio of dimensions for wire BP1 with a diameter (d) of 3.8 mm:
- indentation depth (h) 0.2 mm;
- step of indentations (s) 2.5 mm;
- projection length (b) 0.8 mm.
Technical requirements for welded mesh reinforcement
One of the main requirements for reinforcing meshes is their strength. The strength of the mesh depends on its design: the smaller the mesh size, the stronger the mesh, and the higher its ability to withstand heavy loads. You can check the quality of the mesh by its weight: the larger it is, the more load the mesh can withstand. To do this, weigh the roll of masonry mesh, calculate the weight of 1 sq. m and compare with the theoretical (reference) weight. If the difference in weight is more than 5%, then you should check the other parameters of this roll.






